726
Scientists have developed a new method of water purification using synthetic membranes

Photo: World Bank Photo Collection / Flickr i>
Clean or desalinate water to make it potable and irrigation - not easy and not cheap. Even in California, which is suffering from drought and acute shortage of water, the financial aspect is crucial. Developing countries have even fewer opportunities to obtain clean water, but recently has been invented an ultra-low-cost purification process, which looks very promising.
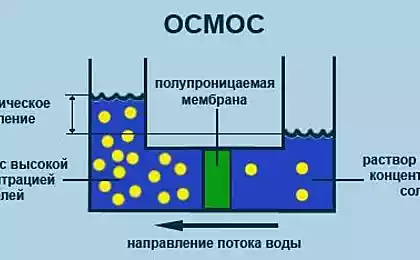
A team of researchers from the University of Alexandria, Egypt, has developed a method of desalination called pervaporation, which allows you to remove excess water from sea salt and make it drinkable. It uses specially manufactured synthetic membranes which filter the large particles of salt and impurities. For the final cleaning after filtration and evaporation of the applied classical collection "drinking" condensate.
It is imperative that the membrane can be manufactured in any laboratory using publicly available, inexpensive materials, and evaporating - only a part of those. process, instead of the whole process. Thus, water can be cleaned continuously, even in conditions of shortages of electricity, which is essential for developing countries.
The developed membrane and the whole method is entirely applicable not only for the desalination of sea water, and sewage treatment. Researchers have used in their work approaches of these areas of knowledge as oceanography, chemistry, agriculture, engineering and the creation of biological systems that allowed them to create a business, engineering, and not a "laboratory" solution.
"We created the technology is much more effective than reverse osmosis technology, now widely used in Egypt, the Middle East and North Africa," said Helmy El Zanfali, professor at the National Research Centre of Egypt. "Our method can efficiently desalinate water with a high concentration of salt, such as the water of the Red Sea, where the cost of desalination is greatest, and the output water less».
In the meantime, scientists are working on a project that should create a pilot desalination plant to test the effectiveness of its development to the industrial scale. Another issue that must be addressed - what to do with waste. If the new technology to be effective, it will have a huge impact on the lives of millions of people. According to the portal water.org about 750 million people around the world lack the fresh water and drinking water, causing annually 840 000 people are killed.
Via sciencealert.com
Source: geektimes.ru/post/262636/