Theoretically, with hydroelectricity it is clear - the water comes from the upper pool to the lower, turns the turbine wheel. The turbine drives the generator that produces electricity and ...
Interesting details.
Housekeeping tip: to get 1 kilowatt-hour of electricity, it is necessary to descend from a height of 27 meters 14 tons of water.
(Detail visit peeped in nine different hydropower plants). I>
To paraphrase a classic: all the thermal power plants are alike, each hydroelectric plant is arranged differently. In other words, the model he's not there, all the different HPP. Everyone has their own water flow, pressure, relief, soil, climate, proximity to the sea, the volume of the reservoir ...
Here, for example, like a conventional turbine room. Except for the fact that all the windows in it - artificial, backlit.
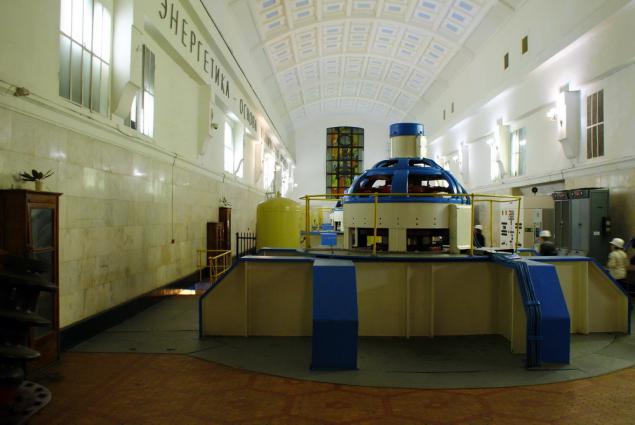

That's because the computer room is in the rock at a depth of 76 meters.
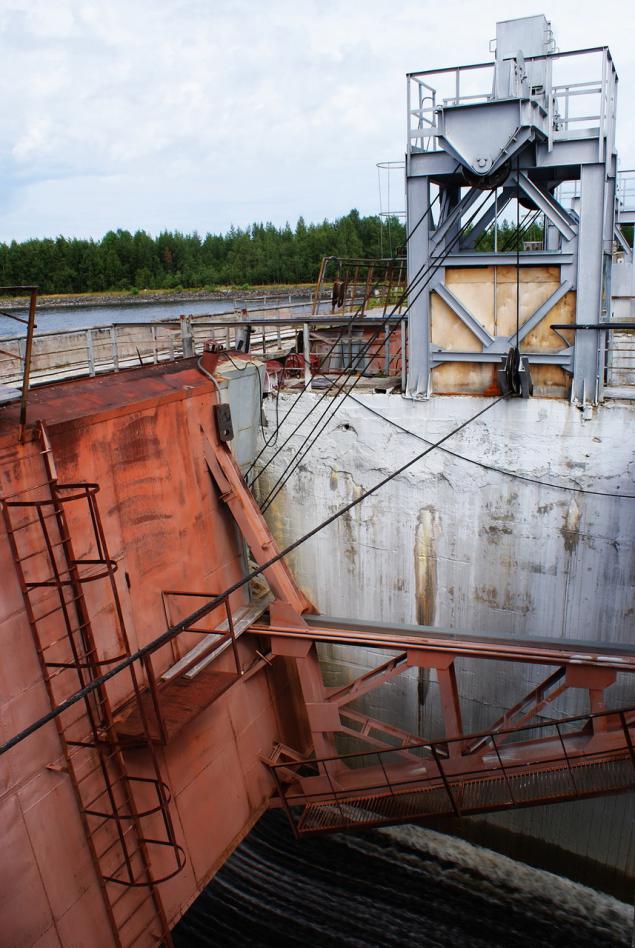
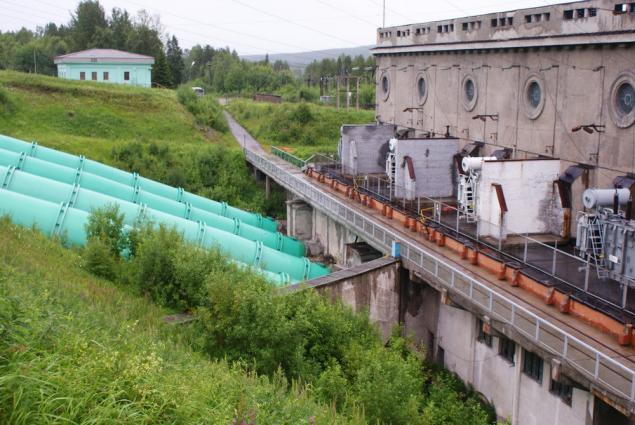
This first Soviet underground hydroelectric , from the surface to the water line there are four 6 m in diameter. This mine, also carved into the bedrock to extract from the deep turbine hall equipment in the event of repair / replacement:
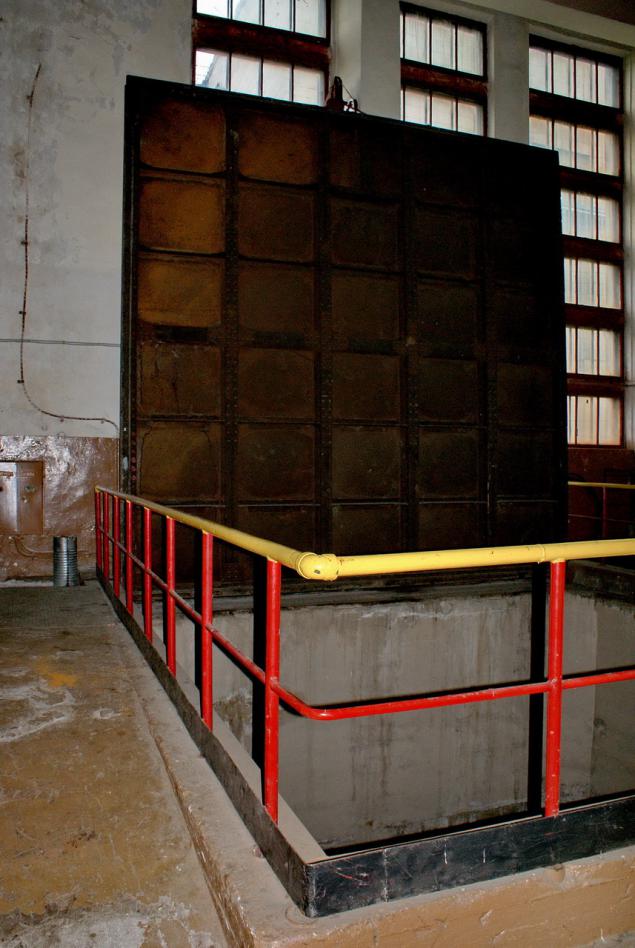

The gates of a relief structures h4> Ideally, all water has to go through the turbines and produce energy. But this is not always possible.
Some of the water is necessary to reset by GES:
- The repair of hydraulic units;
- During spring floods, when there is no long-term regulation of the reservoir (as it frequently is not);
- бывает, that cascade HPP (plants, standing on one river) capacity of the upper station is greater than the bottom; while the lower part of the water should be let by turbines, otherwise it simply will flood;
- Sometimes open idle spillway fish factory on request to skip the fries downstream;
- Etc.
Idle spillway Беломорской GES - the three shutter.
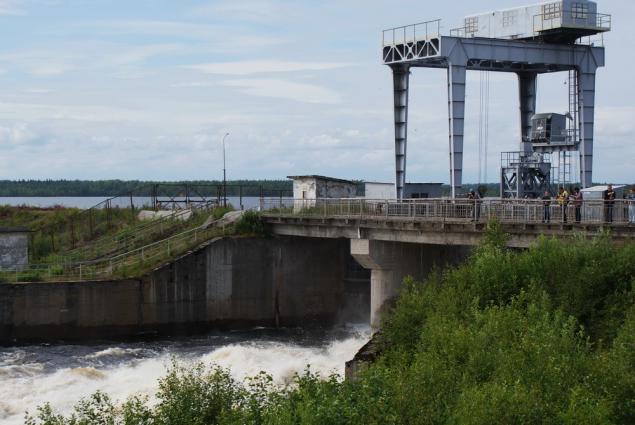

Quite a lot of attention paid to the issue of redundancy, because the time is not able to lower the level in the reservoir - it is fraught. Any of the gate here can be lowered / raised gantry crane, two out of three - electric winch. In an extreme case, and it can be manually (at a rate, however, 3 cm / min).

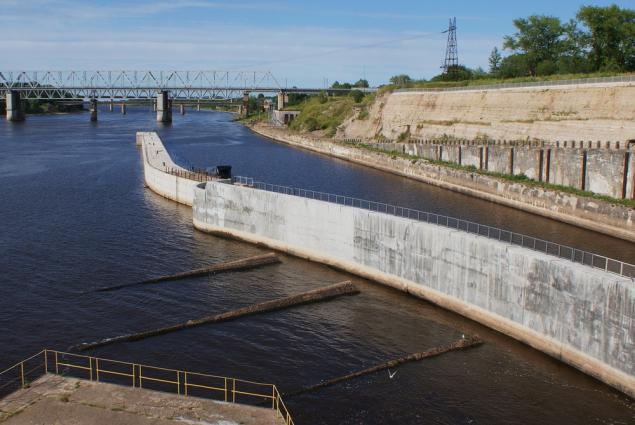
The shutter is raised goes to the idle discharge of water intake of the city of Belomorsk located downstream:

Deicing valves used induction heating. On heating this instance, for example, requires 150 kW:

Sometimes it also makes bubbling - pass the air from the depths along the gate; We see compressed air hose:

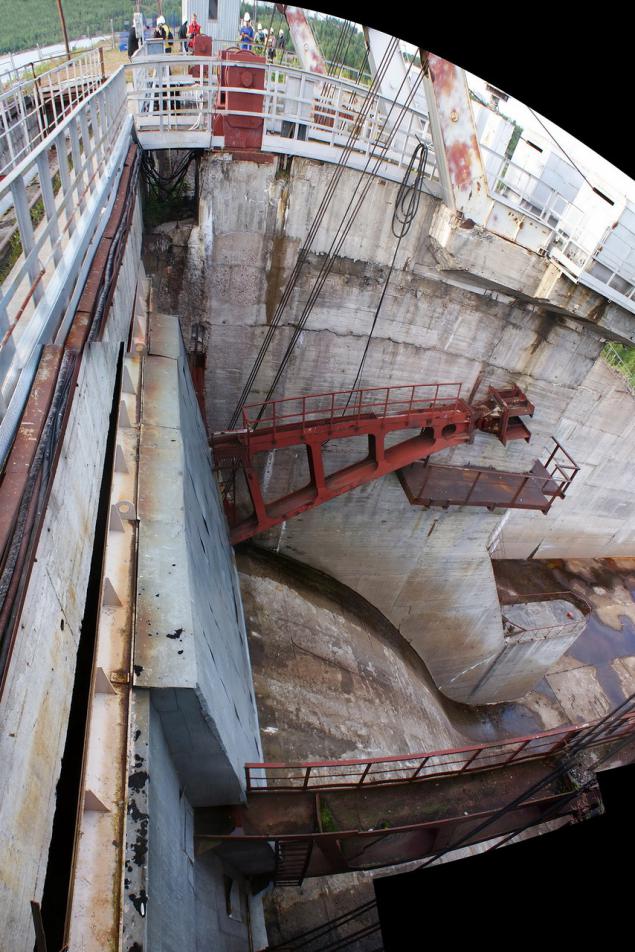
On reset, provide activities for damping the kinetic energy of the flow - stilling basin, the collision flow stage or, as here, in the Волховской GES - stilling plate with absorbers:

On fish h4> On the Нижнетуломской GES made special fish ladder for salmon, rising to spawn upstream. The design mimics a half a kilometer mountain stream with rocks at the bottom, zigzagging walkways and seating fish.
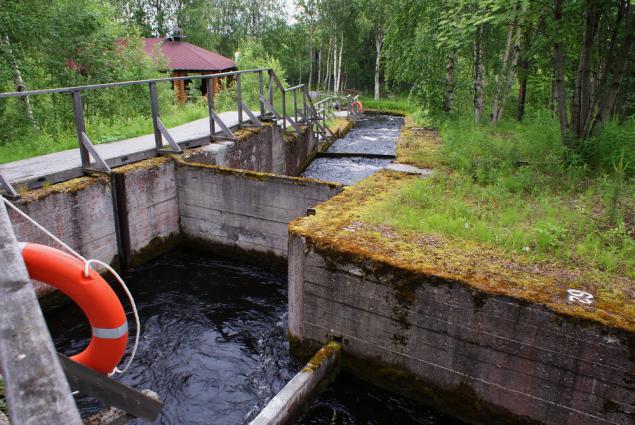

Interestingly, during the spawning hydro shut off closest to the fish ladder 4th hydraulic unit that salmon could hear the noise of the fish ladder and head right place.
At Верхнетуломской station fish ladder made of 2-kilometer tunnel with lighting and special rybolifta, but this design was not successful, the fish did not go. From the position of left - the tunnel was turned into a fish factory and let it warm water from the cooling generators. And fry well, and energy efficiency is evident. Where the generator warm water - see below.
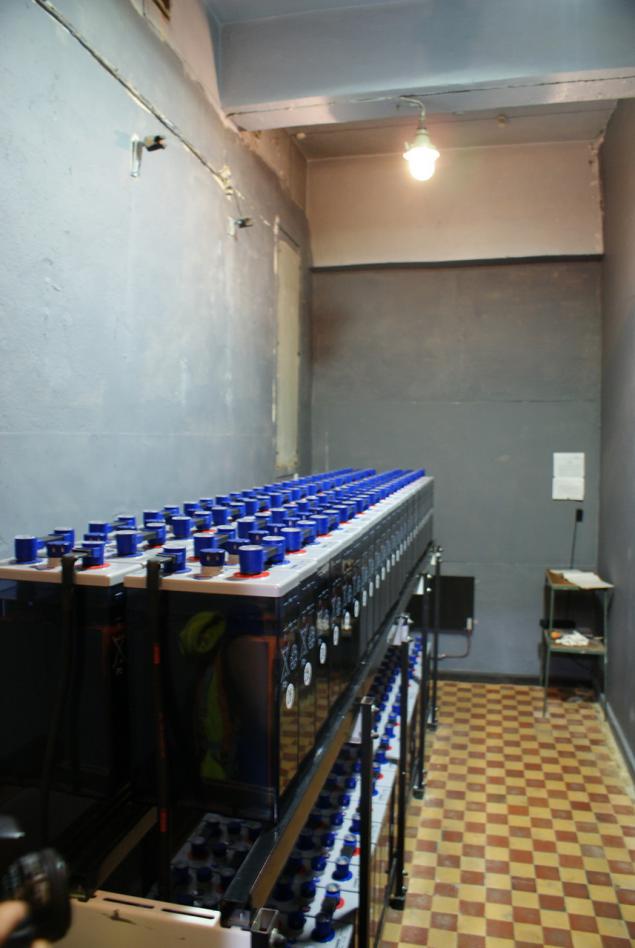
Security h4> Let me remind you that the 2009 accident at the Sayano-Shushenskaya hydropower plant after water break in the engine room was quickly lost the power station's own needs, resulting in the discharge valves to the water intakes had to be done manually. In the wake of this incident, actively engaged in the hydroelectric power backup - emergency diesel generators, batteries.


This is also a safety element - aeration tube in the top of the culverts Кондопожской GES :
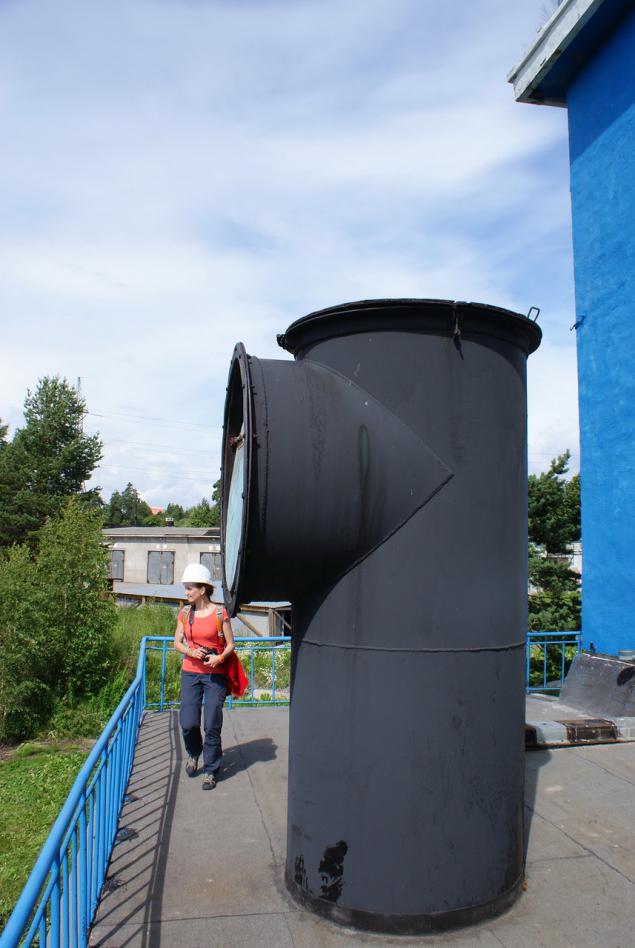


The thickness of the steel wall conduits is relatively small - 12 mm. Rings conduits are designed for high internal pressure or a slight vacuum. But if you close the upper sluice valves and dramatically empty, inside there are high vacuum, and the pipe can be deformed. Aeration pipes let in the air during discharge, and all will be well.
The remains of the wooden sluice 1930:

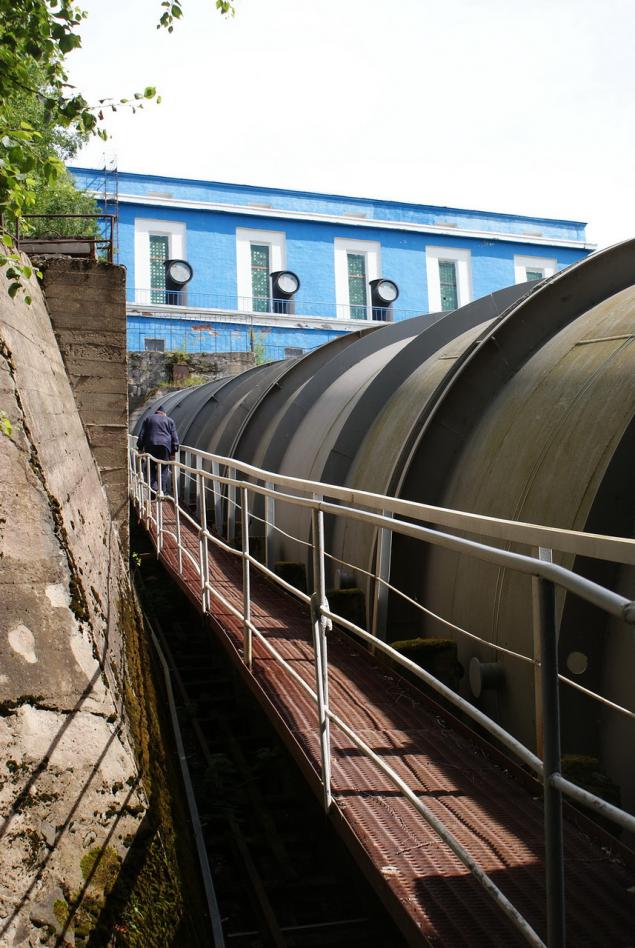
In case during penstock still break out, a security wall (center):

Thanks to her, the water goes to the right - the administrative building, and the station will pass to the left and go into recess downstream.
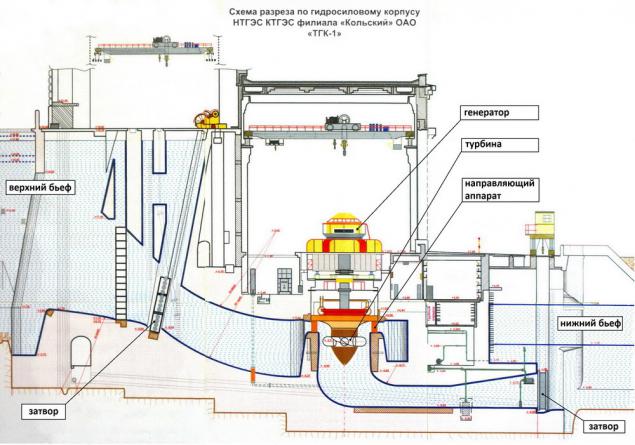
Control and monitoring h4> We are now between the turbine and the generator and observe the shaft connecting them. The left is derived from hydroelectric scheme at her pressure gauge showing pressure in the lubrication system.
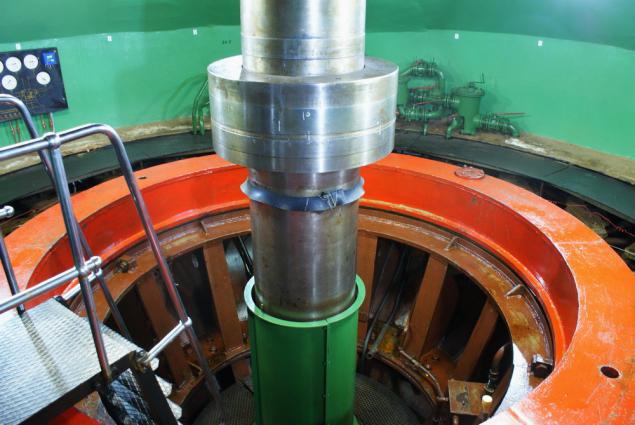

Underfoot - hydraulic, guide vane actuators:
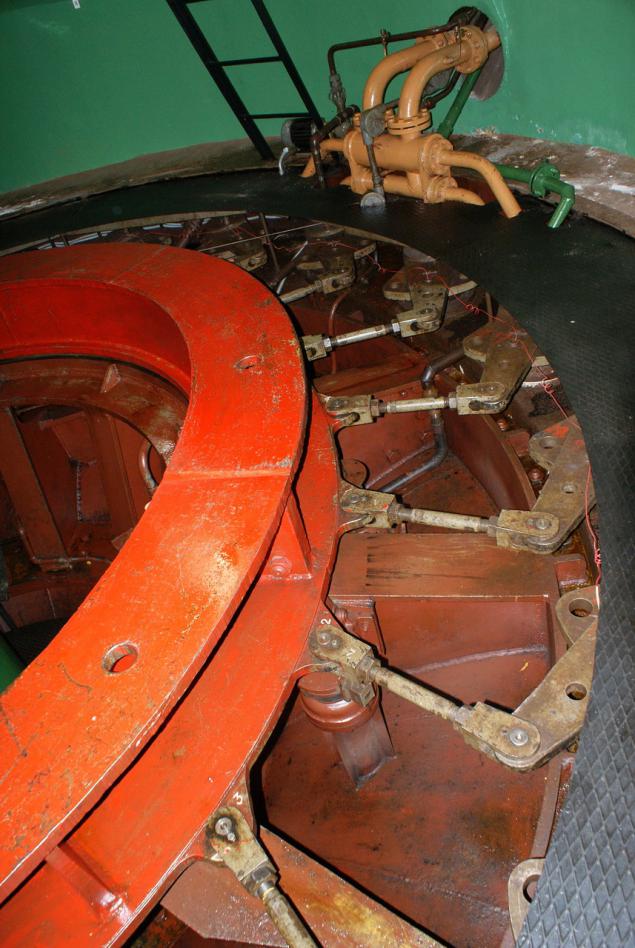

More options can be found in the engine room.
Water and air temperature, water levels in pools of:
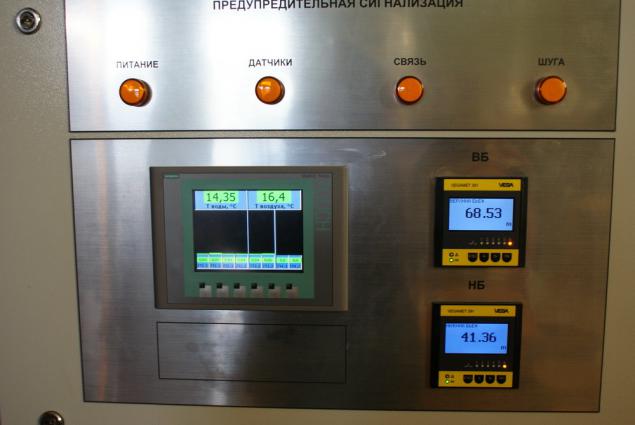

Mimic display.
This hydraulic unit is not working (0 MW capacity, guide vanes closed rotor speed 0%).
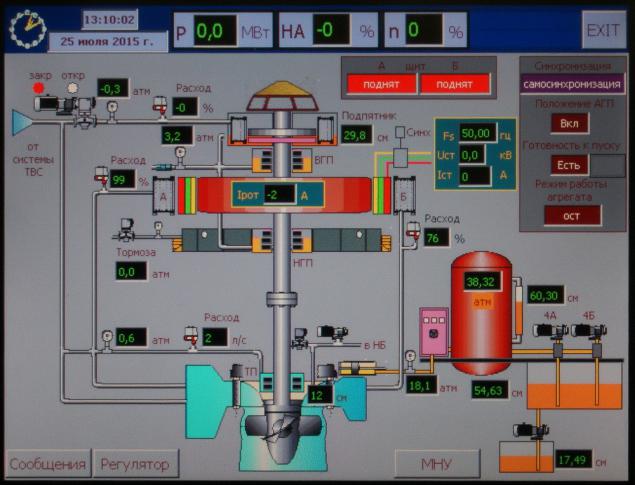
It is clearly seen from both the volute of the turbine (bottom) water is taken and fed to the generator coolers (it in the center, red, coolers A and B) and for the lubrication of the thrust bearing, the upper (AIV) and lower (PNC) generator bearings. Yes, they are lubricated with water. Hence, the warm water is taken to sea farm.
On the right side is visible red tank with oil - a hydraulic control system guide vanes. It also shows the pressure, flow, level of liquids.
Information about vibration:
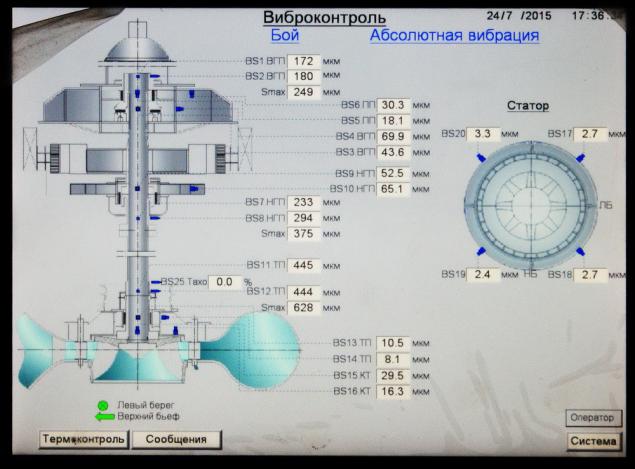
In parentheses: the official reason for the destruction of the hydraulic unit on the same Sayano-Shushenskaya was called fatigue failure of mounting studs of turbine covers due to vibration caused by hydroelectric transitions through a range of "forbidden zone" (there are other Opinions , but now is not about that).
Where is "forbidden zone" seen on the central control panel GES:
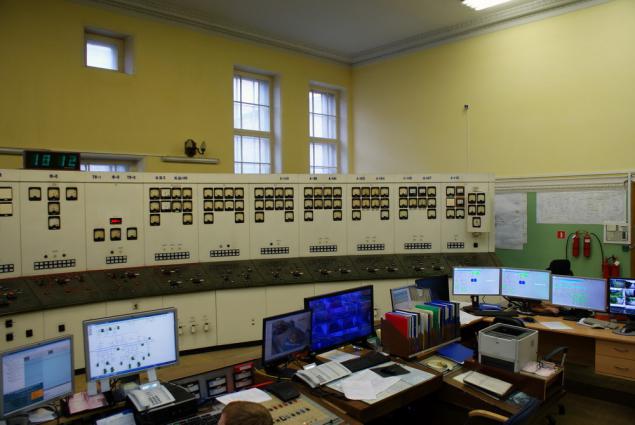

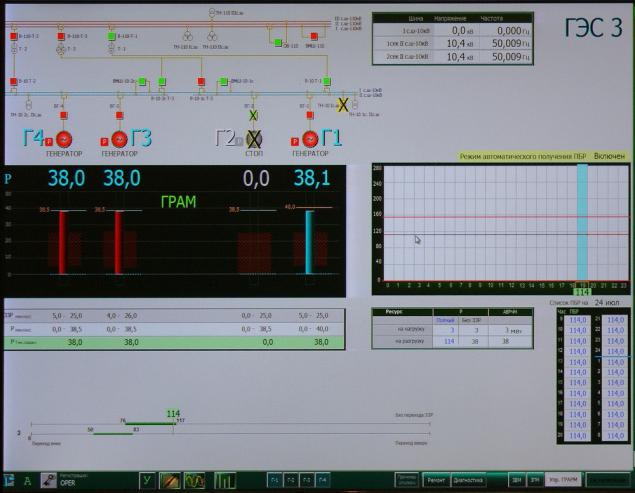
Hydraulic units G1, G3, G4 at work, T2 stopped. On a black background - the power generators that produce 38 MW 1/38/38, respectively. At T3 and T4 poles red because they are operating at full capacity, at the G1 still has reserves. For columns visible red zone - this is the power range in which hydraulic unit is undesirable and that work at the start / stop is necessary to quickly slip.
By the way, who knows the man is still outside the building to say which of the hydraulic units are not working:
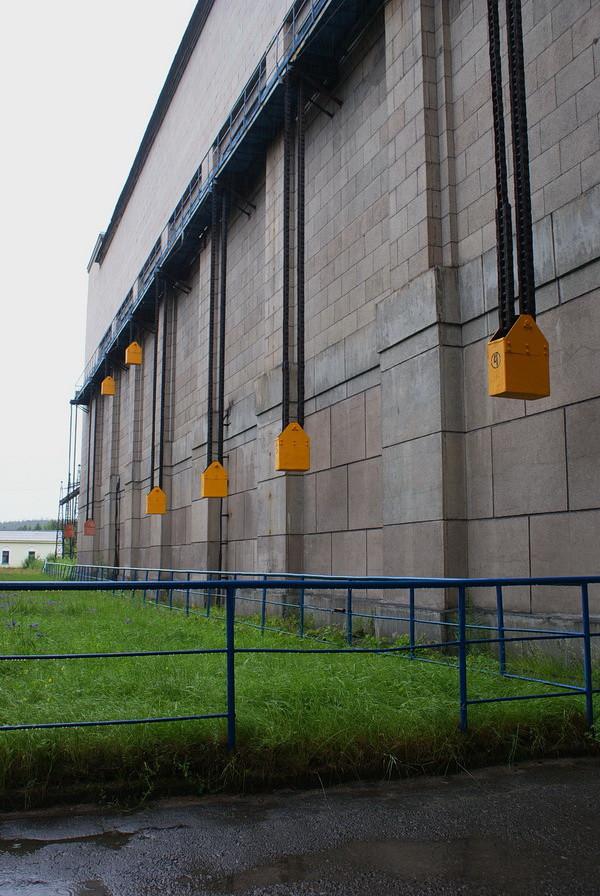

The second pair of counterweights is raised - then locks on penstocks unit number 2 are omitted.
Very actively implement remote control.
For example, the station 60 MW reception, but the staff on it is only during the day on weekdays and in the rest of the time - controlled by remote control including the head HPP:

GES working on the so-called dispatch orders, which regulates when and how to issue power station. Since the hydropower plant - the most maneuverable energy (fast start and fast stop), they are used to cover peak loads and their development varies depending on the time of day and day of the week. Unlike thermal and nuclear power plants, which provide a base portion of consumption and work in a relatively stable manner.
Dispatching the order on the screen (sorry for the quality of the image space; on the horizontal axis - hours, the vertical axis - power):
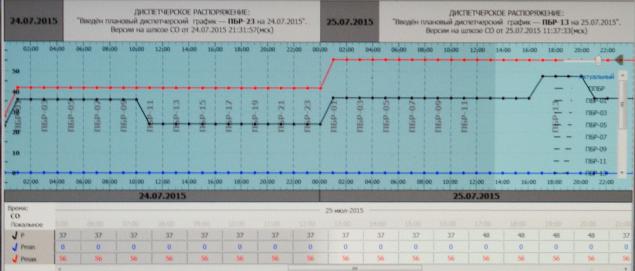
Dispatch task takes into account the mutual influence of HPP cascade, water levels in their reservoirs, consumer demands for water and electricity, etc. and based on this power generation it distributes between stations. Curiously, on the river Paz on the border between Norway and Russia are 5 Russian and Norwegian 2 hydroelectric power station, and the river itself flows from the Finnish lakes. And nothing, once agreed.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/259596/





















































