1781
Zhigulevskaya HPP
Hydropower project construction on the Volga was first considered at the beginning of the last century. In 1910, a talented engineer Krzhizhanovsky Samara (later chairman of the commission of electrification) appealed to the royal government with a proposal to build a hydroelectric station on the Volga in Lada. But only in 1919 at the suggestion of Lenin Gleb Maksimilianovich was instructed to choose a place for waterworks.
Areas surveyed, Krzyzanowski proposed three options for placement of future hydropower plants near the village Perevoloki on Red Glinka near Samara, near the village of Valiant below the city of Stavropol.
In 1940, at the Red Glinka village was laid Management, which was supposed to stay in the headquarters building hydropower. But the Great Patriotic War and all the work was suspended. Additional hydro-geological studies in the post-war years, suggested the feasibility of construction of power plants on the soft ground near the village of Valiant. Here, in 1950, turned a giant building in which was built the largest dam in the country, a huge machine hall and powerful navigation locks.
01. Bank of the Volga, before the construction of power plants, in 1950.

02. Start development of the construction site. Chief of construction of the Kuibyshev hydroelectric been appointed Major General Ivan Komzin.

03. It is no secret that at the front worked thousands of prisoners. Basically, they were kept in Kuneevskom camp on the future site of Komsomolsk district of Togliatti. At the peak of construction in 1955, the number of prisoners reached 46,000!

04. But those years were allowed photographers to shoot only civilian workers.

05. Preparation of the pit station

06. Although it is worth to pay tribute to the leadership on the construction used the most advanced technology at the time - dredgers, excavators, dump trucks.

07. Preparation of a floating bridge on the future site of the spillway dam.

08. Construction of the spillway dam

09. In all, during the construction of the station laid 7 million cubic meters of concrete.

10. spillway dam

11. Drainage concrete dam is located on the left bank of the floodplain. The length of the dam 1 km. It has 38 spillway spans. On the apron of the dam are devices for energy dissipation of water. For maneuvering the gates on the dam mounted 3 gantry cranes, lifting capacity of 250 tons.

12. Detail of the building next to the engine room.

13. At the construction site often visited by government delegations and commissions.

14. Concrete plant.

15. The work of the dredger. Dredgers were used for reclamation of an earth dam.

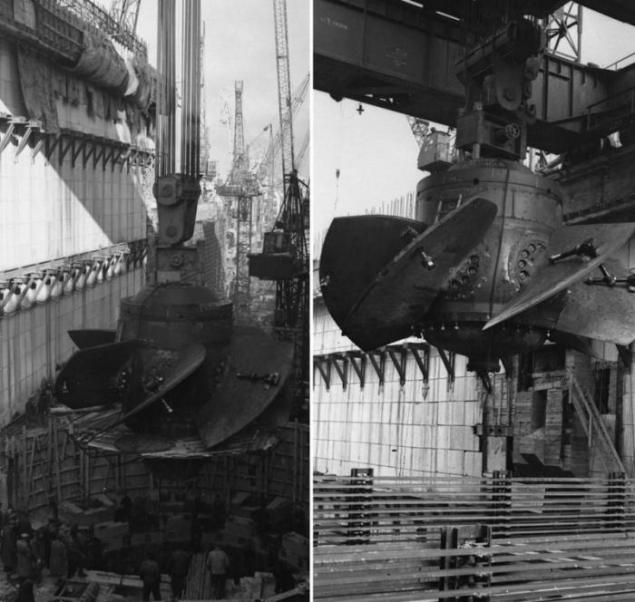
16. Install the impeller hydraulic turbine.
17. earthen dam reclaimed from local fine-grained sand and is located between the power house and overflow dam. The length of the dam is 2800 m, width at the base - 600 m. The highest elevation in the bed part - 50 m.

18. Construction of the turbine hall

19. In the construction of the divers were involved. One of the diving suits kept in the museum Zhigulevskaya HPP.
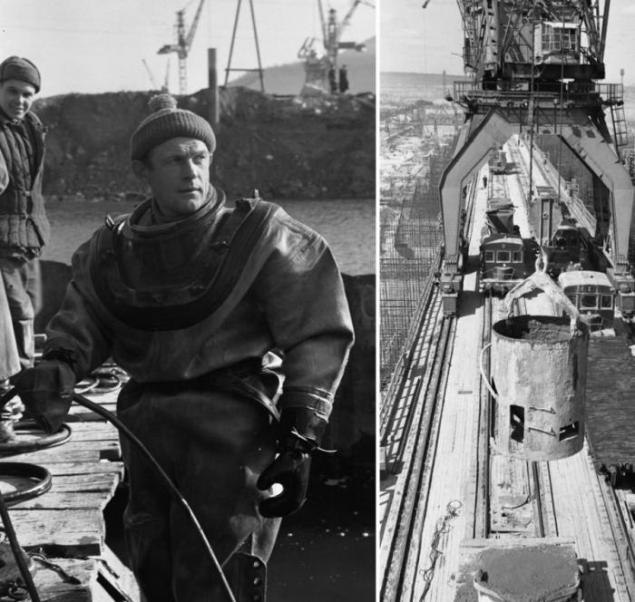

20. At the same time, on the left bank of the Volga, built the twin navigation locks.

21. Fragment gateway

22. Lower gateways

23

24. Upper gateways

25. Check mounting high-voltage line

26. Cement Plant in apple ravine

27. The construction of a pontoon bridge between the power house and the earthen dam.

28. October 30, 1955 began the most crucial part of the job - the overlap of the river.

29. To block the natural course, at the bottom of the Volga, in less than a day, were dropped in 1765 ten-ton pyramid of reinforced concrete.

30.

31. Volga was closed for a record 19 hours and 35 minutes.

32. The water went through the bottom spillways station

33. It began filling the Kuibyshev reservoir.

34. A solemn meeting on the occasion of successful overlap Volga.

35. Top of the hydroelectric dam spilled length of over 600 km. Greatest width - 40 km - reservoir is at the confluence of the Volga and Kama. Maximum depth of the dam - 40 m. The capacity of the reservoir - 58 billion. Cubic meters, it is the largest artificial reservoir in the world.

36. In a flood zone were 270 settlements (17 cities and regional centers), 19 collective farms, two machine-tractor stations (MTS), 175 buildings of various institutions and organizations located outside of Stavropol. Subject to the transfer of built-up areas are not included in the flood zone, but within the zone of land acquisition for the construction of dams and other waterworks facilities. Total in 1953 was moved more than 1,600 households, as well as schools, hospitals, industrial enterprises.

37. August 10, 1958 held a ceremonial start HPP. The celebrations in Stavropol profit leaders of the CPSU and the Soviet government headed by NS Khrushchev.

38. In honor of the successful completion of construction, many prisoners received amnesty, many have reduced terms.

39. The ceremonial passage on a boat through the locks.

40. December 29, 1955 the first unit KuGES was plugged in 18 hours 18 minutes, December 31, 1955 HPS has developed the first million kW / h of electricity. October 14, 1957 HPS reached design capacity - 2.1 million kilowatts.

41. Finally, the circuit construction of the old log of those years.

A little help:
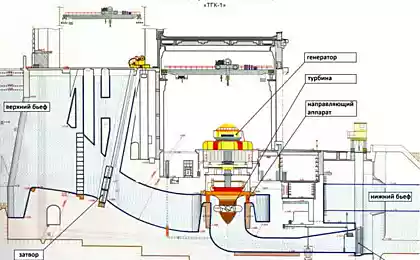
Power house is located on the right bank of the Volga. It consists of 10 sections with dvuhagregatnyh bottom spillways. The engine room installed with a capacity of 20 hydroelectric units with 115 MW Kaplan turbines (impeller diameter - 9 m 3) and the umbrella-type generators (rotor diameter - 14 m 3, the stator - 17, 1 m).
The total length of the power house with the mounting platform - 730 m, width - 100 m, the height from the base to the roof - 80 m. Building volume of the building - 4,500 thousand. Cubic meters. Powerhouse has an extension from bottom water, which is made to equalize the voltage drop under the building and a pond, and the prevention of plastic uplift from beneath the soles of the building. Separate trash facilities located in 33 m from the power house, introduced for the first time in the practice of hydraulic engineering.
Now hydroelectric electricity through two power lines to the integrated power center of the country and along two lines to the Urals and Middle Volga. The level of automation has allowed to reduce the number of staff on duty up to 10 people per shift.
Areas surveyed, Krzyzanowski proposed three options for placement of future hydropower plants near the village Perevoloki on Red Glinka near Samara, near the village of Valiant below the city of Stavropol.
In 1940, at the Red Glinka village was laid Management, which was supposed to stay in the headquarters building hydropower. But the Great Patriotic War and all the work was suspended. Additional hydro-geological studies in the post-war years, suggested the feasibility of construction of power plants on the soft ground near the village of Valiant. Here, in 1950, turned a giant building in which was built the largest dam in the country, a huge machine hall and powerful navigation locks.
01. Bank of the Volga, before the construction of power plants, in 1950.

02. Start development of the construction site. Chief of construction of the Kuibyshev hydroelectric been appointed Major General Ivan Komzin.

03. It is no secret that at the front worked thousands of prisoners. Basically, they were kept in Kuneevskom camp on the future site of Komsomolsk district of Togliatti. At the peak of construction in 1955, the number of prisoners reached 46,000!

04. But those years were allowed photographers to shoot only civilian workers.

05. Preparation of the pit station

06. Although it is worth to pay tribute to the leadership on the construction used the most advanced technology at the time - dredgers, excavators, dump trucks.

07. Preparation of a floating bridge on the future site of the spillway dam.

08. Construction of the spillway dam

09. In all, during the construction of the station laid 7 million cubic meters of concrete.

10. spillway dam

11. Drainage concrete dam is located on the left bank of the floodplain. The length of the dam 1 km. It has 38 spillway spans. On the apron of the dam are devices for energy dissipation of water. For maneuvering the gates on the dam mounted 3 gantry cranes, lifting capacity of 250 tons.

12. Detail of the building next to the engine room.

13. At the construction site often visited by government delegations and commissions.

14. Concrete plant.

15. The work of the dredger. Dredgers were used for reclamation of an earth dam.

16. Install the impeller hydraulic turbine.

17. earthen dam reclaimed from local fine-grained sand and is located between the power house and overflow dam. The length of the dam is 2800 m, width at the base - 600 m. The highest elevation in the bed part - 50 m.

18. Construction of the turbine hall

19. In the construction of the divers were involved. One of the diving suits kept in the museum Zhigulevskaya HPP.

20. At the same time, on the left bank of the Volga, built the twin navigation locks.

21. Fragment gateway

22. Lower gateways

23

24. Upper gateways

25. Check mounting high-voltage line

26. Cement Plant in apple ravine

27. The construction of a pontoon bridge between the power house and the earthen dam.

28. October 30, 1955 began the most crucial part of the job - the overlap of the river.

29. To block the natural course, at the bottom of the Volga, in less than a day, were dropped in 1765 ten-ton pyramid of reinforced concrete.

30.

31. Volga was closed for a record 19 hours and 35 minutes.

32. The water went through the bottom spillways station

33. It began filling the Kuibyshev reservoir.

34. A solemn meeting on the occasion of successful overlap Volga.

35. Top of the hydroelectric dam spilled length of over 600 km. Greatest width - 40 km - reservoir is at the confluence of the Volga and Kama. Maximum depth of the dam - 40 m. The capacity of the reservoir - 58 billion. Cubic meters, it is the largest artificial reservoir in the world.

36. In a flood zone were 270 settlements (17 cities and regional centers), 19 collective farms, two machine-tractor stations (MTS), 175 buildings of various institutions and organizations located outside of Stavropol. Subject to the transfer of built-up areas are not included in the flood zone, but within the zone of land acquisition for the construction of dams and other waterworks facilities. Total in 1953 was moved more than 1,600 households, as well as schools, hospitals, industrial enterprises.

37. August 10, 1958 held a ceremonial start HPP. The celebrations in Stavropol profit leaders of the CPSU and the Soviet government headed by NS Khrushchev.

38. In honor of the successful completion of construction, many prisoners received amnesty, many have reduced terms.

39. The ceremonial passage on a boat through the locks.

40. December 29, 1955 the first unit KuGES was plugged in 18 hours 18 minutes, December 31, 1955 HPS has developed the first million kW / h of electricity. October 14, 1957 HPS reached design capacity - 2.1 million kilowatts.

41. Finally, the circuit construction of the old log of those years.

A little help:
Power house is located on the right bank of the Volga. It consists of 10 sections with dvuhagregatnyh bottom spillways. The engine room installed with a capacity of 20 hydroelectric units with 115 MW Kaplan turbines (impeller diameter - 9 m 3) and the umbrella-type generators (rotor diameter - 14 m 3, the stator - 17, 1 m).
The total length of the power house with the mounting platform - 730 m, width - 100 m, the height from the base to the roof - 80 m. Building volume of the building - 4,500 thousand. Cubic meters. Powerhouse has an extension from bottom water, which is made to equalize the voltage drop under the building and a pond, and the prevention of plastic uplift from beneath the soles of the building. Separate trash facilities located in 33 m from the power house, introduced for the first time in the practice of hydraulic engineering.
Now hydroelectric electricity through two power lines to the integrated power center of the country and along two lines to the Urals and Middle Volga. The level of automation has allowed to reduce the number of staff on duty up to 10 people per shift.