929
Scientists have recorded the process of formation of new knowledge in the brain
Where are the memories i>
Scientists from the University of Carnegie - Mellon впервые It failed to observe , both in the brain form new concepts and show that it occurs in the same areas of the brain in different individuals. The results will help to develop new training methods, as well as to understand the mechanism of memory loss in different brain disorders and injuries
The researchers are confident that they were able to uncover the mechanism of how the brain stores information about certain objects, and that they could, watching the brain works, to determine what kind of object at the moment a person thinks.
This study combined two programs University - Brain-Hub, which studies how the structure and operation of the brain affects the complex behavior, and Simon, which seeks to improve the technique of training of students, so that this improvement is measurable.
Neuroscientist Marcel Just, who led the research, cites as an example of a new concept of learning information about olingito - small mammals animal, which lives in the crowns trees in South America in the humid mountain forests of Ecuador, Colombia and West. Zoologists have found for the first time and described it in 2013.
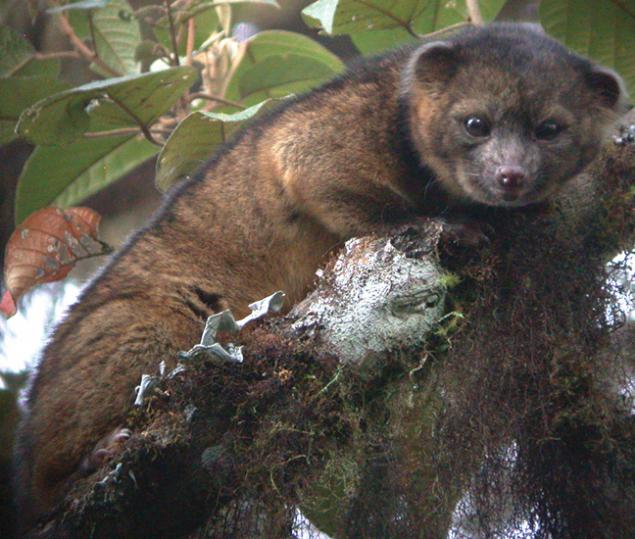

Olingito / Wikipedia i>
"Millions of people read information about olingito and it forever changes the structure of their brains - says Just, a professor of cognitive neuroscience from the College of Humanities and Social Sciences Dietrich owned Carnegie - Mellon University. - And in our study, we studied the brain in the laboratory it is in this moment. When people found out that despite the fact that olingito predator, it feeds mainly fruit, the left inner front part of the brain has retained the information in accordance with its scheme of work. And new knowledge, according to the observations, are preserved in the same parts of the brain in different subjects - apparently, all the brain uses the same storage system ».
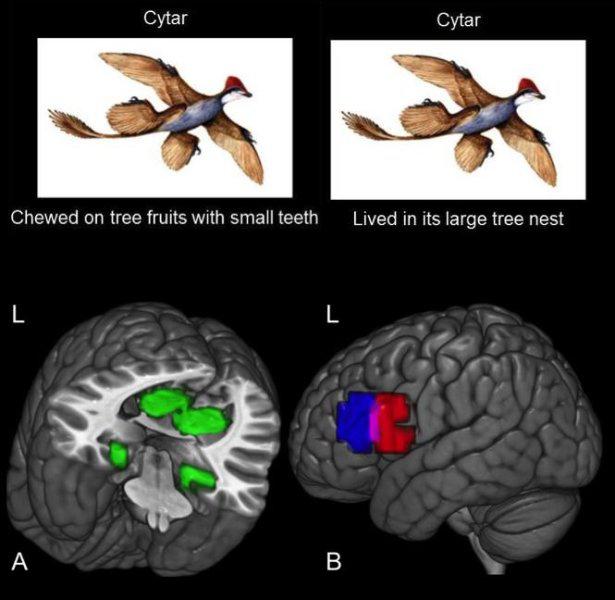
Subjects in the study got acquainted with the life of eight different extinct animals. In the picture are marked in green area of the brain in which the subjects remembered the habitat of the animals, and the red and blue - their eating habits.
Subjects acquainted with the information unit of the life of animals for an hour, but this time their brains, scientists have observed over the apparatuses of functional magnetic resonance imaging. During receive certain part of the brain changed its level of activity.
An important discovery was the fact that for the information submitted by each of the eight animals people were involved their specific areas of the brain. Therefore, a specially developed computer program was able to correctly identify what kind of just thought the subject studied animals. In a sense, it was mind-reading.
It was also found that information about the animals that were somewhat similar to each other, keeping its activation in the brain region also received similar. And besides, it was confirmed that once acquired knowledge about the animal remained in place even after people receive more information about this animal.
Scientists hope that such research ultimately can help in the study of how students understand more complex concepts and notions, and, for example, what part of the student does not understand the concept. It can help to develop new systems of training.

For example, these i>
In addition, research may help to understand why as a result of various diseases, age-related changes and injuries in humans lost access to some of saved memories and skills. Loss of concepts can be a process of reverse acquisition.
By unraveling the brain works different scientists approach from different sides. Psychologists try to understand the logic of the consciousness , physics and watch neurons work at the nanoscale.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/251806/