6514
Thank God, they are extinct! 25 awful creatures
We often hear that now, more and more species are becoming extinct or are on the verge of extinction, and their complete disappearance - only a matter of time. Hunting, destruction of natural habitats, climate change and other factors have led to the fact that the rate of loss of species is 1,000 times greater than the natural background rate of recovery. Although the extinction of animals is always sad, sometimes, for us humans, it can even be beneficial.
From mega snakes in 12 meters length flying creatures the size of a giraffe - look at the list of the 25 animals, the neighborhood that you are unlikely to be happy.
25 photos via list25.com
1. Pelagornis Sandersi
Thanks wingspan that was about 7 meters, bird Pelargonis Sandersi, obviously, was the largest flying bird that ever existed on Earth. Looks like she could fly, just pushed off a cliff, and a large part of their lives over the ocean, relying on wind currents rising from the ocean to stay "afloat". Although compared with pterosaurs wingspan of almost 12 meters, this bird was still quite "moderate" size.

2. Euphoberia
Similar to modern centipedes in form and behavior, Euphoberia still had one major difference - it was more than 90 cm in length! Although scientists are not quite sure what exactly she was fed, we know that some modern millipedes feed on birds, snakes and bats. If the 25-centimeter centipede could hunt the birds, imagine whom could hunt almost meter!

3. Gigantopithecus
Gigantopithecus lived in the period from 9 million to 100 000 years ago in Asia today. It was the largest monkey species on Earth. It is believed that this being the height of 3 meters and weighing up to 540 kg hodilo on four legs like gorillas and chimpanzees, but some believe that they could walk on two legs like humans. Properties of their teeth and jaws suggest that these animals were able to chew coarse fibrous food, bumping and grinding into it.
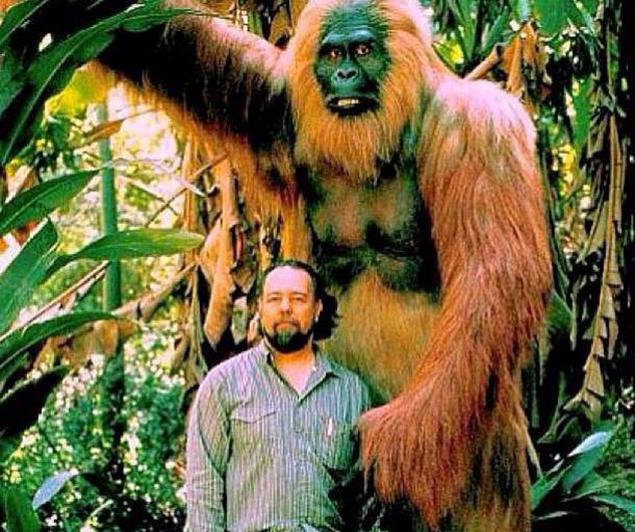

4. Andrewsarchus
This mils lived in the Eocene epoch, about 45 - 30 million years ago. Andrewsarchus was a huge carnivorous mammal. Given the found skull and a few bones, paleontologists suggest that this predator could weigh up to 1800 kg, making it the largest land mammal predator in history. However, the feeding behavior of the animal is not entirely clear, and some theories suggest that Andrewsarchus could be omnivores or scavengers.
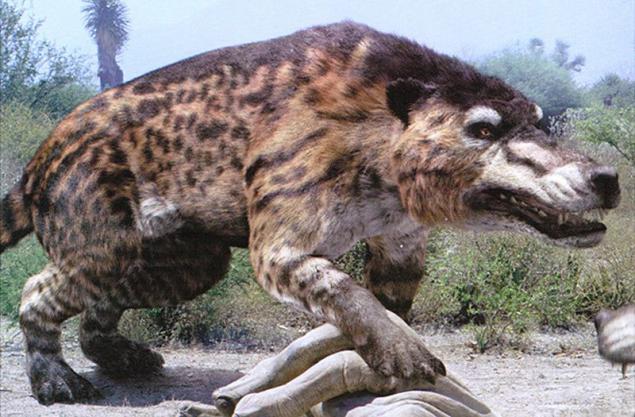

5. Pulmonoscorpius
The scientific name of this being translated as "breathing scorpion." He lived in an era of Visean (c. 345 - 330 million years ago) of the Carboniferous period. Relying on fossils found in Scotland, scientists believe that this species reaches 76 cm in length. He sojourned in the land and ate probably small arthropods.

6. Megalania
Megalania lived in South Australia. It was a huge lizard, extinct about 30 000 years ago, and it means that the first Aborigines of Australia could well meet her. Scientists disagree about the size of this lizard - maybe it reached 7 meters in length, making the largest terrestrial lizard Megalania in history.

7. Helicoprion
One of prehistoric centenarians (310-250 million years ago) - Helicoprion - is a genus of extinct creatures with interesting akulopodobnyh jaw. Up to 4 m in length, but its closest living relatives now - Chimaera - can reach only 1, 5 m in length.

8. Entelodon
Unlike their modern relatives, Entelodon represented a similar boar mammals with special gourmet attitude to meat. Probably one of the scariest-looking creatures in the history Entelodon walked on four legs and were practically with human growth. Some scientists believe that even Entelodon were cannibals. Well, if they ate each other, I think they would not want to try chelovechinki?

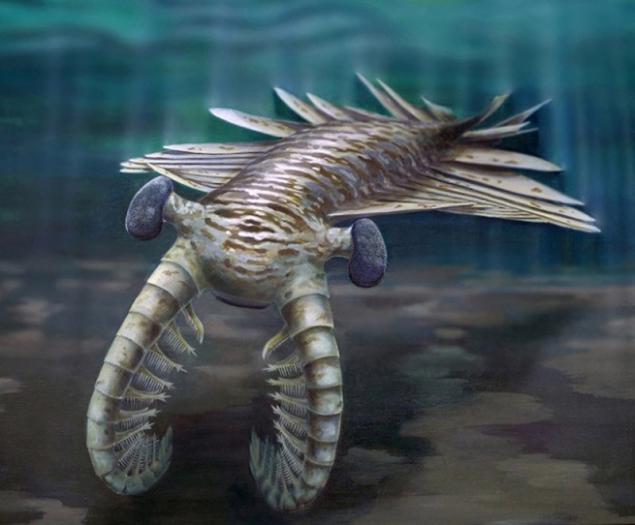
9. Anomalocaris
Probably lived in all the seas of the Cambrian period. In the translation of his name means "abnormal shrimp". This genus of marine animals, close relatives of arthropods. Scientists believe that it preyed on solid-state marine life, including trilobites. They had unique eyes with 30,000 lenses - is that it was one of the most "advanced" eye in the history of the species.

10. Meganeura
Meganeura - a genus of extinct insects from the Carboniferous period. Resembles (and no blood relation) to modern dragonflies. With a wingspan of up to 66 cm it is one of the largest flying insects in the history of our planet. Meganeura was predator and diet consisted mainly of insects and other small amphibians.
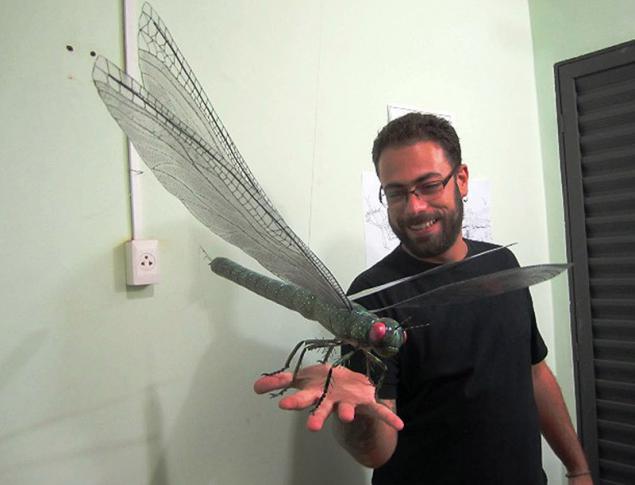

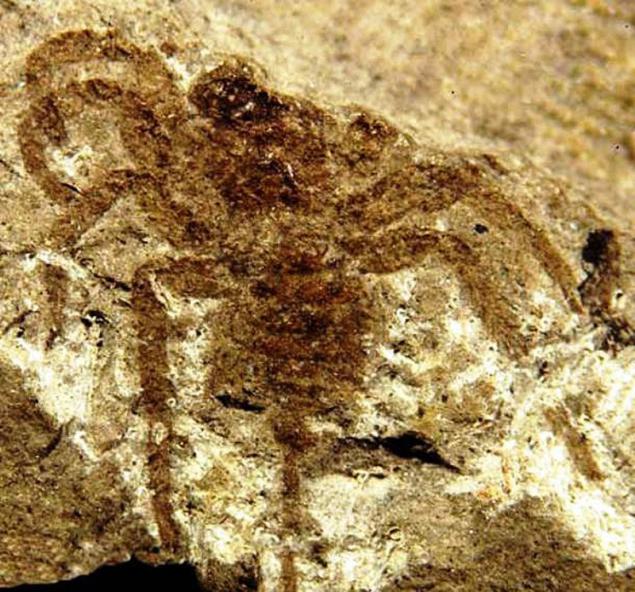
11. Attercopus
Attercopus hailed arachnid animal with a tail like a scorpion. For a long time considered Attercopus prehistoric ancestors of modern spiders, but the scientists who discovered his footprints, soon came to another view. Hardly Attercopus weaving webs, though perhaps used it to wrap the eggs postponed gimp thread or in the construction of the walls of their burrows.

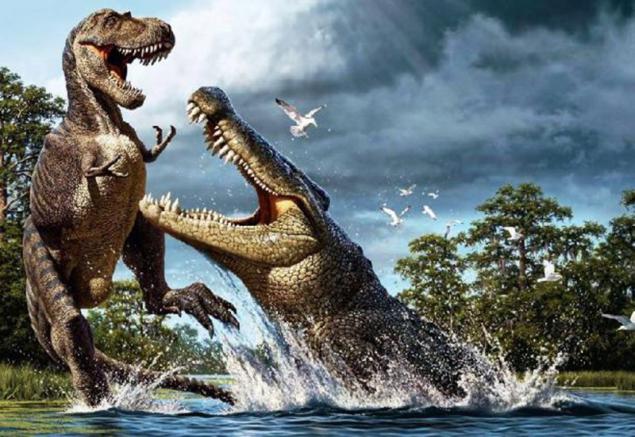
12. Deinosuchus
Deinosuchus - an extinct relative of modern crocodiles alligators lived 80 - 73 million years ago. Although it was the largest of any of the modern species, he looked almost exactly the same. At length he reached 12 meters and have sharp big teeth, able to kill and eat sea turtles, fish and even large dinosaurs.

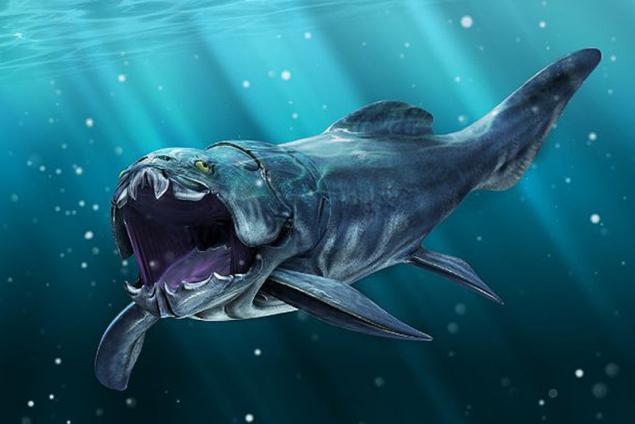
13. Dunkleosteus
Who lived in the late Devonian period, about 380-360 million years ago Dunkleosteus was a huge super-predatory fish. Due to its daunting (up to 10 m in length and weighing nearly 4 tons), he was a top predators of its time. This fish has a strong armor, because of which it was relatively slow, but very powerful swimmer.

14. Spinosaurus
Spinosaurus Tyrannosaurus Rex bigger - is the largest carnivorous dinosaur of all time. It is 18 m in length and weigh up to 10 tons. They eat tons of fish, turtles and even other dinosaurs. If this horror alive today, we likely would not live.

15. Smilodon
Smilodon lived in North and South America in the Pleistocene epoch (2, 5 million - 10,000 years ago). This is the best example of a saber-toothed cat. Great predator with a particularly well-developed forelimbs and incredibly long, sharp fangs. Large individuals can weigh up to 408 kg.

16. Quetzalcoatl
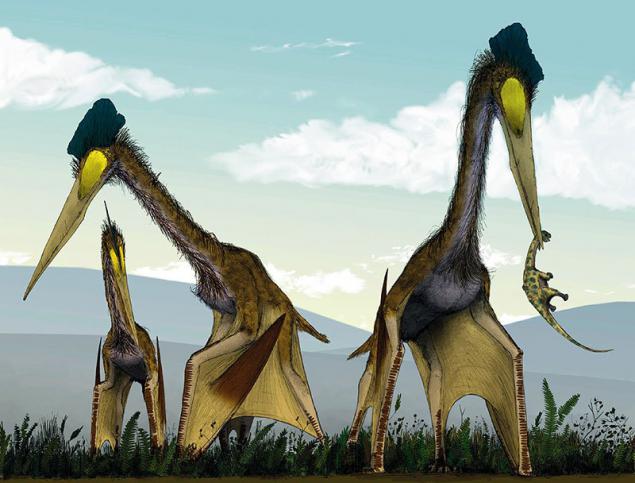
The wingspan of these creatures can reach incredible 12 meters. This pterosaur was the largest ever flying creatures, including those of modern birds. However, to estimate the size and weight of these huge animals is very difficult, because none of the existing animal does not have the same structure of the body, so that the published results vary widely. One characteristic of these animals was that they all had an unusually long and hard neck.

17. Hallucigenia
The name comes from the idea that these creatures - a very strange, almost like a hallucination. These worm-like creatures were 0.5-3 cm in length, and on her head was not some sensory organs such as eyes and nose. Instead Hallucigenia had seven tentacles on each side of the body, as well as three pairs of tentacles behind them. To say that this is a strange creature - consider, say nothing.
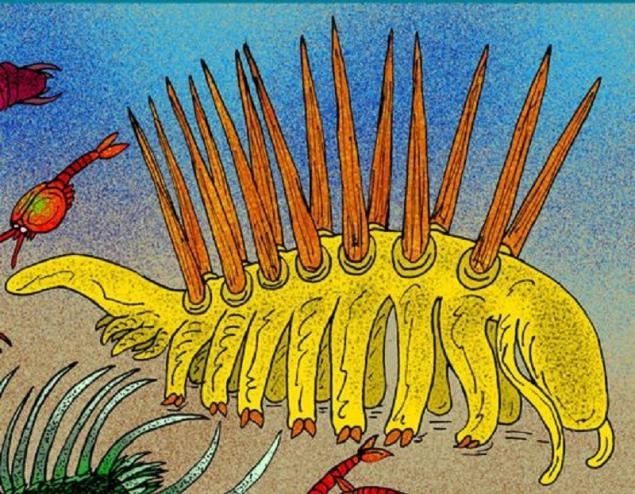
18. Arthropleura
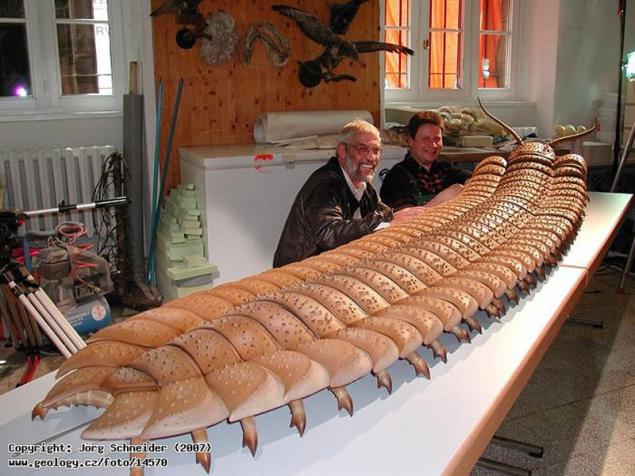
A resident of the Upper Carboniferous period (340-280 million years ago). Living on the territory of modern North America and Scotland. It was the largest species of terrestrial invertebrates in history. Despite its huge length almost 2, 7 meters, Arthropleura were not predators, they eat rotting forest plants.

19. Short-faced bear
Short-faced bear - is an extinct species of bear, who lived in North America during the Pleistocene epoch to 11 000 years ago, making it the "most recent" extinct creatures on our list. However, its size is truly prehistoric. Standing on two hind legs, the bear reached 3, 6 meters high and 4 meters 2, if raised front paw up. It is believed that these giants have weighed more than 1360 kg.

20. Megalodon
The name of this toothy monster translates as "big tooth". This is a huge extinct species of shark that lived about 28 - 1, 5 million years ago. Thanks to its incredible length of 18 meters, it is considered one of the biggest and most powerful predator that ever lived on Earth. Lived almost all over the world, and looked like a larger version of the terrifying and modern great white shark.

21. Titanoboa
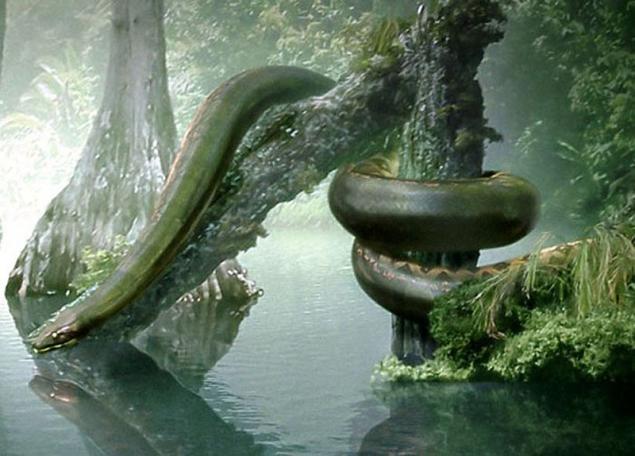
Who lived about 60-58 million years ago during the Paleocene, Titanoboa was the largest, longest and heaviest snake in history. Scientists believe that the individual members of the species reaches 12 meters in length and weighed about 1,133 pounds. Their diet consisted of giant crocodiles and turtles, with whom they shared the territory of modern South America.

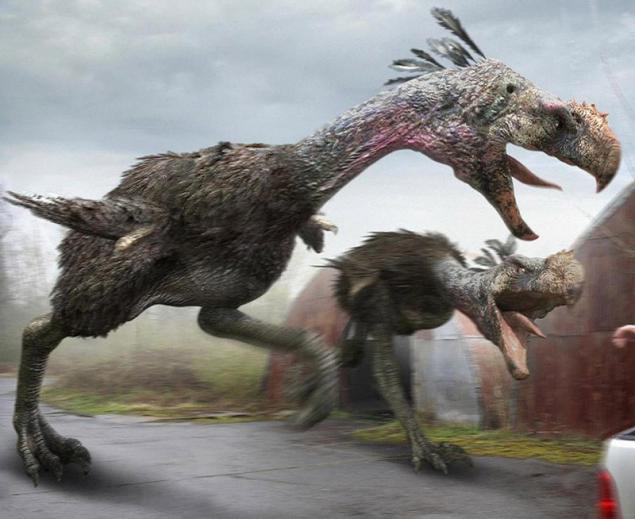
22. Phorusrhacidae
Also called "terrible birds", these prehistoric creatures are extinct genus of large birds of prey that were the largest species in South America during the Cenozoic, about 60 million years ago. Large flightless bird of prey that ever roamed the earth. Reach 3 meters in height, weighed half a ton and is expected to able to run as fast as a cheetah.

23. Cameroceras
He lived in the Ordovician period, 470-460 million years ago. This giant ancestor of modern squids and octopuses. The most characteristic feature of this mollusk was a huge cone-shaped shell and tentacles that he caught the fish and other marine life. It is believed that the size of its shell ranged from 6 to 12 meters.

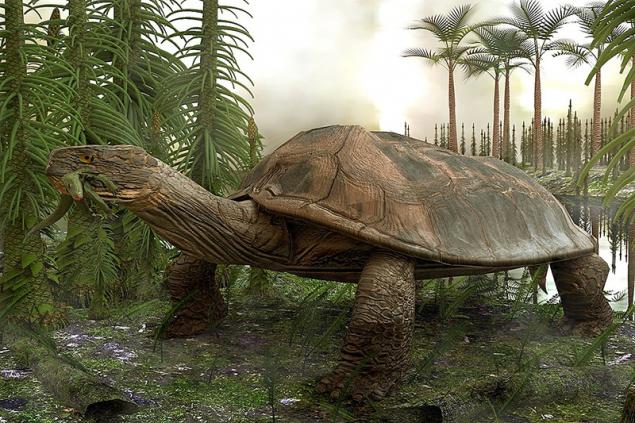
24. Carbonemys
Carbonemys - is an extinct genus of huge turtles that lived about 60 million years ago, ie, they survived the mass extinction of dinosaurs. Fossils found in Colombia, suggest that they had a shell, reaches almost 1, 8 meters. Turtles are carnivores, with huge jaws, powerful enough to eat large mammals such as crocodiles.

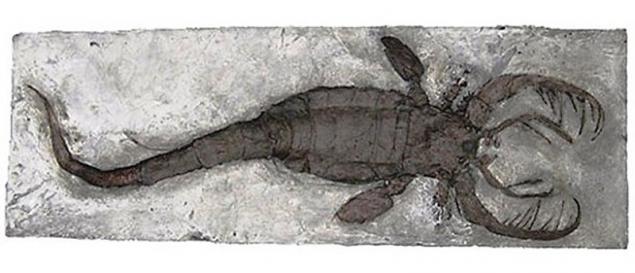
25. Jaekelopterus
Jaekelopterus, without a doubt, you can call one of the largest arthropod in the world - its length reached 2.5 meters. Sometimes it is called "sea scorpion," but in fact it is more about lobster living in freshwater lakes and rivers of modern Western Europe. This horrible creature lived about 390 million years ago, earlier than most dinosaurs.
From mega snakes in 12 meters length flying creatures the size of a giraffe - look at the list of the 25 animals, the neighborhood that you are unlikely to be happy.
25 photos via list25.com
1. Pelagornis Sandersi
Thanks wingspan that was about 7 meters, bird Pelargonis Sandersi, obviously, was the largest flying bird that ever existed on Earth. Looks like she could fly, just pushed off a cliff, and a large part of their lives over the ocean, relying on wind currents rising from the ocean to stay "afloat". Although compared with pterosaurs wingspan of almost 12 meters, this bird was still quite "moderate" size.

2. Euphoberia
Similar to modern centipedes in form and behavior, Euphoberia still had one major difference - it was more than 90 cm in length! Although scientists are not quite sure what exactly she was fed, we know that some modern millipedes feed on birds, snakes and bats. If the 25-centimeter centipede could hunt the birds, imagine whom could hunt almost meter!

3. Gigantopithecus
Gigantopithecus lived in the period from 9 million to 100 000 years ago in Asia today. It was the largest monkey species on Earth. It is believed that this being the height of 3 meters and weighing up to 540 kg hodilo on four legs like gorillas and chimpanzees, but some believe that they could walk on two legs like humans. Properties of their teeth and jaws suggest that these animals were able to chew coarse fibrous food, bumping and grinding into it.

4. Andrewsarchus
This mils lived in the Eocene epoch, about 45 - 30 million years ago. Andrewsarchus was a huge carnivorous mammal. Given the found skull and a few bones, paleontologists suggest that this predator could weigh up to 1800 kg, making it the largest land mammal predator in history. However, the feeding behavior of the animal is not entirely clear, and some theories suggest that Andrewsarchus could be omnivores or scavengers.

5. Pulmonoscorpius
The scientific name of this being translated as "breathing scorpion." He lived in an era of Visean (c. 345 - 330 million years ago) of the Carboniferous period. Relying on fossils found in Scotland, scientists believe that this species reaches 76 cm in length. He sojourned in the land and ate probably small arthropods.

6. Megalania
Megalania lived in South Australia. It was a huge lizard, extinct about 30 000 years ago, and it means that the first Aborigines of Australia could well meet her. Scientists disagree about the size of this lizard - maybe it reached 7 meters in length, making the largest terrestrial lizard Megalania in history.

7. Helicoprion
One of prehistoric centenarians (310-250 million years ago) - Helicoprion - is a genus of extinct creatures with interesting akulopodobnyh jaw. Up to 4 m in length, but its closest living relatives now - Chimaera - can reach only 1, 5 m in length.

8. Entelodon
Unlike their modern relatives, Entelodon represented a similar boar mammals with special gourmet attitude to meat. Probably one of the scariest-looking creatures in the history Entelodon walked on four legs and were practically with human growth. Some scientists believe that even Entelodon were cannibals. Well, if they ate each other, I think they would not want to try chelovechinki?

9. Anomalocaris
Probably lived in all the seas of the Cambrian period. In the translation of his name means "abnormal shrimp". This genus of marine animals, close relatives of arthropods. Scientists believe that it preyed on solid-state marine life, including trilobites. They had unique eyes with 30,000 lenses - is that it was one of the most "advanced" eye in the history of the species.

10. Meganeura
Meganeura - a genus of extinct insects from the Carboniferous period. Resembles (and no blood relation) to modern dragonflies. With a wingspan of up to 66 cm it is one of the largest flying insects in the history of our planet. Meganeura was predator and diet consisted mainly of insects and other small amphibians.

11. Attercopus
Attercopus hailed arachnid animal with a tail like a scorpion. For a long time considered Attercopus prehistoric ancestors of modern spiders, but the scientists who discovered his footprints, soon came to another view. Hardly Attercopus weaving webs, though perhaps used it to wrap the eggs postponed gimp thread or in the construction of the walls of their burrows.

12. Deinosuchus
Deinosuchus - an extinct relative of modern crocodiles alligators lived 80 - 73 million years ago. Although it was the largest of any of the modern species, he looked almost exactly the same. At length he reached 12 meters and have sharp big teeth, able to kill and eat sea turtles, fish and even large dinosaurs.

13. Dunkleosteus
Who lived in the late Devonian period, about 380-360 million years ago Dunkleosteus was a huge super-predatory fish. Due to its daunting (up to 10 m in length and weighing nearly 4 tons), he was a top predators of its time. This fish has a strong armor, because of which it was relatively slow, but very powerful swimmer.

14. Spinosaurus
Spinosaurus Tyrannosaurus Rex bigger - is the largest carnivorous dinosaur of all time. It is 18 m in length and weigh up to 10 tons. They eat tons of fish, turtles and even other dinosaurs. If this horror alive today, we likely would not live.

15. Smilodon
Smilodon lived in North and South America in the Pleistocene epoch (2, 5 million - 10,000 years ago). This is the best example of a saber-toothed cat. Great predator with a particularly well-developed forelimbs and incredibly long, sharp fangs. Large individuals can weigh up to 408 kg.

16. Quetzalcoatl
The wingspan of these creatures can reach incredible 12 meters. This pterosaur was the largest ever flying creatures, including those of modern birds. However, to estimate the size and weight of these huge animals is very difficult, because none of the existing animal does not have the same structure of the body, so that the published results vary widely. One characteristic of these animals was that they all had an unusually long and hard neck.

17. Hallucigenia
The name comes from the idea that these creatures - a very strange, almost like a hallucination. These worm-like creatures were 0.5-3 cm in length, and on her head was not some sensory organs such as eyes and nose. Instead Hallucigenia had seven tentacles on each side of the body, as well as three pairs of tentacles behind them. To say that this is a strange creature - consider, say nothing.

18. Arthropleura
A resident of the Upper Carboniferous period (340-280 million years ago). Living on the territory of modern North America and Scotland. It was the largest species of terrestrial invertebrates in history. Despite its huge length almost 2, 7 meters, Arthropleura were not predators, they eat rotting forest plants.

19. Short-faced bear
Short-faced bear - is an extinct species of bear, who lived in North America during the Pleistocene epoch to 11 000 years ago, making it the "most recent" extinct creatures on our list. However, its size is truly prehistoric. Standing on two hind legs, the bear reached 3, 6 meters high and 4 meters 2, if raised front paw up. It is believed that these giants have weighed more than 1360 kg.

20. Megalodon
The name of this toothy monster translates as "big tooth". This is a huge extinct species of shark that lived about 28 - 1, 5 million years ago. Thanks to its incredible length of 18 meters, it is considered one of the biggest and most powerful predator that ever lived on Earth. Lived almost all over the world, and looked like a larger version of the terrifying and modern great white shark.

21. Titanoboa
Who lived about 60-58 million years ago during the Paleocene, Titanoboa was the largest, longest and heaviest snake in history. Scientists believe that the individual members of the species reaches 12 meters in length and weighed about 1,133 pounds. Their diet consisted of giant crocodiles and turtles, with whom they shared the territory of modern South America.

22. Phorusrhacidae
Also called "terrible birds", these prehistoric creatures are extinct genus of large birds of prey that were the largest species in South America during the Cenozoic, about 60 million years ago. Large flightless bird of prey that ever roamed the earth. Reach 3 meters in height, weighed half a ton and is expected to able to run as fast as a cheetah.

23. Cameroceras
He lived in the Ordovician period, 470-460 million years ago. This giant ancestor of modern squids and octopuses. The most characteristic feature of this mollusk was a huge cone-shaped shell and tentacles that he caught the fish and other marine life. It is believed that the size of its shell ranged from 6 to 12 meters.

24. Carbonemys
Carbonemys - is an extinct genus of huge turtles that lived about 60 million years ago, ie, they survived the mass extinction of dinosaurs. Fossils found in Colombia, suggest that they had a shell, reaches almost 1, 8 meters. Turtles are carnivores, with huge jaws, powerful enough to eat large mammals such as crocodiles.

25. Jaekelopterus
Jaekelopterus, without a doubt, you can call one of the largest arthropod in the world - its length reached 2.5 meters. Sometimes it is called "sea scorpion," but in fact it is more about lobster living in freshwater lakes and rivers of modern Western Europe. This horrible creature lived about 390 million years ago, earlier than most dinosaurs.
























