1251
The reaction to the extreme
++++ We hear about people burned at the stake, frozen and crushed an incredible amount of external force. But what actually happens to the human body when it is exposed to these extremes?
13 photos.
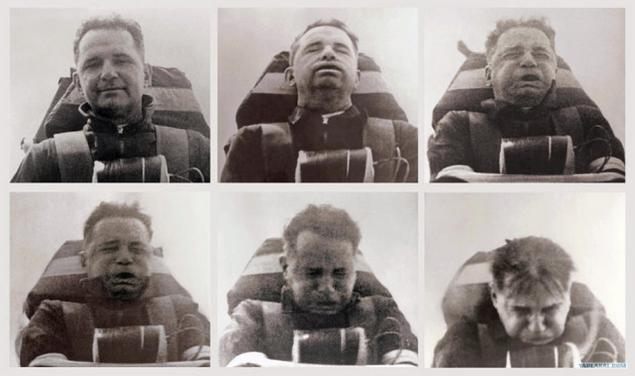
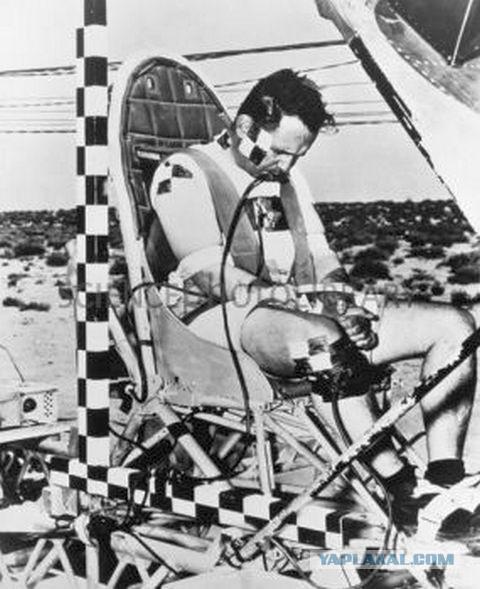
1. Acceleration
Overload did not affect people until the end of World War I, when the pilots for mysterious reasons began to lose consciousness in the middle of the flight. Thanks to the US Air Force officer John Stepp we learned a lot more about how to overload effects on the human body, and began serious study to identify the causes.
Stepp subjected yourself to 35g, which is equivalent to the acceleration of 343 m / s2. His bones cracked and broken, and flew dental fillings. But a greater effect on blood fell.
When acceleration occurs along the horizontal axis, the body can withstand overload quite well because blood flow remains in the same horizontal plane. But when the acceleration of gravity acts vertically, things are not going so well. After a certain level (about 4-5g for most people), our body systems are not strong enough to pump blood, and all of it remains in our lower extremities.
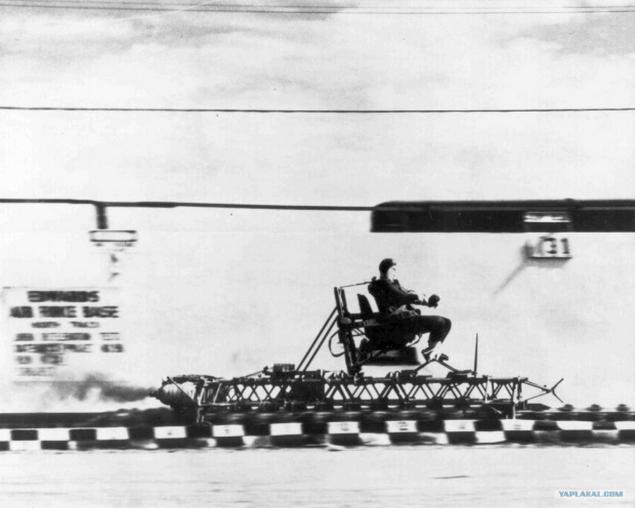
Negative acceleration due to gravity causes the same problems, preventing the bloodstream very quickly accumulating too much blood in one place. That is why there is a G-suit: air suits create sufficient external pressure to keep the blood where it should be, preventing loss of consciousness pilots.
Stapp endured last run, when it accelerated to 1017 km / h, stopped in one second and briefly weighed 3500 kg. In the end, he died peacefully at his home at the age of 89 years.

2. Pressure
Decompression sickness, commonly known as "the bends", occurs when the human body feels a sudden drop in ambient pressure. In the blood can no longer efficiently dissolve gas such as nitrogen. Instead, the gases remain in the blood stream in the form of bubbles. In severe cases, the bubbles accumulate in the blood vessels and block the flow, which could result in dizziness, confusion and even death is possible.
A mild form of "the bends", as a rule, causes joint pain and swelling of tissues. Divers who expose themselves to changes in pressure regularly, can no longer ignore the effects of "the bends", which can lead to permanent joint damage. Decompression sickness can kill the second type. Victims of this type of test conditions such as dizziness, paralysis and shock.

3. Chill
When the body temperature falls to about 30 ° C, all bodily functions are slowed. The first symptoms of this are tiredness, clumsiness, and the delay in responding to external stimuli.
One of the first 30-degree mark thermoregulatory system fails, or the body's ability to maintain its own internal temperature. The heart also will gradually slow down with work light, while the whole body lacks oxygen. In addition, rapid kidney failure, flooding the body with diluted urine. This material infiltrates into the blood and organs, causing shock and other heart problems.
Decreased metabolism and body systems requirements allows some people to survive the extreme cases of hypothermia and fully recover with proper heating.

4. Heat
Thermal shock occurs when the core body temperature rises above 40 degrees. Classic heat stroke develops slowly when exposed to heat, for example, in the summer heat. Heatstroke during physical activity affects people who experience heavy exercise in hot conditions, such as industrial workers and athletes. Only 20% of people who have experienced either of these two types can survive without treatment, and many who have experienced heat stroke, suffered some brain damage.
Humidity increases the chances of getting heat stroke, preventing the evaporation of sweat and reducing the body's ability to protect themselves from the heat. Once the internal temperature of the body will hold on to 42 ° C for 45 minutes, the cells begin to fail. Tissue swell, the digestive system weakens, missing toxins in the body. In lighter cases, called heat exhaustion, only slows the circulatory system. At full heatstroke nervous system is not functioning properly, which leads to confusion, convulsions and dizziness.

5. Fire
Hot air and humidity can push the body to its limits. But the fire, unsurprisingly, takes the body a few steps further - to damage, death and decay.
Researchers from the University of West Florida burned corpses donated to document what happens to the body. Normal human body burns for seven hours. The outer layer of skin is burned first, cracked before burn. The deeper layers of the skin does not hold much longer, disappearing after about five minutes.
By the time the flame is taken as the fat layer. Fat is a good fuel, while the clothes or the wood in the fire act as the candle wick. Fat melts in the soaking "wick", and then remains on for several hours. Flame also dries the muscles, reducing them and causing the body to move.
Fire usually dies himself when there are only bones, if they are not broken, and from them emerged the brain. Teeth also do not burn.
During the cremation, however, is a much hotter the fire, and the body burns faster. The temperature of the fire at the cremation comes to 600-800 ° C. But even at this temperature, the process of transforming the body into ashes can last several hours.
According to the researchers, the human body is burning smells just like pork ribs on the barbecue.

6. Hunger
We all know that hunger kills, but the way it happens, especially appalling. Stomach physically reduced in size, and then can be uncomfortable again is a normal amount of food, even if it is food for your salvation. The heart muscle contracts, reducing the number of strokes and reducing blood pressure. Prolonged fasting leads to anemia, and women can completely stop menstruation.
When the body lacks the sugar begins to burn fat. This may seem like something good, but when fat reserves quickly spent, together with the energy released compounds called ketones. Ketones accumulate, leading to nausea and exhaustion, not to mention bad breath.
Your bones can permanently weaken after a temporary starvation. Perhaps more surprising would be a permanent effect on the brain. Without vital nutrients, such as potassium and phosphorus, the brain can not work normally. You can physically lose some of the gray matter in the brain: even if you continue to have some losses can not be making dysfunction of the brain permanent.
Growing children and adolescents may suffer from a chronic illness throughout his life, such as the inability to make a woman a child to term. Perhaps the most strange that people suffering from long-term starvation, often overgrown with a layer of soft tiny hairs called lanugo, which helps the body to regulate its temperature.

7. Height
Even if you're not afraid of heights, you are likely to experience painful feeling when looked from the top of a skyscraper. This vertigo, and it is not only psychological.
Harmony - a tricky thing. When we are on earth, we focus on sustainable fixed objects. However, when we are at the top of a 30-storey building, it does not work. Nearest immovable object (except the floor under your feet) is located so far that your body can not use it to reassure himself that he, too, is stationary.
Rocking the building creates an additional problem. When you are high enough, all lightly swinging, and our bodies feel it, even if we are not aware of. The more we are, the more rocking, and the harder we adjust our balance. If the effect is strong enough, it can affect our own center of gravity.
People, bad estimates the distance to suffer from acrophobia stronger. In the study, University of California considered how people value the height of buildings. Those who overestimated the height of the building, showed a strong reaction, standing at a height. These results suggest a direct link between perception and fear.

8. Chemicals
Hydrogen sulfide is a pretty nasty thing. He smell rancid eggs, and a large number of possibly killed the dinosaurs and countless other forms of prehistoric life. But all living things produce this substance in very small quantities, and it helps to regulate the speed of our internal processes. And most recently, hydrogen sulfide was found a new use - the introduction of the mice in the state of suspended animation.
When introducing the correct dose sulfide metabolism slows and lowers the body temperature much lower than the internal threshold hypothermia. All functions of the body, including the blood circulation and lungs work virtually stopped.
Tests on animals have shown that hydrogen sulfide inhibits the normal operation of the body, but it can make it the ideal tool to slow the damage from burns and diseases, while the person is unable to obtain the necessary assistance.

9. Radiation
Radioactive decay releases energy in the environment. This energy interacts with the cells of the body, either destroying them or forcing mutate. Mutations develop into cancer, and some radioactive materials affect specific parts of the body especially hard. For example, radioactive iodine accumulates in the thyroid gland, causing thyroid cancer, especially in children.
To develop significantly the risk of cancer in humans requires a relatively large amount of radiation. Usually a person is exposed to 0, 24 to 0, 3 rems of radiation per year. To the risk of cancer increased by 0, 5% must be about 10 rem.
Radiation sickness kills at 200 rem. Radiation sickness is instantaneous effects such as vomiting, reduction in the number of erythrocytes and bone marrow damage. Bone damage caused another, more serious problem: the bone marrow is responsible for the production of blood platelets needed in the process of blood clotting.

10. Loneliness
The feeling of loneliness - normally. Even in a room filled we can feel an overwhelming sense of loneliness, if anyone of us have no links. But chronic loneliness can have a real impact on our body.
According to psychologists, University of Chicago, in lonely people seriously suppressed immune system for an interesting reason. Because people feel lonely world of danger, unfriendly place, their immune system to fixate on the fight against bacterial infections. This makes them unable to produce sufficient amounts of antiviral antibodies, making them more susceptible to viral diseases.
Do single people also often have high blood pressure, as well as atherosclerosis and sleep problems. A high level of stress makes the lonely people more vulnerable to heart disease and stroke.

11. Water
We all know about the dangers of dehydration, but not less, and we hear about the dangers of excess water in the body.
Water intoxication causes all kinds of problems, the most deadly of which is hyponatremia. When the kidneys can not get rid of excess water, they push it into the bloodstream, where it thins the blood and causes a serious drop in the number of electrolytes. Without enough salt in the body you suffer from headaches, exhaustion, vomiting and disorientation.
After the blood can not cope with it, water is directed into the cells to swell. This process is fatal when the cells are not able to grow, e.g., in the spinal cord or brain. This causes brain swelling, coma, seizures and, eventually, death.
Also, excessive drinking can be another problem. The water contains contaminants. If you regularly drink more water than the recommended safe amount (which is actually much smaller than the lauded eight glasses a day), contaminants can quickly reach a level at which the body can no longer cope with the situation.
Source

13 photos.

1. Acceleration
Overload did not affect people until the end of World War I, when the pilots for mysterious reasons began to lose consciousness in the middle of the flight. Thanks to the US Air Force officer John Stepp we learned a lot more about how to overload effects on the human body, and began serious study to identify the causes.
Stepp subjected yourself to 35g, which is equivalent to the acceleration of 343 m / s2. His bones cracked and broken, and flew dental fillings. But a greater effect on blood fell.
When acceleration occurs along the horizontal axis, the body can withstand overload quite well because blood flow remains in the same horizontal plane. But when the acceleration of gravity acts vertically, things are not going so well. After a certain level (about 4-5g for most people), our body systems are not strong enough to pump blood, and all of it remains in our lower extremities.

Negative acceleration due to gravity causes the same problems, preventing the bloodstream very quickly accumulating too much blood in one place. That is why there is a G-suit: air suits create sufficient external pressure to keep the blood where it should be, preventing loss of consciousness pilots.
Stapp endured last run, when it accelerated to 1017 km / h, stopped in one second and briefly weighed 3500 kg. In the end, he died peacefully at his home at the age of 89 years.

2. Pressure
Decompression sickness, commonly known as "the bends", occurs when the human body feels a sudden drop in ambient pressure. In the blood can no longer efficiently dissolve gas such as nitrogen. Instead, the gases remain in the blood stream in the form of bubbles. In severe cases, the bubbles accumulate in the blood vessels and block the flow, which could result in dizziness, confusion and even death is possible.
A mild form of "the bends", as a rule, causes joint pain and swelling of tissues. Divers who expose themselves to changes in pressure regularly, can no longer ignore the effects of "the bends", which can lead to permanent joint damage. Decompression sickness can kill the second type. Victims of this type of test conditions such as dizziness, paralysis and shock.

3. Chill
When the body temperature falls to about 30 ° C, all bodily functions are slowed. The first symptoms of this are tiredness, clumsiness, and the delay in responding to external stimuli.
One of the first 30-degree mark thermoregulatory system fails, or the body's ability to maintain its own internal temperature. The heart also will gradually slow down with work light, while the whole body lacks oxygen. In addition, rapid kidney failure, flooding the body with diluted urine. This material infiltrates into the blood and organs, causing shock and other heart problems.
Decreased metabolism and body systems requirements allows some people to survive the extreme cases of hypothermia and fully recover with proper heating.

4. Heat
Thermal shock occurs when the core body temperature rises above 40 degrees. Classic heat stroke develops slowly when exposed to heat, for example, in the summer heat. Heatstroke during physical activity affects people who experience heavy exercise in hot conditions, such as industrial workers and athletes. Only 20% of people who have experienced either of these two types can survive without treatment, and many who have experienced heat stroke, suffered some brain damage.
Humidity increases the chances of getting heat stroke, preventing the evaporation of sweat and reducing the body's ability to protect themselves from the heat. Once the internal temperature of the body will hold on to 42 ° C for 45 minutes, the cells begin to fail. Tissue swell, the digestive system weakens, missing toxins in the body. In lighter cases, called heat exhaustion, only slows the circulatory system. At full heatstroke nervous system is not functioning properly, which leads to confusion, convulsions and dizziness.

5. Fire
Hot air and humidity can push the body to its limits. But the fire, unsurprisingly, takes the body a few steps further - to damage, death and decay.
Researchers from the University of West Florida burned corpses donated to document what happens to the body. Normal human body burns for seven hours. The outer layer of skin is burned first, cracked before burn. The deeper layers of the skin does not hold much longer, disappearing after about five minutes.
By the time the flame is taken as the fat layer. Fat is a good fuel, while the clothes or the wood in the fire act as the candle wick. Fat melts in the soaking "wick", and then remains on for several hours. Flame also dries the muscles, reducing them and causing the body to move.
Fire usually dies himself when there are only bones, if they are not broken, and from them emerged the brain. Teeth also do not burn.
During the cremation, however, is a much hotter the fire, and the body burns faster. The temperature of the fire at the cremation comes to 600-800 ° C. But even at this temperature, the process of transforming the body into ashes can last several hours.
According to the researchers, the human body is burning smells just like pork ribs on the barbecue.

6. Hunger
We all know that hunger kills, but the way it happens, especially appalling. Stomach physically reduced in size, and then can be uncomfortable again is a normal amount of food, even if it is food for your salvation. The heart muscle contracts, reducing the number of strokes and reducing blood pressure. Prolonged fasting leads to anemia, and women can completely stop menstruation.
When the body lacks the sugar begins to burn fat. This may seem like something good, but when fat reserves quickly spent, together with the energy released compounds called ketones. Ketones accumulate, leading to nausea and exhaustion, not to mention bad breath.
Your bones can permanently weaken after a temporary starvation. Perhaps more surprising would be a permanent effect on the brain. Without vital nutrients, such as potassium and phosphorus, the brain can not work normally. You can physically lose some of the gray matter in the brain: even if you continue to have some losses can not be making dysfunction of the brain permanent.
Growing children and adolescents may suffer from a chronic illness throughout his life, such as the inability to make a woman a child to term. Perhaps the most strange that people suffering from long-term starvation, often overgrown with a layer of soft tiny hairs called lanugo, which helps the body to regulate its temperature.

7. Height
Even if you're not afraid of heights, you are likely to experience painful feeling when looked from the top of a skyscraper. This vertigo, and it is not only psychological.
Harmony - a tricky thing. When we are on earth, we focus on sustainable fixed objects. However, when we are at the top of a 30-storey building, it does not work. Nearest immovable object (except the floor under your feet) is located so far that your body can not use it to reassure himself that he, too, is stationary.
Rocking the building creates an additional problem. When you are high enough, all lightly swinging, and our bodies feel it, even if we are not aware of. The more we are, the more rocking, and the harder we adjust our balance. If the effect is strong enough, it can affect our own center of gravity.
People, bad estimates the distance to suffer from acrophobia stronger. In the study, University of California considered how people value the height of buildings. Those who overestimated the height of the building, showed a strong reaction, standing at a height. These results suggest a direct link between perception and fear.

8. Chemicals
Hydrogen sulfide is a pretty nasty thing. He smell rancid eggs, and a large number of possibly killed the dinosaurs and countless other forms of prehistoric life. But all living things produce this substance in very small quantities, and it helps to regulate the speed of our internal processes. And most recently, hydrogen sulfide was found a new use - the introduction of the mice in the state of suspended animation.
When introducing the correct dose sulfide metabolism slows and lowers the body temperature much lower than the internal threshold hypothermia. All functions of the body, including the blood circulation and lungs work virtually stopped.
Tests on animals have shown that hydrogen sulfide inhibits the normal operation of the body, but it can make it the ideal tool to slow the damage from burns and diseases, while the person is unable to obtain the necessary assistance.

9. Radiation
Radioactive decay releases energy in the environment. This energy interacts with the cells of the body, either destroying them or forcing mutate. Mutations develop into cancer, and some radioactive materials affect specific parts of the body especially hard. For example, radioactive iodine accumulates in the thyroid gland, causing thyroid cancer, especially in children.
To develop significantly the risk of cancer in humans requires a relatively large amount of radiation. Usually a person is exposed to 0, 24 to 0, 3 rems of radiation per year. To the risk of cancer increased by 0, 5% must be about 10 rem.
Radiation sickness kills at 200 rem. Radiation sickness is instantaneous effects such as vomiting, reduction in the number of erythrocytes and bone marrow damage. Bone damage caused another, more serious problem: the bone marrow is responsible for the production of blood platelets needed in the process of blood clotting.

10. Loneliness
The feeling of loneliness - normally. Even in a room filled we can feel an overwhelming sense of loneliness, if anyone of us have no links. But chronic loneliness can have a real impact on our body.
According to psychologists, University of Chicago, in lonely people seriously suppressed immune system for an interesting reason. Because people feel lonely world of danger, unfriendly place, their immune system to fixate on the fight against bacterial infections. This makes them unable to produce sufficient amounts of antiviral antibodies, making them more susceptible to viral diseases.
Do single people also often have high blood pressure, as well as atherosclerosis and sleep problems. A high level of stress makes the lonely people more vulnerable to heart disease and stroke.

11. Water
We all know about the dangers of dehydration, but not less, and we hear about the dangers of excess water in the body.
Water intoxication causes all kinds of problems, the most deadly of which is hyponatremia. When the kidneys can not get rid of excess water, they push it into the bloodstream, where it thins the blood and causes a serious drop in the number of electrolytes. Without enough salt in the body you suffer from headaches, exhaustion, vomiting and disorientation.
After the blood can not cope with it, water is directed into the cells to swell. This process is fatal when the cells are not able to grow, e.g., in the spinal cord or brain. This causes brain swelling, coma, seizures and, eventually, death.
Also, excessive drinking can be another problem. The water contains contaminants. If you regularly drink more water than the recommended safe amount (which is actually much smaller than the lauded eight glasses a day), contaminants can quickly reach a level at which the body can no longer cope with the situation.
Source