1615
Scientific photography contest
The Cambridge University held a competition of scientific works, among which are separately held a competition of scientific photography,
which was presented 155 works - photographs taken during various scientific studies.
Another impressive shot - "Farewell to the King," which captures the moment when a bullet cuts the playing card with the king of diamonds.
The picture was taken student Nate Sharpe via playing cards, stroboscopic flash 400 nanoseconds
and shotgun cartridges with high-speed Viper 22.
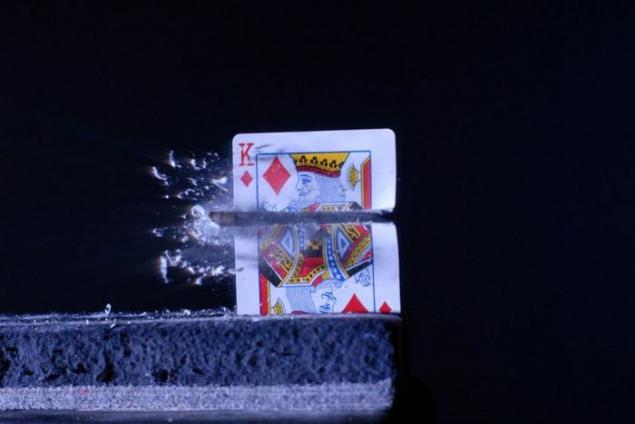

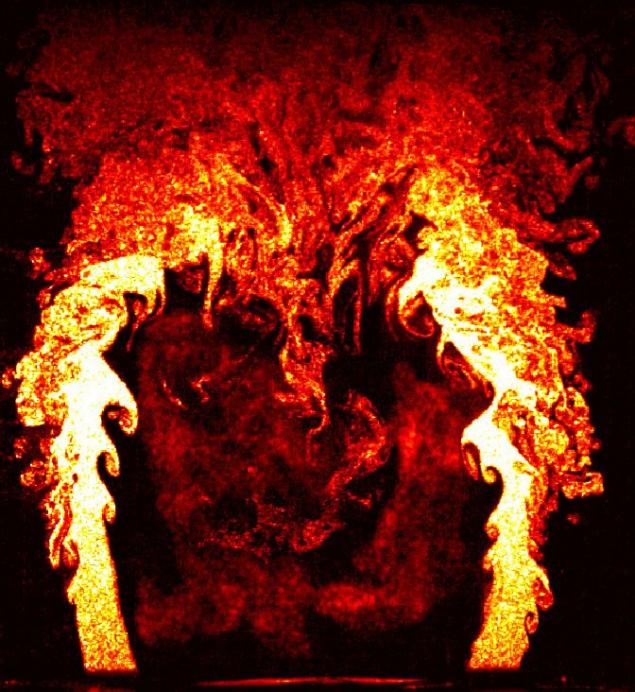
Photo flame struggling for survival, for a split second before it will extinguish the rush of cold air, took first place in the competition of scientific photography at the University of Cambridge. This picture was taken during a research project on the physics of combustion fire. Dr. Rob Gordon studied the structure of the fire, to aircraft engines are not glohli due to the sudden extinction of the fire. The photo was taken using two high-speed cameras at 5000 frames per second.
Second place was awarded the Ivor photos Daisy "Rotor" made during the study of flow irregularities on the blades of the turbine. The blades were painted with a mixture of bright poster paint and light oil, and then unwound at full speed until the paint has dried. This has created a stunning range of colors, which has been enhanced by ultraviolet radiation. Dr. Day says that his research can improve the fuel consumption.
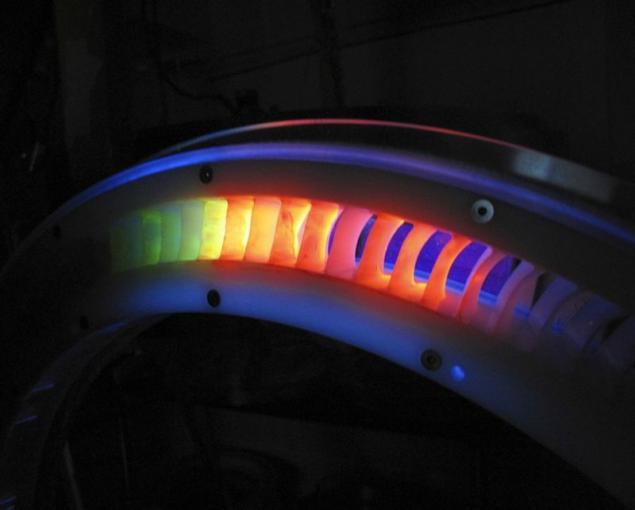

Photo "crystalline substance", ranked third, demonstrates amazing sharp crystal of zinc oxide in the form of golden stars in the structure of amorphous carbon. Rami RM Luca and Yong Tai Lee, made this picture, investigating the material used in transistors, light-emitting diodes and solar cells. Their work can give their results in the development of cheaper alternatives existing technology used in computers, mobile phones and chargers working on solar energy.

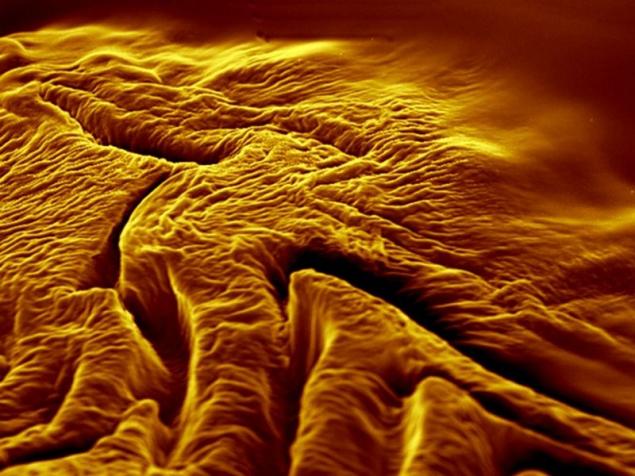
"Tiny Canyon" Christoph Meyer took fourth place in the university competition, which showcases the work and research at the Faculty of Engineering.
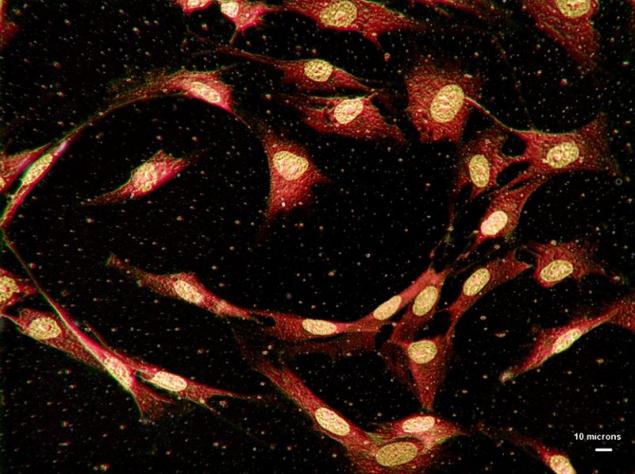
Additional microscopic images - substance only nanometers in length, invisible to the naked eye, such as human bone cells.
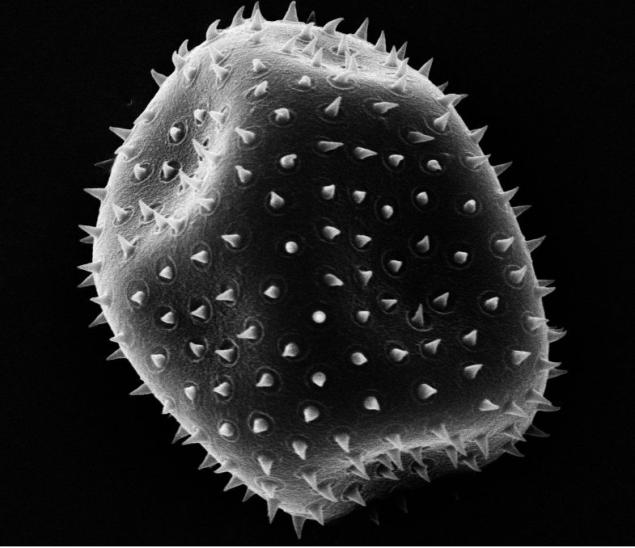
"Space invaders" Anna Banveg - black and white tone picture motes, which was made with a scanning electron microscope.
This image "nano-field" was made by Dr. Aruna Ivatury. The field was created from microscopic sensitive dye solar cells capable of artificial photosynthesis.
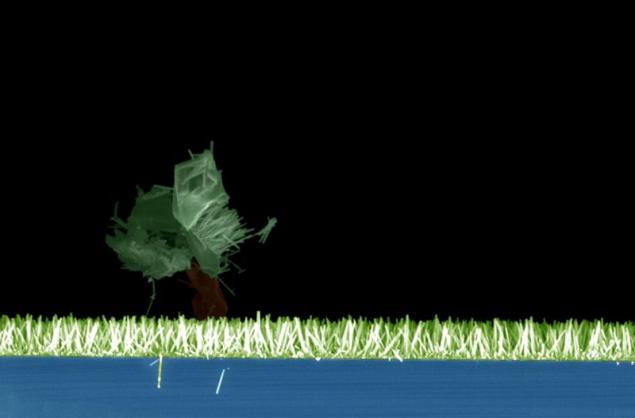

Professors, students and university staff have presented at the annual competition of 155 photographs, which show how amazing scientific development, and no less amazing humane initiative. Chris Forman took this picture Drosophila legs during a demonstration scanning electron microscope in action during the week of science.
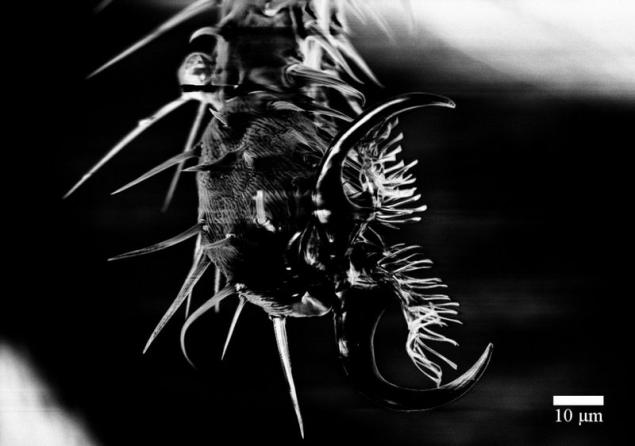

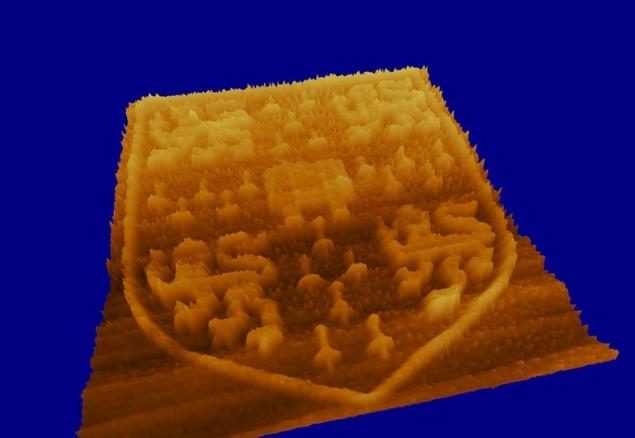
Tim Ehtermayer provided this photograph titled "Coat of Cambridge University on graphene." The coat of arms of the University was made up of modified graphene electron beam and captured using atomic force microscopy. The smallest side dimensions of the element was 100 nm and 1 nm.
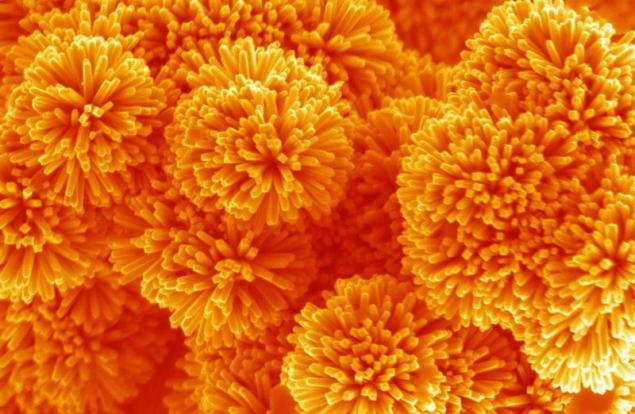
"Nanosterzhnevye dandelions" - a picture taken by a scanning electron microscope, demonstrates "nano dandelions" nanorods formed of tin oxide (50 nm in diameter and 1 .mu.m in length) grown by the hydrothermal method. Comment Dr. Aruna Ivatury, took this picture: "Incredibly extraordinary architecture of these nanoserzhnevyh dandelions makes them promising candidates for the material of the electrode in devices for the storage and collection of energy, which include low-cost rechargeable batteries and a new generation of solar cells».
"In this picture depicts diatoms and clumps of glue, - says photographer Matthew Kuo. - The photo was taken using environmental scanning electron microscope. I found these patterns in West Africa at a depth of about 1400 meters. "
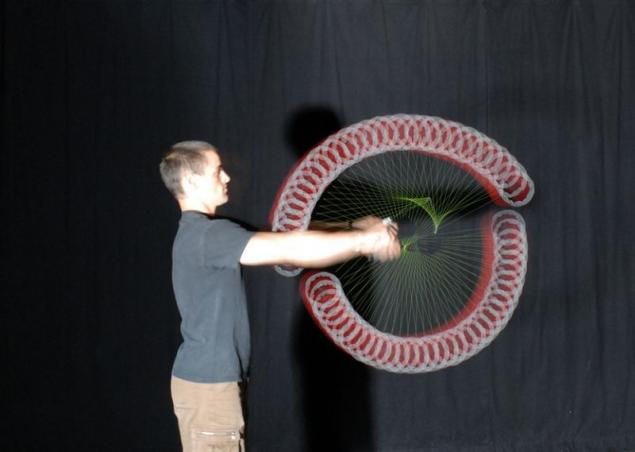
This photo Knight Sharp performs a trick with the help of diabolo, known as the "fan". To trick used two diabolo. For photos used with multiple strobe flash at a frequency of 80 Hz with a delay of 0.4 seconds.

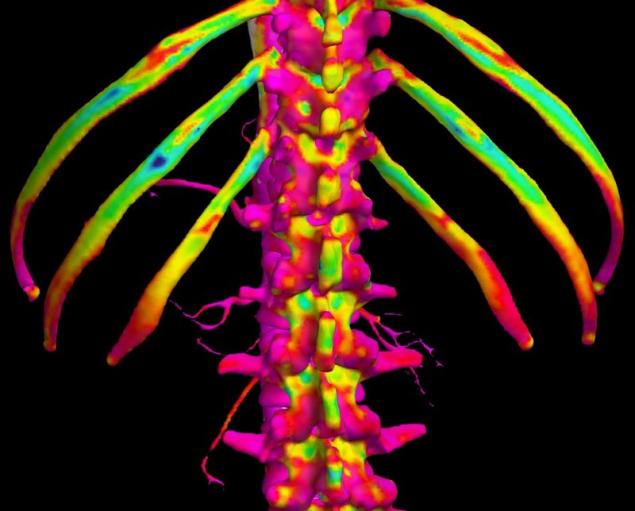
Dr. Graham Tris called this picture "Map of the bone cortex." This computer-generated image from a CT scan of the abdominal cavity.
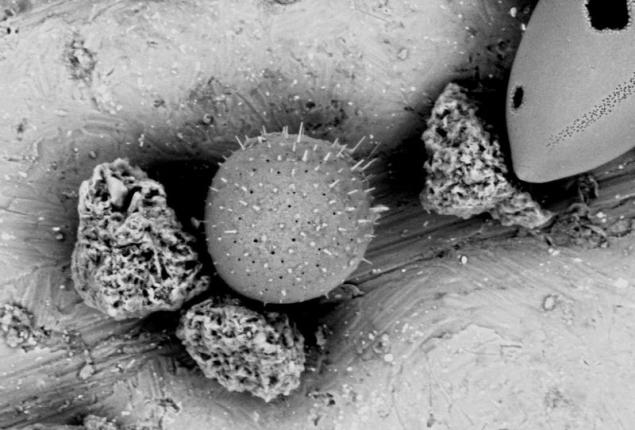
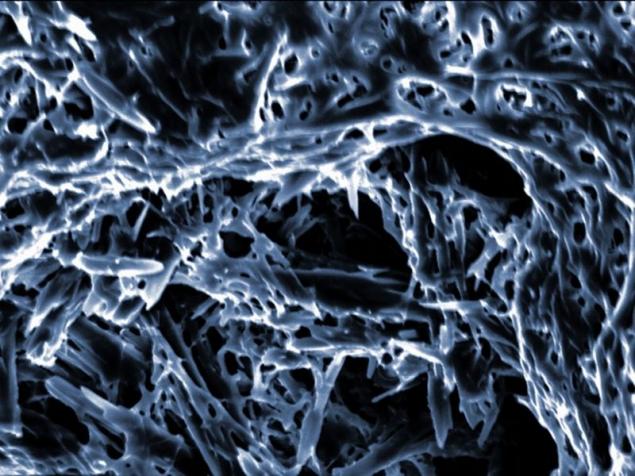
The structure of the ordinary kitchen sponge inside.
via source
which was presented 155 works - photographs taken during various scientific studies.
Another impressive shot - "Farewell to the King," which captures the moment when a bullet cuts the playing card with the king of diamonds.
The picture was taken student Nate Sharpe via playing cards, stroboscopic flash 400 nanoseconds
and shotgun cartridges with high-speed Viper 22.

Photo flame struggling for survival, for a split second before it will extinguish the rush of cold air, took first place in the competition of scientific photography at the University of Cambridge. This picture was taken during a research project on the physics of combustion fire. Dr. Rob Gordon studied the structure of the fire, to aircraft engines are not glohli due to the sudden extinction of the fire. The photo was taken using two high-speed cameras at 5000 frames per second.

Second place was awarded the Ivor photos Daisy "Rotor" made during the study of flow irregularities on the blades of the turbine. The blades were painted with a mixture of bright poster paint and light oil, and then unwound at full speed until the paint has dried. This has created a stunning range of colors, which has been enhanced by ultraviolet radiation. Dr. Day says that his research can improve the fuel consumption.

Photo "crystalline substance", ranked third, demonstrates amazing sharp crystal of zinc oxide in the form of golden stars in the structure of amorphous carbon. Rami RM Luca and Yong Tai Lee, made this picture, investigating the material used in transistors, light-emitting diodes and solar cells. Their work can give their results in the development of cheaper alternatives existing technology used in computers, mobile phones and chargers working on solar energy.

"Tiny Canyon" Christoph Meyer took fourth place in the university competition, which showcases the work and research at the Faculty of Engineering.

Additional microscopic images - substance only nanometers in length, invisible to the naked eye, such as human bone cells.

"Space invaders" Anna Banveg - black and white tone picture motes, which was made with a scanning electron microscope.

This image "nano-field" was made by Dr. Aruna Ivatury. The field was created from microscopic sensitive dye solar cells capable of artificial photosynthesis.

Professors, students and university staff have presented at the annual competition of 155 photographs, which show how amazing scientific development, and no less amazing humane initiative. Chris Forman took this picture Drosophila legs during a demonstration scanning electron microscope in action during the week of science.

Tim Ehtermayer provided this photograph titled "Coat of Cambridge University on graphene." The coat of arms of the University was made up of modified graphene electron beam and captured using atomic force microscopy. The smallest side dimensions of the element was 100 nm and 1 nm.

"Nanosterzhnevye dandelions" - a picture taken by a scanning electron microscope, demonstrates "nano dandelions" nanorods formed of tin oxide (50 nm in diameter and 1 .mu.m in length) grown by the hydrothermal method. Comment Dr. Aruna Ivatury, took this picture: "Incredibly extraordinary architecture of these nanoserzhnevyh dandelions makes them promising candidates for the material of the electrode in devices for the storage and collection of energy, which include low-cost rechargeable batteries and a new generation of solar cells».

"In this picture depicts diatoms and clumps of glue, - says photographer Matthew Kuo. - The photo was taken using environmental scanning electron microscope. I found these patterns in West Africa at a depth of about 1400 meters. "

This photo Knight Sharp performs a trick with the help of diabolo, known as the "fan". To trick used two diabolo. For photos used with multiple strobe flash at a frequency of 80 Hz with a delay of 0.4 seconds.

Dr. Graham Tris called this picture "Map of the bone cortex." This computer-generated image from a CT scan of the abdominal cavity.

The structure of the ordinary kitchen sponge inside.

via source























