882
Combat helicopter AH-64 Apache
Successful application of AH-1 "Cobra" in Vietnam has confirmed the viability of the idea of the combat helicopter. At the same time, the situation with the supposed "successor" "Cobra" remained unclear. An ambitious and expensive program of AH-56 "Cheyenne" lasted about a decade and was finally closed in 1972. Attempts to find a temporary replacement in the form of model Sikorsky S-67, S-61 modification and other helicopters were also unsuccessful. Finally in 1972 the US Army began a program of advanced combat helicopter (Advanced Attack Helicopter, AAH), designed primarily to deal with enemy tanks at any time and in poor weather conditions.
The basic requirements put forward to the helicopter AAH:
* Weapons - 30-mm gun, 16 anti-tank missiles "TOW" or 72 rockets [next]
* Crew - 2 people
* Features: The estimated takeoff weight - 7260 kg, rate of climb - 2, 5 m / s Ferry range with PTB - 1,850 km
* The navigation equipment to fly at night and in bad weather at an altitude of less than 30 m
* Engine - XT-700 gas turbine, thus ensuring harmonization with the developed military transport helicopter UH-60
* Reduction System IR
* Reservation ensuring the continuation of the task after the defeat of the bullet caliber 12, 7 mm and maximum survivability in contact with the shell of caliber 23 mm
* Life expectancy - 15 years
* Estimated value of the serial machine - 1, 4-1, 6 million. Dollars.

Participation in the contest took five aircraft manufacturers: Boeing Vertol, Bell, Hughes, Lockheed, Sikorsky. In June 1973, two of these companies (Bell and Hughes) have been given contracts for the development and production of prototypes. The company offered to Bell YAH-63 (Model 409), representing the development of the AH-1; prototype made its first flight on Nov. 22, 1975. Earlier, on September 30 first flew Hughes YAH-64, piloted by test pilots Robert Ferry (Robert Ferry) and Fletcher Raleigh (Raleigh Fletcher). In the army conducted comparative tests of a sample of firms Hughes showed his considerable superiority over competitor in the climb and maneuverability, and its characteristics in general, superior military requirements. His role was played by accident YAH-63 in one of the test flights. In December 1976 it was announced that the victory in the competition with the company Hughes YAH-64 helicopter.
After winning the competition for many company continued testing of the helicopter, making a number of changes in its structure and on-board equipment. The total amount of flight tests was 2,400 hours. Due to the number of challenges a decision on mass production was delayed for two years. Only the summer of 1981 began military tests of the helicopter. Drill crews were satisfied with the new car, and 19 December of the same year it was decided to mass production of the helicopter under the designation AH-64A and the name "Apache».
For the release of "Apache" was built factory in Mesa (Arizona). Roll-out of the first production car on 30 September 1983, exactly eight years after the first flight AH-64. The following year the company was bought by Hughes McDonnell Douglas Corporation, which took over the production and the helicopter. "Apaches" were supplied to the troops and distributed to 18 helicopters in the squadron. The first squadron of combat readiness reached in July 1986. Since 1989, the "Apache" began arriving in the US National Guard. Series production for the needs of the US armed forces was completed in December 1994, after the construction of 827 machines. The average cost of a helicopter early modification of AH-64A is estimated at about 14, 5 million. Dollars.
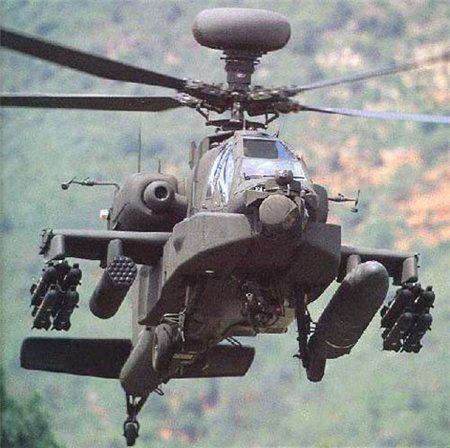

Modifications
* YAH-64 - prototype. Built 5 copies.
* AH-64A - first production version.
* GAH-64A - version of the AH-64A, converted into a ground simulator. Converted 17 helicopters.
* JAH-64A - a modification for special flight research. Built 7 machines.
* AH-64B - an option, upgraded in view of the combat experience of the operation "Desert Storm." I had a larger wing, new means of communication and navigation, enhanced armor protection. Development ceased in 1992.
* AH-64C - an upgraded AH-64A. Before the closure of the program in 1993 it was modernized only two helicopter.
* AH-64D «Apache Longbow" - the second major modification "Apache" ("Longbow" means "long bow"). The main feature - millimeter-wave radar AN / APG-78 "Longbow", placed in a streamlined container on the rotor hub. Moreover, reinforced installed engines and new avionics. It entered service in 1995, but until 1997, "Apache" this modification is not installed nadvtulochnaya radar. It is planned to upgrade to this version of all the remaining AH-64A.

"Baptism of fire» AH-64 took place during the US invasion of Panama in December 1989. The resulting combat experience was quite symbolic: in the operation was attended by a total of 11 machines. There were several successful launches of missiles AGM-114. There were no losses, three helicopters received light damage.
A more serious test was the operation "Desert Storm" in 1991. It is the "Apache" fired the first shot of the war, attacked on the night of January 17, two Iraqi radar station in the Baghdad area, is a threat to coalition aircraft over the Iraqi capital. Both were destroyed by the radar. Later AH-64 took part in a number of border clashes with Iraqi forces during the air phase of the campaign. February 24 began the ground offensive of the multinational forces; for four days of the ground war AH-64 have proven to be effective antitank weapon. They also carried out direct support of troops, sometimes interacting with the A-10 attack aircraft. Losses were very not high for such a large-scale operation - only three helicopters (including one lost by enemy fire), and one of them was lost in the fire before ground fighting.

During the NATO operation against Yugoslavia in 1999, a squadron of AH-64 was transferred to Albania and intended to support a possible land offensive in Kosovo. However, in late April - early May, two "Apache" was lost during training flights over Albania, the crew of one of them died. Ultimately AH-64 did not participate in combat operations. According to some unofficial Serb sources, about a dozen "Apaches" were put out of action on April 26 by Serbian aircraft flying at Rinas air base, but the fact that this operation is not supported by either the command of NATO nor the Serbian official representatives.

AH-64 actively used the first day of the invasion of Iraq in March 2003. The first machines were involved modifying AH-64D. In general, "Apache" confirmed its reputation in this conflict. Problems arose mainly because of failed tactics of the most famous example being the raid against teams from the division of the Republican Guard "Medina" March 24, 2003. Faced with unsuppressed and well-organized system of air defense, 30 of the 33 who participated in the raid, "Apache" received combat damage. In this episode, again confirmed the high survivability of AH-64: only one of the wrecked helicopter made a forced landing in enemy territory (the crew was captured, and the helicopter was destroyed by air strikes to his equipment did not fall into the hands of the enemy).

However, with the beginning of the Iraq guerrilla war losses AH-64 began to increase. The main reason for this is typical of guerilla warfare surprise fire from the ground, particularly during a flight over city blocks, where it is impossible to determine where the fire is conducted. The helicopter just does not have time to make the maneuver flak. In addition, the book "Apache" is designed only to protect against fire from machine guns and part - small-caliber anti-aircraft guns. Like any other helicopter, it is vulnerable to MANPADS missiles. According to incomplete statistics, since the beginning of the war until the end of 2007 in Iraq for various reasons lost at least 17 "Apache»

US, British and Dutch helicopters used in combat operations in Afghanistan. The loss here was small and mainly related to technical problems.
Israeli helicopters were first engaged in combat in 1991 in Lebanon. They were used during the limited military operations against "Hezbollah" in 1993 and 1996. The widespread use of "Apache" received in the course of the second Palestinian Intifada 2000-2005. As a rule, they applied demonstrative strikes against targets Palestinian terrorist organizations in response to the ongoing attacks, but took part in this and support ground forces during Operation "Defensive Shield" in March-April 2002. During the Lebanon campaign in summer 2006 AH-64 were used for strikes against targets in Lebanon. It lost three cars, including the two faced each other in the air. According to preliminary data, all the losses were non-combat, though "Hezbollah" has claimed responsibility for the downing of three helicopters.

Shot down a gun?
March 24, 2003 television all over the world showed a video of Iraqi television: Iraqis surrounded AH-64D, lying "on its belly" without any visible damage. Official Baghdad announced that the helicopter was shot down by a farmer Ali Obeid Mangashem from his hunting rifle. Sharpshooter received the Order of Saddam Hussein and the appointment of a downed US helicopter monetary compensation - about 20 thousand dollars.
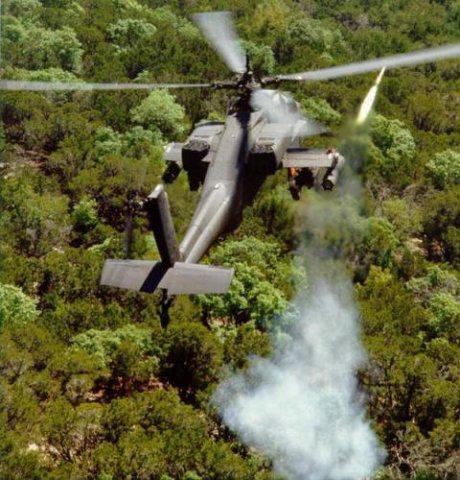

It should be noted that a similar incident in itself is not impossible, because the design of the helicopter has a number of very vulnerable people. However, the story of the AH-64 was somewhat different. After the end of active hostilities Western journalists found Mangasha and learned that in fact he had not received any orders or money. On the morning of March 24 he discovered in his field thrown by an American helicopter (one of the "Apache", wrecked during the raid on the position of division "Medina") and reported the find to the authorities. It instructed the crew arrived to tell the group that the helicopter was shot down his rifle, which was a good propaganda move.

The crew of the helicopter was later found and captured. This story turned into "urban legend", still having some distribution on the Internet.

Features
* Crew - 2 people
* The length - 17, 73 m
* Height - 3, 87 m
* The diameter of the rotor - 14, 63 m
* Engines: General Electric T700-GE-701 (2x1695 hp)
* Empty weight - 5165 kg
* Curb weight - 8,000 kg
* Maximum takeoff weight - 9500 kg
* Never exceed speed (to dive) - 365 km / h
* The maximum speed - 293 km / h
* Cruising speed - 165 km / h
* Combat radius - 480 km
* Ferry range - 1900 km
* Practical ceiling - 6400 m
* Rate of climb - 12, 7 m / s
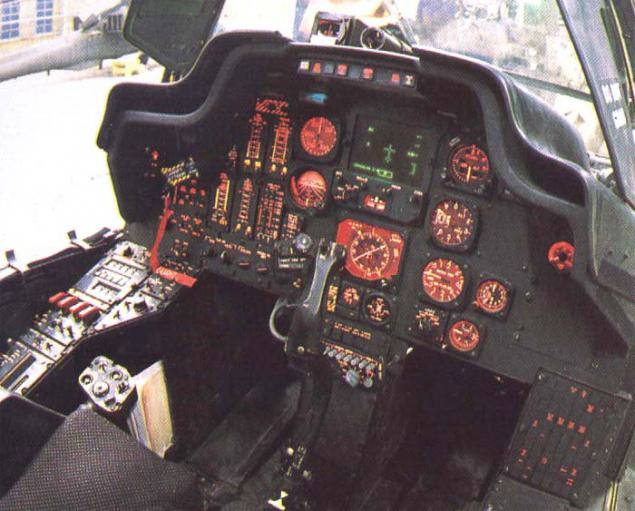

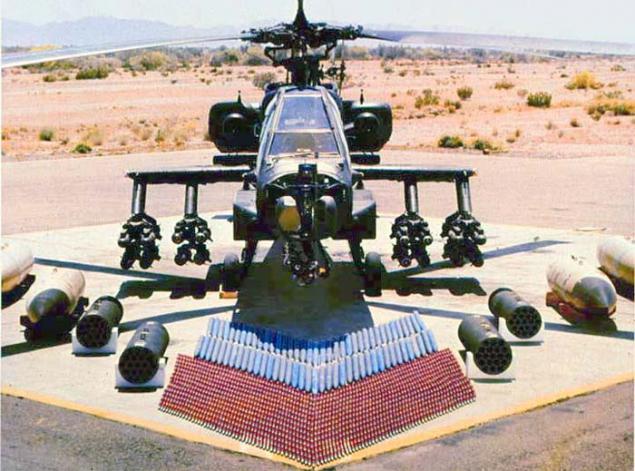
* Weapons:
o 30-mm gun M230 (rate of fire - 625 rds. / min ammunition - 1200 shells)
o missiles "air-to-air» AIM-92, AIM-9
o missiles "air-to-ground» AGM-114
o rockets "Hydra 70»

Hello from Pindos))

Source:
The basic requirements put forward to the helicopter AAH:
* Weapons - 30-mm gun, 16 anti-tank missiles "TOW" or 72 rockets [next]
* Crew - 2 people
* Features: The estimated takeoff weight - 7260 kg, rate of climb - 2, 5 m / s Ferry range with PTB - 1,850 km
* The navigation equipment to fly at night and in bad weather at an altitude of less than 30 m
* Engine - XT-700 gas turbine, thus ensuring harmonization with the developed military transport helicopter UH-60
* Reduction System IR
* Reservation ensuring the continuation of the task after the defeat of the bullet caliber 12, 7 mm and maximum survivability in contact with the shell of caliber 23 mm
* Life expectancy - 15 years
* Estimated value of the serial machine - 1, 4-1, 6 million. Dollars.

Participation in the contest took five aircraft manufacturers: Boeing Vertol, Bell, Hughes, Lockheed, Sikorsky. In June 1973, two of these companies (Bell and Hughes) have been given contracts for the development and production of prototypes. The company offered to Bell YAH-63 (Model 409), representing the development of the AH-1; prototype made its first flight on Nov. 22, 1975. Earlier, on September 30 first flew Hughes YAH-64, piloted by test pilots Robert Ferry (Robert Ferry) and Fletcher Raleigh (Raleigh Fletcher). In the army conducted comparative tests of a sample of firms Hughes showed his considerable superiority over competitor in the climb and maneuverability, and its characteristics in general, superior military requirements. His role was played by accident YAH-63 in one of the test flights. In December 1976 it was announced that the victory in the competition with the company Hughes YAH-64 helicopter.
After winning the competition for many company continued testing of the helicopter, making a number of changes in its structure and on-board equipment. The total amount of flight tests was 2,400 hours. Due to the number of challenges a decision on mass production was delayed for two years. Only the summer of 1981 began military tests of the helicopter. Drill crews were satisfied with the new car, and 19 December of the same year it was decided to mass production of the helicopter under the designation AH-64A and the name "Apache».
For the release of "Apache" was built factory in Mesa (Arizona). Roll-out of the first production car on 30 September 1983, exactly eight years after the first flight AH-64. The following year the company was bought by Hughes McDonnell Douglas Corporation, which took over the production and the helicopter. "Apaches" were supplied to the troops and distributed to 18 helicopters in the squadron. The first squadron of combat readiness reached in July 1986. Since 1989, the "Apache" began arriving in the US National Guard. Series production for the needs of the US armed forces was completed in December 1994, after the construction of 827 machines. The average cost of a helicopter early modification of AH-64A is estimated at about 14, 5 million. Dollars.

Modifications
* YAH-64 - prototype. Built 5 copies.
* AH-64A - first production version.
* GAH-64A - version of the AH-64A, converted into a ground simulator. Converted 17 helicopters.
* JAH-64A - a modification for special flight research. Built 7 machines.
* AH-64B - an option, upgraded in view of the combat experience of the operation "Desert Storm." I had a larger wing, new means of communication and navigation, enhanced armor protection. Development ceased in 1992.
* AH-64C - an upgraded AH-64A. Before the closure of the program in 1993 it was modernized only two helicopter.
* AH-64D «Apache Longbow" - the second major modification "Apache" ("Longbow" means "long bow"). The main feature - millimeter-wave radar AN / APG-78 "Longbow", placed in a streamlined container on the rotor hub. Moreover, reinforced installed engines and new avionics. It entered service in 1995, but until 1997, "Apache" this modification is not installed nadvtulochnaya radar. It is planned to upgrade to this version of all the remaining AH-64A.

"Baptism of fire» AH-64 took place during the US invasion of Panama in December 1989. The resulting combat experience was quite symbolic: in the operation was attended by a total of 11 machines. There were several successful launches of missiles AGM-114. There were no losses, three helicopters received light damage.
A more serious test was the operation "Desert Storm" in 1991. It is the "Apache" fired the first shot of the war, attacked on the night of January 17, two Iraqi radar station in the Baghdad area, is a threat to coalition aircraft over the Iraqi capital. Both were destroyed by the radar. Later AH-64 took part in a number of border clashes with Iraqi forces during the air phase of the campaign. February 24 began the ground offensive of the multinational forces; for four days of the ground war AH-64 have proven to be effective antitank weapon. They also carried out direct support of troops, sometimes interacting with the A-10 attack aircraft. Losses were very not high for such a large-scale operation - only three helicopters (including one lost by enemy fire), and one of them was lost in the fire before ground fighting.

During the NATO operation against Yugoslavia in 1999, a squadron of AH-64 was transferred to Albania and intended to support a possible land offensive in Kosovo. However, in late April - early May, two "Apache" was lost during training flights over Albania, the crew of one of them died. Ultimately AH-64 did not participate in combat operations. According to some unofficial Serb sources, about a dozen "Apaches" were put out of action on April 26 by Serbian aircraft flying at Rinas air base, but the fact that this operation is not supported by either the command of NATO nor the Serbian official representatives.

AH-64 actively used the first day of the invasion of Iraq in March 2003. The first machines were involved modifying AH-64D. In general, "Apache" confirmed its reputation in this conflict. Problems arose mainly because of failed tactics of the most famous example being the raid against teams from the division of the Republican Guard "Medina" March 24, 2003. Faced with unsuppressed and well-organized system of air defense, 30 of the 33 who participated in the raid, "Apache" received combat damage. In this episode, again confirmed the high survivability of AH-64: only one of the wrecked helicopter made a forced landing in enemy territory (the crew was captured, and the helicopter was destroyed by air strikes to his equipment did not fall into the hands of the enemy).

However, with the beginning of the Iraq guerrilla war losses AH-64 began to increase. The main reason for this is typical of guerilla warfare surprise fire from the ground, particularly during a flight over city blocks, where it is impossible to determine where the fire is conducted. The helicopter just does not have time to make the maneuver flak. In addition, the book "Apache" is designed only to protect against fire from machine guns and part - small-caliber anti-aircraft guns. Like any other helicopter, it is vulnerable to MANPADS missiles. According to incomplete statistics, since the beginning of the war until the end of 2007 in Iraq for various reasons lost at least 17 "Apache»

US, British and Dutch helicopters used in combat operations in Afghanistan. The loss here was small and mainly related to technical problems.
Israeli helicopters were first engaged in combat in 1991 in Lebanon. They were used during the limited military operations against "Hezbollah" in 1993 and 1996. The widespread use of "Apache" received in the course of the second Palestinian Intifada 2000-2005. As a rule, they applied demonstrative strikes against targets Palestinian terrorist organizations in response to the ongoing attacks, but took part in this and support ground forces during Operation "Defensive Shield" in March-April 2002. During the Lebanon campaign in summer 2006 AH-64 were used for strikes against targets in Lebanon. It lost three cars, including the two faced each other in the air. According to preliminary data, all the losses were non-combat, though "Hezbollah" has claimed responsibility for the downing of three helicopters.

Shot down a gun?
March 24, 2003 television all over the world showed a video of Iraqi television: Iraqis surrounded AH-64D, lying "on its belly" without any visible damage. Official Baghdad announced that the helicopter was shot down by a farmer Ali Obeid Mangashem from his hunting rifle. Sharpshooter received the Order of Saddam Hussein and the appointment of a downed US helicopter monetary compensation - about 20 thousand dollars.

It should be noted that a similar incident in itself is not impossible, because the design of the helicopter has a number of very vulnerable people. However, the story of the AH-64 was somewhat different. After the end of active hostilities Western journalists found Mangasha and learned that in fact he had not received any orders or money. On the morning of March 24 he discovered in his field thrown by an American helicopter (one of the "Apache", wrecked during the raid on the position of division "Medina") and reported the find to the authorities. It instructed the crew arrived to tell the group that the helicopter was shot down his rifle, which was a good propaganda move.

The crew of the helicopter was later found and captured. This story turned into "urban legend", still having some distribution on the Internet.

Features
* Crew - 2 people
* The length - 17, 73 m
* Height - 3, 87 m
* The diameter of the rotor - 14, 63 m
* Engines: General Electric T700-GE-701 (2x1695 hp)
* Empty weight - 5165 kg
* Curb weight - 8,000 kg
* Maximum takeoff weight - 9500 kg
* Never exceed speed (to dive) - 365 km / h
* The maximum speed - 293 km / h
* Cruising speed - 165 km / h
* Combat radius - 480 km
* Ferry range - 1900 km
* Practical ceiling - 6400 m
* Rate of climb - 12, 7 m / s

* Weapons:
o 30-mm gun M230 (rate of fire - 625 rds. / min ammunition - 1200 shells)
o missiles "air-to-air» AIM-92, AIM-9
o missiles "air-to-ground» AGM-114
o rockets "Hydra 70»

Hello from Pindos))

Source: