713
On an inflatable tower - space
Canadian scientists have proposed a new way to efficiently get to the near-Earth space: they propose to build a giant inflatable tower. It is reported by New Scientist, researchers and article appeared in the journal Acta Astronautica.
As part of the construction of the scientists suggest using inflatable units height of about 150 meters and a width of 230 meters, made of a composite of Kevlar and polyethylene. Each unit is made up of inflatable tubes with a diameter of about 7 meters. Units will be pumped by any inert gas such as helium.
Text + 3 Photo © Irina Yakutenko

In the study, experts studied the possibility of building a tower height of about 15 kilometers. Dynamic stability of this design, weighing about 300 tons is planned to provide through a system of gyroscopes, which should be monitored computer. According to the researchers, the system is robust enough - calculations show that the destruction of several blocks does not lead to the fall of the entire structure.
To verify the calculations, scientists have built 7-meter tower model, consisting of six modules, each of which is composed of a pipe diameter of 8 centimeters. Model pumped ordinary air.
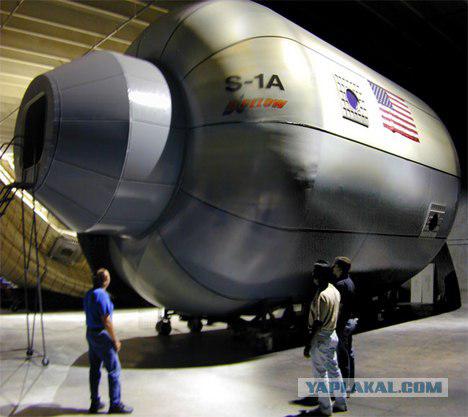
Inflatable space station fragment company Bigelow Aerospace. The inflatable part consists of the same material that will be used for the construction of the tower Canadians.
According to the researchers, the installation of a similar tower on the mountain will allow to achieve a suitable height of the construction of 20 kilometers above sea level. According to the researchers, from the observation deck at the top of this tower will open review of 600 kilometers around. This will make this facility a wonderful tourist attraction, scientists believe.
In addition, the researchers note that in theory such a tower height can reach 200 kilometers, which will display the objects in near-Earth space. According to scientists, the inflatable tower technology is very similar in functionality to the so-called space elevator. Elevators, however, require for its creation of materials which are not yet in nature, while the inflatable tower uses materials already available.

Towers, ropes and spiders
The idea to create the lift, where you can get to outer space, appeared before people really got there. The first draft of such a vehicle has been created by the Russian scientist, the founder of cosmonautics Konstantin Tsiolkovsky in 1895. Space elevator reminded of Tsiolkovsky built shortly afterwards in Paris, the Eiffel Tower, was only a hundred thousand times greater.
The top of this tower would move at a speed of 11 kilometers per second - this speed is called the second space. That's as fast running fly from Earth to other planets devices. This means that they could be run directly on top of the tower.
Tsiolkovsky's idea, with all its temptations was absolutely unrealizable: even made of the strongest steel elevator could not withstand its own weight. The rebirth of a space elevator was in 1960, now is not in Russia and in the Soviet Union. In an interview with the newspaper "Komsomolskaya Pravda" Leningrad engineer Yuri Artsutanov outlined a new concept of "umbilical cord" linking Earth and the sky.
Artsutanov refused bulky and heavy structures. According to his plan, the lift was to consist of a thin thread, one end of which is fixed to the surface of our planet, and another tied counterweight in orbit. The taut strand will support the centrifugal force: at an altitude of about 35 thousand kilometers, it compensates for the force of attraction of the Earth, and the counterweight still hangs over one point. Due to the same law on the orbits of the satellites are kept.
Assembling the thread will be carried out in stages. First satellite in geostationary orbit, will release the first strand "thinner than a human hair." The free end of the thread needs to be fixed on the "ground floor" - on Earth. To turn this into a full seed thin wire, the filament must be issued a special spidering. Moving along the filament, they are wound on her extra layers of material.
"Komsomolskaya Pravda" is not a recognized scientific journals. In addition, the newspaper is published only in Russian. These two circumstances are not allowed to get the idea Artsutanova fame. The international scientific community to think seriously about the elevator leading to the space in 1966, when an article devoted to this project was published in the journal Science. In addition to the study stranded structure of an elevator, the authors suggested possible materials from which to this thread "to spin." Among others mentioned graphite, quartz and diamond.
Far from being a science, but science fiction interests of the public learned about the space elevator and the engineer Artsutanova in 1979, when his novel American scientist and science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke's "The Fountains of Paradise." In the foreword to the novel Clarke admitted that he tried to calculate the parameters of the elevator on the mail envelope in 1964, but rejected the idea as hopeless. Later, the writer lamented that he had at hand was not an envelope a little more.
Apart from leading to space the threads, and Clark, and Artsutanov and the authors of the Science paper ponders the actual elevator car. In order to raise it to a height of 35,000 kilometers above the Earth, it was suggested, for example, to use solar energy, lasers, microwave ovens. Descent cockpit is also a challenge: if you just let it go down, it will burn from the friction of the atmosphere without going half way.
Engineers and scientists sluggish offers various options to overcome these difficulties, but doing it is more of academic interest. Until 1991, the constructors of the elevator had no idea of what to do basic detail - cable. Without a cable all the other calculations were simply an exercise in applied mathematics.
In order to withstand the regular ascent and descent of cargo space, the strength of the rope should be in the range of 65 to 120 GPa. This option is for most types of steel (which, moreover, very difficult) does not exceed 5 GPa for Kevlar - 2, 5-4 GPa, from quartz fiber slightly exceeds 20 GPa.
In 1991 were invented nanotubes - hollow cylinders, the walls of which are made of a single layer of carbon atoms. It quickly became clear that the nanotubes can be used almost anywhere, including in outer lift division. In theory, cable, built from nanotubes, could be 3-5 times stronger than is required for reliable operation.
Amendments to the reality
With the advent of technologies that promise to make the dream a reality, the development of various models of space elevators intensified. For example, the project for several years engaged in the Institute of Advanced Concepts NASA (Institute for Advanced Concepts - NIAC). Since 2005, the US space agency supports the competition "space elevator." Participants must submit a draft of the jury elevators in miniature.
Terms of the contest every year becoming more and more severe. In 2006, judges were required to show a structure consisting of a 60-meter rope and cabins capable of climbing at a rate of not less than one meter per second. The competition of 2007 demands were even tougher: the length of the cable should be 100 meters, and the speed of the cabin - at least two meters per second. In 2008, the distance is increased to 1 kilometer, and the speed - up to five meters per second (for second place was only two meters per second).
The prize fund of the competition gradually increased: none of the participants could not fulfill the necessary requirements. In 2009, the organizers of the contest have decided to support the enthusiasm of the participants and left the job last year.
Dreaming is not bad
In spite of the active work of many researchers, is the space elevator is a fantastic project rather than scientific. The length of the longest of the synthesized nanotubes to date does not exceed several millimeters. In addition, while the ropes made of nanotubes lose in strength ropes made of other materials. However, scientists continue to work on the creation of a space elevator. Along the way, they invent new materials and unwittingly create new technologies. So even if the attempt to reach heaven and will not succeed, they will bring real benefits to the world.

Source:
As part of the construction of the scientists suggest using inflatable units height of about 150 meters and a width of 230 meters, made of a composite of Kevlar and polyethylene. Each unit is made up of inflatable tubes with a diameter of about 7 meters. Units will be pumped by any inert gas such as helium.
Text + 3 Photo © Irina Yakutenko

In the study, experts studied the possibility of building a tower height of about 15 kilometers. Dynamic stability of this design, weighing about 300 tons is planned to provide through a system of gyroscopes, which should be monitored computer. According to the researchers, the system is robust enough - calculations show that the destruction of several blocks does not lead to the fall of the entire structure.
To verify the calculations, scientists have built 7-meter tower model, consisting of six modules, each of which is composed of a pipe diameter of 8 centimeters. Model pumped ordinary air.
Inflatable space station fragment company Bigelow Aerospace. The inflatable part consists of the same material that will be used for the construction of the tower Canadians.
According to the researchers, the installation of a similar tower on the mountain will allow to achieve a suitable height of the construction of 20 kilometers above sea level. According to the researchers, from the observation deck at the top of this tower will open review of 600 kilometers around. This will make this facility a wonderful tourist attraction, scientists believe.
In addition, the researchers note that in theory such a tower height can reach 200 kilometers, which will display the objects in near-Earth space. According to scientists, the inflatable tower technology is very similar in functionality to the so-called space elevator. Elevators, however, require for its creation of materials which are not yet in nature, while the inflatable tower uses materials already available.

Towers, ropes and spiders
The idea to create the lift, where you can get to outer space, appeared before people really got there. The first draft of such a vehicle has been created by the Russian scientist, the founder of cosmonautics Konstantin Tsiolkovsky in 1895. Space elevator reminded of Tsiolkovsky built shortly afterwards in Paris, the Eiffel Tower, was only a hundred thousand times greater.
The top of this tower would move at a speed of 11 kilometers per second - this speed is called the second space. That's as fast running fly from Earth to other planets devices. This means that they could be run directly on top of the tower.
Tsiolkovsky's idea, with all its temptations was absolutely unrealizable: even made of the strongest steel elevator could not withstand its own weight. The rebirth of a space elevator was in 1960, now is not in Russia and in the Soviet Union. In an interview with the newspaper "Komsomolskaya Pravda" Leningrad engineer Yuri Artsutanov outlined a new concept of "umbilical cord" linking Earth and the sky.
Artsutanov refused bulky and heavy structures. According to his plan, the lift was to consist of a thin thread, one end of which is fixed to the surface of our planet, and another tied counterweight in orbit. The taut strand will support the centrifugal force: at an altitude of about 35 thousand kilometers, it compensates for the force of attraction of the Earth, and the counterweight still hangs over one point. Due to the same law on the orbits of the satellites are kept.
Assembling the thread will be carried out in stages. First satellite in geostationary orbit, will release the first strand "thinner than a human hair." The free end of the thread needs to be fixed on the "ground floor" - on Earth. To turn this into a full seed thin wire, the filament must be issued a special spidering. Moving along the filament, they are wound on her extra layers of material.
"Komsomolskaya Pravda" is not a recognized scientific journals. In addition, the newspaper is published only in Russian. These two circumstances are not allowed to get the idea Artsutanova fame. The international scientific community to think seriously about the elevator leading to the space in 1966, when an article devoted to this project was published in the journal Science. In addition to the study stranded structure of an elevator, the authors suggested possible materials from which to this thread "to spin." Among others mentioned graphite, quartz and diamond.
Far from being a science, but science fiction interests of the public learned about the space elevator and the engineer Artsutanova in 1979, when his novel American scientist and science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke's "The Fountains of Paradise." In the foreword to the novel Clarke admitted that he tried to calculate the parameters of the elevator on the mail envelope in 1964, but rejected the idea as hopeless. Later, the writer lamented that he had at hand was not an envelope a little more.
Apart from leading to space the threads, and Clark, and Artsutanov and the authors of the Science paper ponders the actual elevator car. In order to raise it to a height of 35,000 kilometers above the Earth, it was suggested, for example, to use solar energy, lasers, microwave ovens. Descent cockpit is also a challenge: if you just let it go down, it will burn from the friction of the atmosphere without going half way.
Engineers and scientists sluggish offers various options to overcome these difficulties, but doing it is more of academic interest. Until 1991, the constructors of the elevator had no idea of what to do basic detail - cable. Without a cable all the other calculations were simply an exercise in applied mathematics.
In order to withstand the regular ascent and descent of cargo space, the strength of the rope should be in the range of 65 to 120 GPa. This option is for most types of steel (which, moreover, very difficult) does not exceed 5 GPa for Kevlar - 2, 5-4 GPa, from quartz fiber slightly exceeds 20 GPa.
In 1991 were invented nanotubes - hollow cylinders, the walls of which are made of a single layer of carbon atoms. It quickly became clear that the nanotubes can be used almost anywhere, including in outer lift division. In theory, cable, built from nanotubes, could be 3-5 times stronger than is required for reliable operation.
Amendments to the reality
With the advent of technologies that promise to make the dream a reality, the development of various models of space elevators intensified. For example, the project for several years engaged in the Institute of Advanced Concepts NASA (Institute for Advanced Concepts - NIAC). Since 2005, the US space agency supports the competition "space elevator." Participants must submit a draft of the jury elevators in miniature.
Terms of the contest every year becoming more and more severe. In 2006, judges were required to show a structure consisting of a 60-meter rope and cabins capable of climbing at a rate of not less than one meter per second. The competition of 2007 demands were even tougher: the length of the cable should be 100 meters, and the speed of the cabin - at least two meters per second. In 2008, the distance is increased to 1 kilometer, and the speed - up to five meters per second (for second place was only two meters per second).
The prize fund of the competition gradually increased: none of the participants could not fulfill the necessary requirements. In 2009, the organizers of the contest have decided to support the enthusiasm of the participants and left the job last year.
Dreaming is not bad
In spite of the active work of many researchers, is the space elevator is a fantastic project rather than scientific. The length of the longest of the synthesized nanotubes to date does not exceed several millimeters. In addition, while the ropes made of nanotubes lose in strength ropes made of other materials. However, scientists continue to work on the creation of a space elevator. Along the way, they invent new materials and unwittingly create new technologies. So even if the attempt to reach heaven and will not succeed, they will bring real benefits to the world.

Source: