531
Detected "new" Earth
Hence
A team of specialists NASA, which operates using the telescope Kepler. Because of long work on the analysis of the detected planets eventually experts group has officially confirmed that they have discovered a planet really is Earth-like, and is located in the zone of possible emergence of life on its surface. This is the first time in history when the planet has the status of "candidate" received the status of a "confirmed".
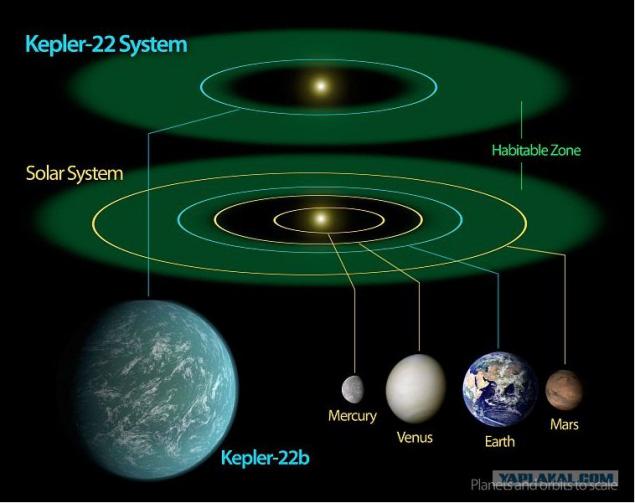
The planet in question is called Kerler 22-b, and is located 600 light years from Earth. It is superior to its diameter of our planet into 2, 4 times. The surface temperature of the planet is about 22 degrees above zero Celsius. Scientists can not yet say for sure what material is its surface - liquid soil or rock. Located Kerler 22-b 15% closer to the central star system than the Earth relative to the Sun. Planetary year Kepler 22-b lasts 290 days. However, the fact that Kerler 22-b is closer to its star than the Earth relative to the Sun is offset by the fact that the star is almost ¼ of fainter than the sun. so the surface Kerler 22-b, there are all necessary conditions for that would be there was water in its liquid state and could harbor life.
Initially, the list of criteria that had to meet the world that have been recognized as probably-habitable planets, consisted of 54 items. Then, it was cut to 48 points. Currently, the number of Earth-like planets, which are candidates for what they saw as the likely inhabited planet, consisted of 2,326 planets. Of this total, the list of potentially habitable planets, allocated 207 planets that are so-called "super-Earths" - they are similar in size and distance from the star to our planet.
How to confirm the status of the habitability of the planet, its transition from the status of "candidate" status to "confirmed", rather laborious and time consuming. Astronomers capture at least three passes of the planet, using different telescopes, between the Earth and its star. To do this, you must wait at least five or even more years.
In the case of Kerler 22-b, astronomers simply lucky. Her first pass between the Earth and the star system which is this planet took place just three days after the telescope Kerler started to work. |
Source:
A team of specialists NASA, which operates using the telescope Kepler. Because of long work on the analysis of the detected planets eventually experts group has officially confirmed that they have discovered a planet really is Earth-like, and is located in the zone of possible emergence of life on its surface. This is the first time in history when the planet has the status of "candidate" received the status of a "confirmed".
The planet in question is called Kerler 22-b, and is located 600 light years from Earth. It is superior to its diameter of our planet into 2, 4 times. The surface temperature of the planet is about 22 degrees above zero Celsius. Scientists can not yet say for sure what material is its surface - liquid soil or rock. Located Kerler 22-b 15% closer to the central star system than the Earth relative to the Sun. Planetary year Kepler 22-b lasts 290 days. However, the fact that Kerler 22-b is closer to its star than the Earth relative to the Sun is offset by the fact that the star is almost ¼ of fainter than the sun. so the surface Kerler 22-b, there are all necessary conditions for that would be there was water in its liquid state and could harbor life.
Initially, the list of criteria that had to meet the world that have been recognized as probably-habitable planets, consisted of 54 items. Then, it was cut to 48 points. Currently, the number of Earth-like planets, which are candidates for what they saw as the likely inhabited planet, consisted of 2,326 planets. Of this total, the list of potentially habitable planets, allocated 207 planets that are so-called "super-Earths" - they are similar in size and distance from the star to our planet.
How to confirm the status of the habitability of the planet, its transition from the status of "candidate" status to "confirmed", rather laborious and time consuming. Astronomers capture at least three passes of the planet, using different telescopes, between the Earth and its star. To do this, you must wait at least five or even more years.
In the case of Kerler 22-b, astronomers simply lucky. Her first pass between the Earth and the star system which is this planet took place just three days after the telescope Kerler started to work. |

Source: