1019
Five scientific discoveries made with the help of Google Earth (5 photos)
Thanks to satellite images across the Earth's surface, scientists were able to explore the area, where anyone and thought to send scientific expeditions, as well as a new angle to look at the long-studied places. Over the past few years, thanks to Google Earth, made a number of important discoveries. Sometimes these discoveries are made completely random people.
Remains of an ancient Roman villa, Italy, 2005

One of the oldest archaeological discoveries made in Google Earth, took place in 2005. Ironically, the author of the discovery, a local resident Luca Mori (Luca Mori) just launched a program to explore the area near his home in Parma. Quite unexpectedly, he noticed a strange oval artifact in the fields near the city. One of the oldest archaeological discoveries made in Google Earth, took place in 2005. Ironically, the author of the discovery, a local resident Luca Mori (Luca Mori) just launched a program to explore the area near his home in Parma. Quite unexpectedly, he noticed a strange oval artifact in the fields near the city.
Luca Mori took him for a computer glitch, but still informed the specialists of the National Archaeological Museum, which organized the expedition. Immediately after the excavation, they found the remains of ancient pottery and Roman villa built BC.
Australopithecus sediba age 2 million years, South Africa, 2008

Bold paleoanthropologist Lee Berger went to brave the study of South Africa, running Google Earth in the comfort of his office. Professor began to explore the limestone caves in the area of South Africa, which is known to scientists as the Cradle of Humankind.
Berger found on satellite images previously unknown caves suitable for the life of ancient people. In 2008, he organized an expedition polulyubitelsky, taking with him only one student and son and dog. At the site they found fifty alleged places of residence of Australopithecus (the higher primates, hominids dvunogohodyaschie with a small volume of the brain).
Visit one of the caves, his father sent a 9-year-old son to look around, and after 15 minutes he brought the stone with beautifully preserved fossilized fragments of the clavicle and mandible. Excavations at the site have revealed fragments of skeletons and other women and adolescents, whose age is estimated at 1, 78-1, 95 million years.
The importance of this discovery is that the found samples belong to a new, previously unknown type of Australopithecus, very similar to humans. That's two million years ago, the great apes began to walk on two legs, to use tools and form the beginnings of speech. The new species is named Australopithecus sediba (Australopithecus sediba). Perhaps it is this kind of an ancestor of Homo habilis, ie the transition from ape-like hominids link to the people of the modern species.
Tropical forest on the mountain Mabou, Mozambique, 2008
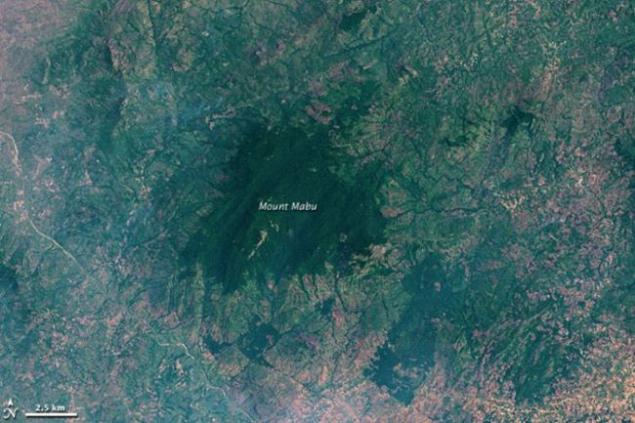

On satellite images of northern Mozambique British scientist Julian Bailey (Julian Bayliss) found completely unknown "oasis" - an isolated tropical forest, located high in the mountains in a remote place. It turned out that this forest is known to locals, but there has never fitted out a scientific expedition. But these isolated areas are especially interesting for biologists, because there are often new species of animals and plants. Mountain Mabou did not disappoint - in 2008 an expedition was sent there, the results of which are still studying. A total ease was discovered more than a hundred (!) New species - plants, birds, butterflies, monkeys, snakes - in just three weeks. This tropical forest experts jokingly called called Google Forest.
Stone artifacts, Saudi Arabia, 2011

As the wilds of Mozambique, the deserts of Saudi Arabia only unfriendly to travelers and explorers. In early 2011, Australian scientist David Kennedy (David Kennedy) decided it would be easier to first explore the area on satellite images than to look for something in the sand. Desert Research meter by meter bore fruit - was discovered more than 2,000 places where something visible. These coordinates are entered on the list, and on-site study has revealed several thousand different artifacts of ancient civilization - stone wheels, traps for birds, odd-shaped tombs, and more. Artifacts, scattered over a vast territory from Syria to Yemen, are more than 9,000 years.
Ancient pyramids, Peru, 2008
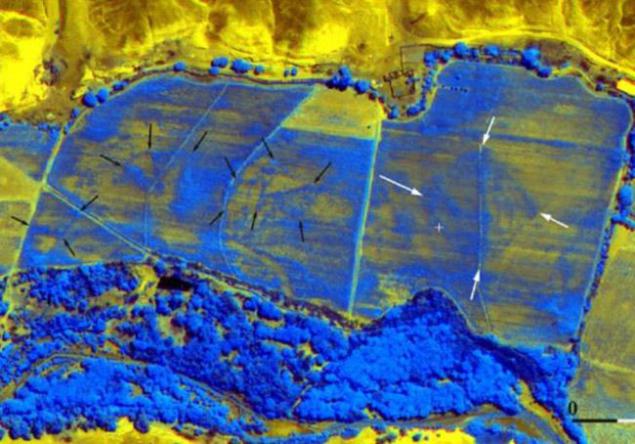
In 2008, scientists were able to detect a large number of ancient pyramids under a layer of soil in the desert of Peru, combining images from Google Earth infrared shooting.
Pyramids were found under a field of wheat, a kilometer from the famous Nazca Lines - a group of giant geometric shapes, each the size of a hundred meters (triangles, spirals, birds, monkeys, spider, flowers). These geoglyphs noticed only in the 20th century, when the plane flew over them. Due to enormous size drawings can not be viewed from the ground.
Remains of an ancient Roman villa, Italy, 2005

One of the oldest archaeological discoveries made in Google Earth, took place in 2005. Ironically, the author of the discovery, a local resident Luca Mori (Luca Mori) just launched a program to explore the area near his home in Parma. Quite unexpectedly, he noticed a strange oval artifact in the fields near the city. One of the oldest archaeological discoveries made in Google Earth, took place in 2005. Ironically, the author of the discovery, a local resident Luca Mori (Luca Mori) just launched a program to explore the area near his home in Parma. Quite unexpectedly, he noticed a strange oval artifact in the fields near the city.
Luca Mori took him for a computer glitch, but still informed the specialists of the National Archaeological Museum, which organized the expedition. Immediately after the excavation, they found the remains of ancient pottery and Roman villa built BC.
Australopithecus sediba age 2 million years, South Africa, 2008

Bold paleoanthropologist Lee Berger went to brave the study of South Africa, running Google Earth in the comfort of his office. Professor began to explore the limestone caves in the area of South Africa, which is known to scientists as the Cradle of Humankind.
Berger found on satellite images previously unknown caves suitable for the life of ancient people. In 2008, he organized an expedition polulyubitelsky, taking with him only one student and son and dog. At the site they found fifty alleged places of residence of Australopithecus (the higher primates, hominids dvunogohodyaschie with a small volume of the brain).
Visit one of the caves, his father sent a 9-year-old son to look around, and after 15 minutes he brought the stone with beautifully preserved fossilized fragments of the clavicle and mandible. Excavations at the site have revealed fragments of skeletons and other women and adolescents, whose age is estimated at 1, 78-1, 95 million years.
The importance of this discovery is that the found samples belong to a new, previously unknown type of Australopithecus, very similar to humans. That's two million years ago, the great apes began to walk on two legs, to use tools and form the beginnings of speech. The new species is named Australopithecus sediba (Australopithecus sediba). Perhaps it is this kind of an ancestor of Homo habilis, ie the transition from ape-like hominids link to the people of the modern species.
Tropical forest on the mountain Mabou, Mozambique, 2008

On satellite images of northern Mozambique British scientist Julian Bailey (Julian Bayliss) found completely unknown "oasis" - an isolated tropical forest, located high in the mountains in a remote place. It turned out that this forest is known to locals, but there has never fitted out a scientific expedition. But these isolated areas are especially interesting for biologists, because there are often new species of animals and plants. Mountain Mabou did not disappoint - in 2008 an expedition was sent there, the results of which are still studying. A total ease was discovered more than a hundred (!) New species - plants, birds, butterflies, monkeys, snakes - in just three weeks. This tropical forest experts jokingly called called Google Forest.
Stone artifacts, Saudi Arabia, 2011

As the wilds of Mozambique, the deserts of Saudi Arabia only unfriendly to travelers and explorers. In early 2011, Australian scientist David Kennedy (David Kennedy) decided it would be easier to first explore the area on satellite images than to look for something in the sand. Desert Research meter by meter bore fruit - was discovered more than 2,000 places where something visible. These coordinates are entered on the list, and on-site study has revealed several thousand different artifacts of ancient civilization - stone wheels, traps for birds, odd-shaped tombs, and more. Artifacts, scattered over a vast territory from Syria to Yemen, are more than 9,000 years.
Ancient pyramids, Peru, 2008

In 2008, scientists were able to detect a large number of ancient pyramids under a layer of soil in the desert of Peru, combining images from Google Earth infrared shooting.
Pyramids were found under a field of wheat, a kilometer from the famous Nazca Lines - a group of giant geometric shapes, each the size of a hundred meters (triangles, spirals, birds, monkeys, spider, flowers). These geoglyphs noticed only in the 20th century, when the plane flew over them. Due to enormous size drawings can not be viewed from the ground.
Filling the Chinese punching bag (2 photos)
He is so fond of the singer, he decided to get a tattoo with his name.