916
Galaxy in the form of "snowflakes"
Galaxy NGC 1376 is located at a distance of more than 180 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Eridanus (Eridanus) and belongs to a class of spiral. One feature of the galaxy is that its brightness changes with time.

Bright blue glowing gas clusters are formed due to the active star formation, releasing excess ultraviolet light. Less intense red areas around the core and between the arms are formed mainly due to the glow of older stars. Scarlet Dust strips colder and denser than the rest of the field, and they are formed from collapsing clouds of interstellar forming new stars.
Map of the constellation Eridanus:
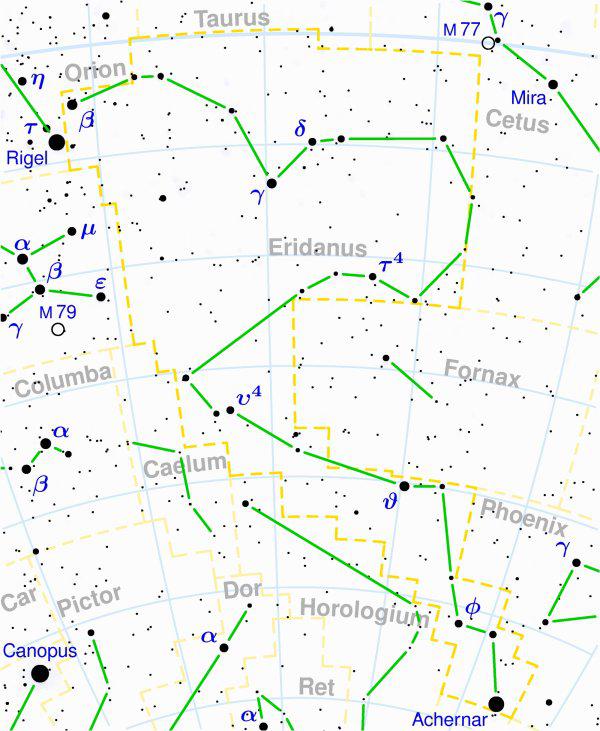
Eridanus (Eridanus, Eri) - a constellation of the southern hemisphere, the sixth in size among the modern constellations. It contains 187 stars visible to the naked eye.

Bright blue glowing gas clusters are formed due to the active star formation, releasing excess ultraviolet light. Less intense red areas around the core and between the arms are formed mainly due to the glow of older stars. Scarlet Dust strips colder and denser than the rest of the field, and they are formed from collapsing clouds of interstellar forming new stars.
Map of the constellation Eridanus:

Eridanus (Eridanus, Eri) - a constellation of the southern hemisphere, the sixth in size among the modern constellations. It contains 187 stars visible to the naked eye.