2082
25 years with the "Hubble"
The most famous space telescope for a quarter century in orbit
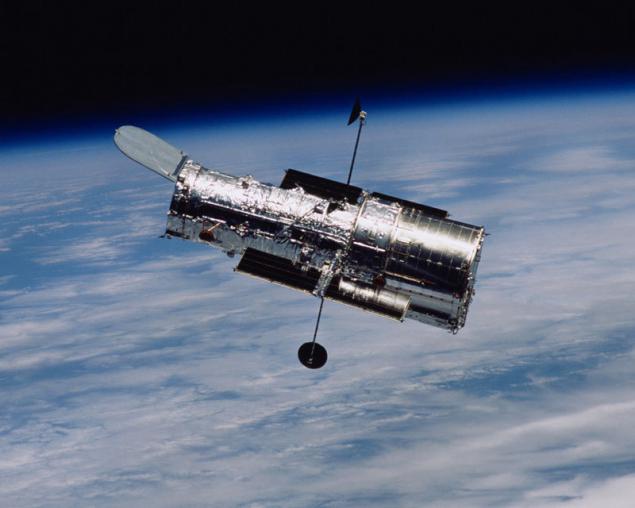

April 24, 1990 at the Earth's orbit was launched space telescope, named after the American astronomer Edwin Hubble . Since the start of work has grown a whole generation of people who take "Hubble" for granted, so it's easy to forget how revolutionary was this device. At the moment it is still running, it may hold more five years. In the week telescope passes about 120 gigabytes of scientific data during the operation of images accumulated on more than 10 thousand scientific articles.
Follower "Hubble" Space Telescope will be the James Webb. The project recently experienced significant cost overruns and Delays for more than 5 years. From "Hubble" everything happened exactly the same even worse - imposed financial problems and катастрофа "Challenger» , and later - «Колумбии». In 1972 considered , that the program will cost $ 300 million (adjusted for inflation it is about 590 million). By the time when the telescope is finally reached the launch pad, the price has increased several times to about 2, 5 billion dollars. By 2006, it was estimated , that "Hubble" cost the 9 billion (10 , 75 billion with inflation), plus five space flights of the space shuttle for maintenance and repairs, each run which costs about 500 million.
The main part of the telescope - a mirror diameter of 2, 4 meters. Generally, planned a telescope with a mirror diameter of 3 meters, and run it like in 1979. But in 1974 the program deleted from the budget, and only thanks to lobbying astronomers were able to get the amount of half the originally requested. Therefore, it was necessary to restrain the ardor and reduce the scope of a future project.
Optically "Hubble" - is the realization of common among scientific telescope Ritchey - Chretien with two mirrors. It allows you to get a good viewing angle and excellent image quality, but the mirrors are difficult to manufacture and test the form. Optical system and the mirror should be made with minimal tolerances. Mirror polished to conventional telescopes tolerance in about a tenth of the length of visible light, but "Hubble" was to make observations including ultraviolet light with shorter wavelengths. Therefore, mirror polished with a tolerance of 10 nanometers, 1 sup> / 65 sub> wavelength of red light. By the way, the mirrors are heated to a temperature of 15 degrees, which limits the performance of the infrared - the other limit of the visible spectrum.
One mirror company produced "Kodak", the other - the corporation Itek. The first is in the National Air and Space Museum, and the second is used in the Magdalena Ridge Observatory. These were replacement mirror, and what is in the "Hubble" was produced by "Perkin Elmer" using sophisticated CNC machines, which led to another and Delays. Work on the polished workpiece from Corning (the same one that makes Gorilla Glass) began only in 1979. Simulate microgravity by placing mirrors on the 130 rods, the force of which ranged support. The process continued until May 1981. Glass washed with 9100 liters of hot demineralized water and caused two layers of 65-nanometer aluminum reflective layer and 25-nanometer protective magnesium fluoride.
A launch date continued to pull away: first, until October 1984, after until April 1985 to March 1986 to September. Each quarter, the work "Perkin Elmer" leads to a shift in the timing of the month, in some moments each day drew back the launch date. Schedules the company did not meet its rasplyvachatostyu NASA and uncertainty. The cost of the project has grown to 1.175 billion dollars.
The casing was another headache, he had to be able to withstand both direct sunlight and darkness of Earth's shadow. And these changes in temperature threatened precise system of scientific telescope. Wall "Hubble" are composed of several layers of insulation, which are surrounded by light aluminum shell. Inside the equipment is placed in grafitoepoksidnom frame. To avoid water absorption hygroscopic compounds of graphite and falling ice instruments inside to run pumped nitrogen. Although production of the spacecraft went far more stable than the optical telescope systems, organizational problems were here. By the summer of 1985 the corporation "Lockheed" worked on the machine, came to 30% over budget and three months behind schedule.
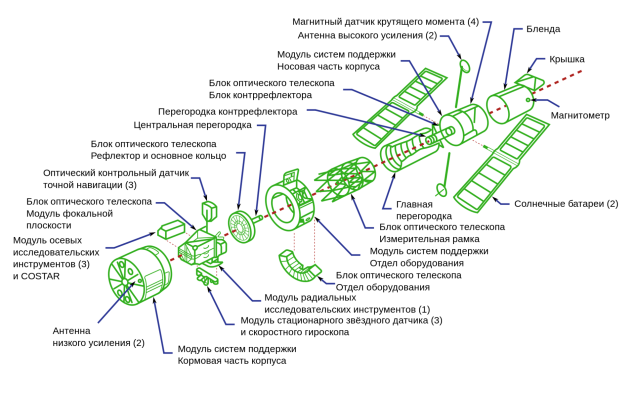
The "Hubble" at startup had five scientific instruments, and later they were replaced during maintenance in orbit. Wide Field and Planetary Camera perform optical observations. In the filter unit 48 was the spectral lines for the isolation of specific elements. Eight CCDs were divided between the two chambers, four each. Each matrix has a resolution of 0, 64 megapixels. Wide-angle camera possesses a large viewing angle, while the planetary had a longer focal length and, therefore, gave a greater increase.
AndrewBuck, Distorted, Erden Karsybekov, Vort, Dodonov; Wikimedia Commons em>
A high-resolution spectrograph created Space Flight Center Goddard worked in the ultraviolet range. Also observed in the UV camera shooting faint objects developed by the European Space Agency, and the Faint Object Spectrograph on the University of California and the corporation "Martin Marietta." University of Wisconsin-Madison has created a high-speed photometer observations of visible light and ultraviolet radiation of stars and other astronomical objects with varying brightness. He could produce up to 100,000 measurements per second with a photometric accuracy of 2% or better. Finally, as a scientific tool can be used datichiki pointing of the telescope, they are allowed to apply precise astrometry.
On Earth, the study "Hubble" controls specially created in 1981 Space Telescope Science Institute. Its formation was not without a fight: NASA wanted to personally control the device, but the scientific community was not in accordance.
Orbit "Hubble" has been chosen so that the telescope could fly up and perform maintenance. Gender-orbit observations prevents land on the way should not be in the sun, moon, and scientific process prevents Brazilian magnetic anomaly, with the span over which sharply increases the level of radiation. Hubble is at an altitude of 569 kilometers, the inclination of its orbit - 28 to 5 °. Because of the presence of the upper atmosphere of the telescope position can vary unpredictably, so accurately predict the position for prolonged periods of time is not possible. The daily work is usually approved only a few days before the start, since it is unclear whether it will be by the time to observe the desired object.
By early 1986, began to emerge launch in October, but a disaster "Challenger" pushed all the time. Space shuttle - like the one that was supposed to deliver a unique telescope worth a billion into orbit - exploded in a cloudless sky at 73 seconds of flight, killing seven people. Until 1988, the entire fleet of shuttles was laid up until the incident was under investigation. By the way, waiting too were costly: "Hubble" kept in a clean room bathed in nitrogen condition. Each month, cost about $ 6 million. Time is not lost in vain, the machine changed the battery is unreliable and made some other improvements. In 1986, there was no program filling of ground control systems, and the launch in 1990, the software was nearly ready.
April 24, 1990, 25 years ago, over budget several times telescope was finally launched to orbit. But the difficulties just begun.
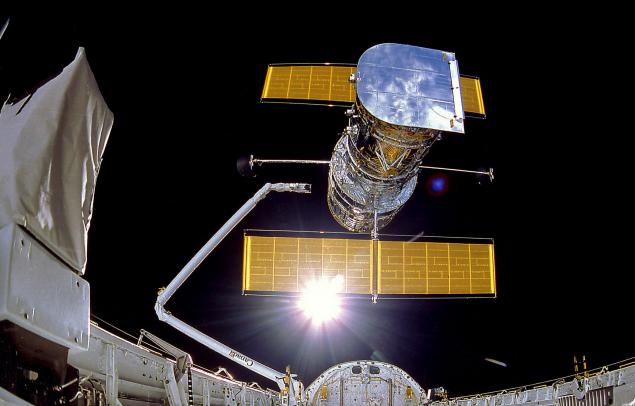

STS-31, the telescope leaves the cargo bay of the shuttle "Discovery» em>
Within a few weeks it became clear that the optical system has a serious defect. Yes, the first images were sharper than ground-based telescopes, but the "Hubble" failed to achieve its stated haraktestik. Point sources look like a circle the size of a 1 arc second circle instead of a 0, 1 arcsecond. As it turns out, NASA does not annoy the competence "Perkin Elmer" - the deviation of the mirror was on the edges to about 2200 nanometers. Defect was disastrous, because it leads to a strong spherical aberration, that is, light reflected from the edges of the mirror, was focused at a point different from that in which the focused light reflected from the center. Because of this, do not hit hard spectroscopy, but seeing faint objects were difficult, which puts an end to most of the cosmological programs.
Despite the fact that he made some observations possible thanks to sophisticated techniques of image processing in the world, "Hubble" is considered failed project, and NASA's reputation was severely tarnished. The telescope started to joke, for example, in the movie "The Naked Gun 2½: The Smell of Fear" spacecraft compared with the "Titanic", the car failed brand Edsel and most famous fall of the airship - accident «Гинденбурга».

Black-and-white telescope is present on one of the pictures em>
It is believed that the cause of the defect was the error during the installation of the main null corrector, a device that helps to achieve the desired parameter of surface curvature. One of the lens unit has been shifted by 1, 3 millimeters. During operation, the specialists' Perkin-Elmer "analyzed surface with two null correctors, and then to the final stage using a special null corrector designed to very tight tolerances. As a result, the mirror turned out very precise, but it was the wrong shape. Later, the error was discovered - two regular null corrector indicates the presence of spherical aberration, but the company chose to ignore their measurement. "Perkin Elmer" and NASA began to sort things out. The American space agency believes that the company does not follow the manufacturing process properly and not used in the manufacturing process and quality control of their best employees. However, it was clear that some of the blame lay and NASA.
The good news is that the design of the telescope requires it to maintain - the first as early as 1993, so have been looked for solutions. On Earth, it was backed by a mirror "Kodak", but change it to orbit was impossible, and the lander on the shuttle would be too expensive and time consuming. Mirror manufactured fine, but it was the wrong shape, so it was suggested to add a new optical components to compensate for the error. By the analysis of point light sources, it was determined that the mirror is a conical constant -1, 0 01,390 ± 0002 instead necessary -1 00230. The same figure was obtained by processing the error-corrector zero "Perkin-Elmer" Test and analysis of interferograms .
In the CCD the second version of the Wide Field and Planetary Camera add the correction of mistakes, but to make the other tools like this was impossible. For them require other external device optical correction, which was called Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR). Roughly speaking, the telescope made glasses. Designated COSTAR was not enough, so I had to give up the high-speed photometer.
In December 1993, was held the first flight maintenance. The first mission was the most important. There have been conducted five, while each space shuttle came closer to the telescope, then with the help of the manipulator tools were replaced and failed devices. For one to two weeks to carry out several spacewalks, and after orbit telescope corrected - he constantly fell due to the impact of the upper atmosphere. Thus, it was possible to update aging equipment "Hubble" to the most modern.
The first operation of the maintenance was carried out with "Inedevora" and lasted 10 days. In place of the high-speed photometer put a corrective optics COSTAR, the first version of the Wide Field and Planetary Camera has been replaced by the second. Were replaced by solar panels and electronics, four gyro guidance system of the telescope, two magnetometer onboard computers and various electrical systems. Flight was considered a success.

Photo galaxy M 100 before and after the installation of correction em>
The second operation maintenance was carried out in February 1997 with the space shuttle "Discovery". With the telescope removed high-resolution spectrograph and Faint Object Spectrograph. They were replaced by STIS (Space Telescope registering spectrograph) and NICMOS (camera and multiob- near-infrared spectrometer). NICMOS cooled with liquid nitrogen to reduce noise, but as a result of an unforeseen extension parts and the heating rate increased lifetime fell from 4 to 5 years 2. Initially data storage "Hubble" tape was, it was replaced by a solid state. Also, the unit trimmed insulation.
Flight service was five, but they are considered in the order 1, 2, 3A, 3B and 4, and despite the proximity of the names, 3A and 3B were not carried out immediately one after the other, as you might expect. The third flight took place in December 1999 on the shuttle "Discovery", he was called a breakdown of four of the six gyroscopes telescope. Were replaced all six gyroscopes, sensors, guidance, on-board computer - now there was an Intel 80486 25 MHz. Prior to that, "Hubble" used DF-224 with the main processor at 1, 25 MHz and two the same backup, Floppy wire of the six banks with 8K 24-bit words, and at the same time could work four banks.
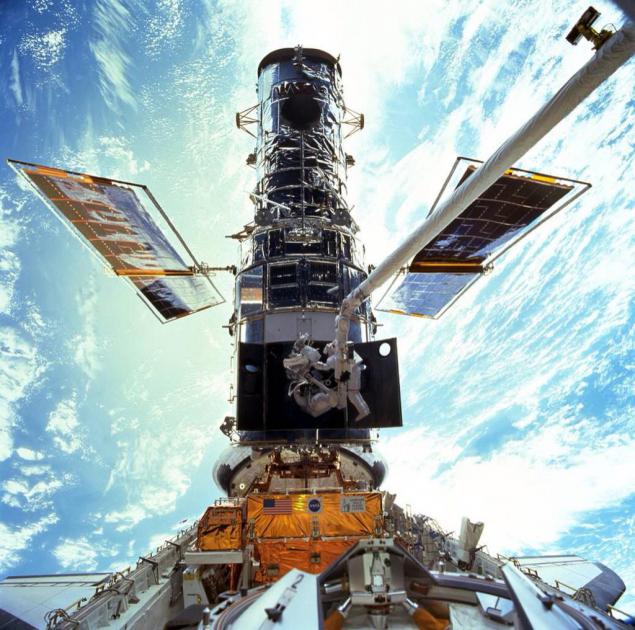

This picture during the third maintenance did Scott Kelly. Today he is the ISS as part of an experiment to study the biological effects of long-term space flight on the human body. Em>
The fourth (or 3B) flight was conducted on the "Columbia" in March 2002. Last original device - camera shooting faint objects - has been replaced by an improved overview camera. The second time the solar panels have been replaced by new were 30% stronger. NICMOS was able to continue functioning with the installation of a pilot krioohlazhdeniya.
From that moment all the tools "Hubble" had error correction mirror, and the need for COSTAR disappeared. But it was removed only in the final flight service, which occurred after the disaster, "Columbia." During the next shuttle flight for Hubble collapsed while returning to Earth - this resulted in a violation of the heat-shielding layer. The death of seven people pushed the original date in February 2005 for an indefinite period. The fact that now all the shuttle flights were to be held in orbit, allows to reach the International Space Station in case of unforeseen problems. But none of the shuttle could not reach a flight orbit as "Hubble" and ISS - not enough fuel. James Webb Telescope behalf planned to start only in 2018, which meant a blank space after the end of "Hubble". Many astronomers came up with the idea that the last maintenance is worth the risk of human lives.
Under pressure from Congress in January 2004, the Administration, NASA stated that the decision to cancel will be reviewed. In August, the Goddard Space Flight Center began to prepare proposals for fully remote controlled flight, but later plans were canceled - they were found impracticable. In April 2005, a new NASA administrator Michael Griffin admitted the possibility of a manned flight to the "Hubble". In October 2006, the intentions were finally confirmed, and the 11-day flight was scheduled for September 2008.
Pozzhё flight was postponed until May 2009. With the "Atlantis" was performed repair STIS and advanced Camera for Surveys. On the "Hubble" established two new nickel-hydrogen battery, replace the sensor guidance and other systems.

April 24, 1990 at the Earth's orbit was launched space telescope, named after the American astronomer Edwin Hubble . Since the start of work has grown a whole generation of people who take "Hubble" for granted, so it's easy to forget how revolutionary was this device. At the moment it is still running, it may hold more five years. In the week telescope passes about 120 gigabytes of scientific data during the operation of images accumulated on more than 10 thousand scientific articles.
Follower "Hubble" Space Telescope will be the James Webb. The project recently experienced significant cost overruns and Delays for more than 5 years. From "Hubble" everything happened exactly the same even worse - imposed financial problems and катастрофа "Challenger» , and later - «Колумбии». In 1972 considered , that the program will cost $ 300 million (adjusted for inflation it is about 590 million). By the time when the telescope is finally reached the launch pad, the price has increased several times to about 2, 5 billion dollars. By 2006, it was estimated , that "Hubble" cost the 9 billion (10 , 75 billion with inflation), plus five space flights of the space shuttle for maintenance and repairs, each run which costs about 500 million.
The main part of the telescope - a mirror diameter of 2, 4 meters. Generally, planned a telescope with a mirror diameter of 3 meters, and run it like in 1979. But in 1974 the program deleted from the budget, and only thanks to lobbying astronomers were able to get the amount of half the originally requested. Therefore, it was necessary to restrain the ardor and reduce the scope of a future project.
Optically "Hubble" - is the realization of common among scientific telescope Ritchey - Chretien with two mirrors. It allows you to get a good viewing angle and excellent image quality, but the mirrors are difficult to manufacture and test the form. Optical system and the mirror should be made with minimal tolerances. Mirror polished to conventional telescopes tolerance in about a tenth of the length of visible light, but "Hubble" was to make observations including ultraviolet light with shorter wavelengths. Therefore, mirror polished with a tolerance of 10 nanometers, 1 sup> / 65 sub> wavelength of red light. By the way, the mirrors are heated to a temperature of 15 degrees, which limits the performance of the infrared - the other limit of the visible spectrum.
One mirror company produced "Kodak", the other - the corporation Itek. The first is in the National Air and Space Museum, and the second is used in the Magdalena Ridge Observatory. These were replacement mirror, and what is in the "Hubble" was produced by "Perkin Elmer" using sophisticated CNC machines, which led to another and Delays. Work on the polished workpiece from Corning (the same one that makes Gorilla Glass) began only in 1979. Simulate microgravity by placing mirrors on the 130 rods, the force of which ranged support. The process continued until May 1981. Glass washed with 9100 liters of hot demineralized water and caused two layers of 65-nanometer aluminum reflective layer and 25-nanometer protective magnesium fluoride.
A launch date continued to pull away: first, until October 1984, after until April 1985 to March 1986 to September. Each quarter, the work "Perkin Elmer" leads to a shift in the timing of the month, in some moments each day drew back the launch date. Schedules the company did not meet its rasplyvachatostyu NASA and uncertainty. The cost of the project has grown to 1.175 billion dollars.
The casing was another headache, he had to be able to withstand both direct sunlight and darkness of Earth's shadow. And these changes in temperature threatened precise system of scientific telescope. Wall "Hubble" are composed of several layers of insulation, which are surrounded by light aluminum shell. Inside the equipment is placed in grafitoepoksidnom frame. To avoid water absorption hygroscopic compounds of graphite and falling ice instruments inside to run pumped nitrogen. Although production of the spacecraft went far more stable than the optical telescope systems, organizational problems were here. By the summer of 1985 the corporation "Lockheed" worked on the machine, came to 30% over budget and three months behind schedule.
The "Hubble" at startup had five scientific instruments, and later they were replaced during maintenance in orbit. Wide Field and Planetary Camera perform optical observations. In the filter unit 48 was the spectral lines for the isolation of specific elements. Eight CCDs were divided between the two chambers, four each. Each matrix has a resolution of 0, 64 megapixels. Wide-angle camera possesses a large viewing angle, while the planetary had a longer focal length and, therefore, gave a greater increase.

AndrewBuck, Distorted, Erden Karsybekov, Vort, Dodonov; Wikimedia Commons em>
A high-resolution spectrograph created Space Flight Center Goddard worked in the ultraviolet range. Also observed in the UV camera shooting faint objects developed by the European Space Agency, and the Faint Object Spectrograph on the University of California and the corporation "Martin Marietta." University of Wisconsin-Madison has created a high-speed photometer observations of visible light and ultraviolet radiation of stars and other astronomical objects with varying brightness. He could produce up to 100,000 measurements per second with a photometric accuracy of 2% or better. Finally, as a scientific tool can be used datichiki pointing of the telescope, they are allowed to apply precise astrometry.
On Earth, the study "Hubble" controls specially created in 1981 Space Telescope Science Institute. Its formation was not without a fight: NASA wanted to personally control the device, but the scientific community was not in accordance.
Orbit "Hubble" has been chosen so that the telescope could fly up and perform maintenance. Gender-orbit observations prevents land on the way should not be in the sun, moon, and scientific process prevents Brazilian magnetic anomaly, with the span over which sharply increases the level of radiation. Hubble is at an altitude of 569 kilometers, the inclination of its orbit - 28 to 5 °. Because of the presence of the upper atmosphere of the telescope position can vary unpredictably, so accurately predict the position for prolonged periods of time is not possible. The daily work is usually approved only a few days before the start, since it is unclear whether it will be by the time to observe the desired object.
By early 1986, began to emerge launch in October, but a disaster "Challenger" pushed all the time. Space shuttle - like the one that was supposed to deliver a unique telescope worth a billion into orbit - exploded in a cloudless sky at 73 seconds of flight, killing seven people. Until 1988, the entire fleet of shuttles was laid up until the incident was under investigation. By the way, waiting too were costly: "Hubble" kept in a clean room bathed in nitrogen condition. Each month, cost about $ 6 million. Time is not lost in vain, the machine changed the battery is unreliable and made some other improvements. In 1986, there was no program filling of ground control systems, and the launch in 1990, the software was nearly ready.
April 24, 1990, 25 years ago, over budget several times telescope was finally launched to orbit. But the difficulties just begun.

STS-31, the telescope leaves the cargo bay of the shuttle "Discovery» em>
Within a few weeks it became clear that the optical system has a serious defect. Yes, the first images were sharper than ground-based telescopes, but the "Hubble" failed to achieve its stated haraktestik. Point sources look like a circle the size of a 1 arc second circle instead of a 0, 1 arcsecond. As it turns out, NASA does not annoy the competence "Perkin Elmer" - the deviation of the mirror was on the edges to about 2200 nanometers. Defect was disastrous, because it leads to a strong spherical aberration, that is, light reflected from the edges of the mirror, was focused at a point different from that in which the focused light reflected from the center. Because of this, do not hit hard spectroscopy, but seeing faint objects were difficult, which puts an end to most of the cosmological programs.
Despite the fact that he made some observations possible thanks to sophisticated techniques of image processing in the world, "Hubble" is considered failed project, and NASA's reputation was severely tarnished. The telescope started to joke, for example, in the movie "The Naked Gun 2½: The Smell of Fear" spacecraft compared with the "Titanic", the car failed brand Edsel and most famous fall of the airship - accident «Гинденбурга».

Black-and-white telescope is present on one of the pictures em>
It is believed that the cause of the defect was the error during the installation of the main null corrector, a device that helps to achieve the desired parameter of surface curvature. One of the lens unit has been shifted by 1, 3 millimeters. During operation, the specialists' Perkin-Elmer "analyzed surface with two null correctors, and then to the final stage using a special null corrector designed to very tight tolerances. As a result, the mirror turned out very precise, but it was the wrong shape. Later, the error was discovered - two regular null corrector indicates the presence of spherical aberration, but the company chose to ignore their measurement. "Perkin Elmer" and NASA began to sort things out. The American space agency believes that the company does not follow the manufacturing process properly and not used in the manufacturing process and quality control of their best employees. However, it was clear that some of the blame lay and NASA.
The good news is that the design of the telescope requires it to maintain - the first as early as 1993, so have been looked for solutions. On Earth, it was backed by a mirror "Kodak", but change it to orbit was impossible, and the lander on the shuttle would be too expensive and time consuming. Mirror manufactured fine, but it was the wrong shape, so it was suggested to add a new optical components to compensate for the error. By the analysis of point light sources, it was determined that the mirror is a conical constant -1, 0 01,390 ± 0002 instead necessary -1 00230. The same figure was obtained by processing the error-corrector zero "Perkin-Elmer" Test and analysis of interferograms .
In the CCD the second version of the Wide Field and Planetary Camera add the correction of mistakes, but to make the other tools like this was impossible. For them require other external device optical correction, which was called Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR). Roughly speaking, the telescope made glasses. Designated COSTAR was not enough, so I had to give up the high-speed photometer.
In December 1993, was held the first flight maintenance. The first mission was the most important. There have been conducted five, while each space shuttle came closer to the telescope, then with the help of the manipulator tools were replaced and failed devices. For one to two weeks to carry out several spacewalks, and after orbit telescope corrected - he constantly fell due to the impact of the upper atmosphere. Thus, it was possible to update aging equipment "Hubble" to the most modern.
The first operation of the maintenance was carried out with "Inedevora" and lasted 10 days. In place of the high-speed photometer put a corrective optics COSTAR, the first version of the Wide Field and Planetary Camera has been replaced by the second. Were replaced by solar panels and electronics, four gyro guidance system of the telescope, two magnetometer onboard computers and various electrical systems. Flight was considered a success.

Photo galaxy M 100 before and after the installation of correction em>
The second operation maintenance was carried out in February 1997 with the space shuttle "Discovery". With the telescope removed high-resolution spectrograph and Faint Object Spectrograph. They were replaced by STIS (Space Telescope registering spectrograph) and NICMOS (camera and multiob- near-infrared spectrometer). NICMOS cooled with liquid nitrogen to reduce noise, but as a result of an unforeseen extension parts and the heating rate increased lifetime fell from 4 to 5 years 2. Initially data storage "Hubble" tape was, it was replaced by a solid state. Also, the unit trimmed insulation.
Flight service was five, but they are considered in the order 1, 2, 3A, 3B and 4, and despite the proximity of the names, 3A and 3B were not carried out immediately one after the other, as you might expect. The third flight took place in December 1999 on the shuttle "Discovery", he was called a breakdown of four of the six gyroscopes telescope. Were replaced all six gyroscopes, sensors, guidance, on-board computer - now there was an Intel 80486 25 MHz. Prior to that, "Hubble" used DF-224 with the main processor at 1, 25 MHz and two the same backup, Floppy wire of the six banks with 8K 24-bit words, and at the same time could work four banks.

This picture during the third maintenance did Scott Kelly. Today he is the ISS as part of an experiment to study the biological effects of long-term space flight on the human body. Em>
The fourth (or 3B) flight was conducted on the "Columbia" in March 2002. Last original device - camera shooting faint objects - has been replaced by an improved overview camera. The second time the solar panels have been replaced by new were 30% stronger. NICMOS was able to continue functioning with the installation of a pilot krioohlazhdeniya.
From that moment all the tools "Hubble" had error correction mirror, and the need for COSTAR disappeared. But it was removed only in the final flight service, which occurred after the disaster, "Columbia." During the next shuttle flight for Hubble collapsed while returning to Earth - this resulted in a violation of the heat-shielding layer. The death of seven people pushed the original date in February 2005 for an indefinite period. The fact that now all the shuttle flights were to be held in orbit, allows to reach the International Space Station in case of unforeseen problems. But none of the shuttle could not reach a flight orbit as "Hubble" and ISS - not enough fuel. James Webb Telescope behalf planned to start only in 2018, which meant a blank space after the end of "Hubble". Many astronomers came up with the idea that the last maintenance is worth the risk of human lives.
Under pressure from Congress in January 2004, the Administration, NASA stated that the decision to cancel will be reviewed. In August, the Goddard Space Flight Center began to prepare proposals for fully remote controlled flight, but later plans were canceled - they were found impracticable. In April 2005, a new NASA administrator Michael Griffin admitted the possibility of a manned flight to the "Hubble". In October 2006, the intentions were finally confirmed, and the 11-day flight was scheduled for September 2008.
Pozzhё flight was postponed until May 2009. With the "Atlantis" was performed repair STIS and advanced Camera for Surveys. On the "Hubble" established two new nickel-hydrogen battery, replace the sensor guidance and other systems.























