923
Best photos of space objects. Top 20 in the rankings space.com

1. Amazing panoramic view of Saturn was shot camera angles of the probe Cassini September 15, 2006. Along with the giant Saturn hanging in the blackness and protect Cassini from the blinding brightness of the Sun, considered the ring probe as clearly as never before, revealing previously unknown faint rings, as well as the atmosphere and the planet's surface.
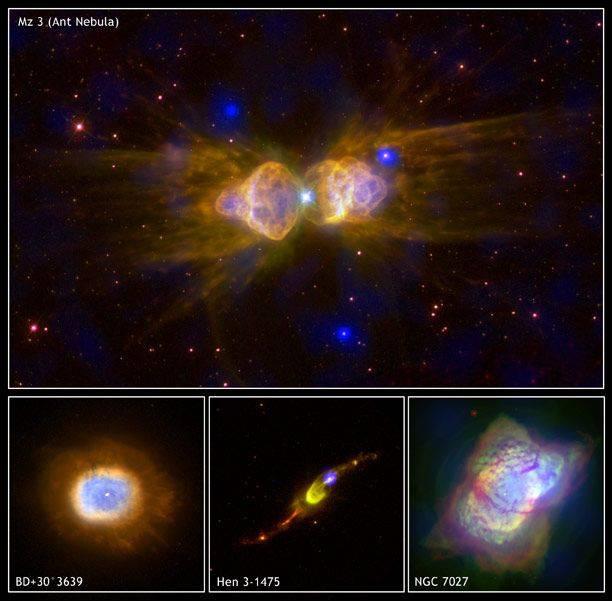
2. Planetary Nebula, located at a distance of about 3,000 light years from Earth. This group of pictures shows the unfolding drama, which takes place on the last stages of sun-like stars. The elongated clouds envelop bubbles of gas, heated to multimillion-degree temperatures that have occurred as a result of high-speed wind of gas from dying stars. This photo was taken May 10, 2006.
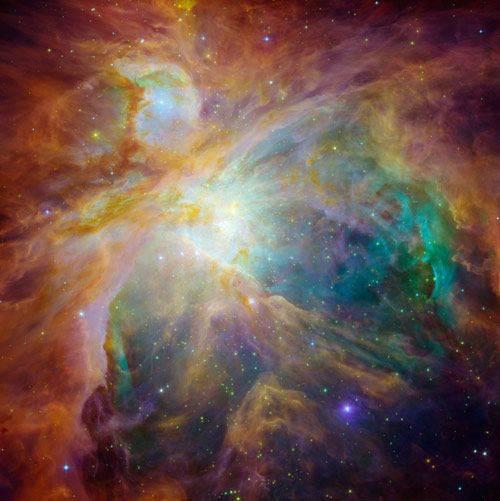

3. Joint Photo Spitzer Space Telescope and Hubble shows us the chaos going on in the formation of new young stars that formed at a distance of 1,500 light years away in a cosmic cloud, called "Orion Nebula".

4. Messier 83 - a neighboring galaxy, located outside the boundaries of our local group of galaxies. The central bulge has a distinctive yellow color of old stars, while its spiral environment shown scattered blue light and red nodes to form new stars, has a much younger age.
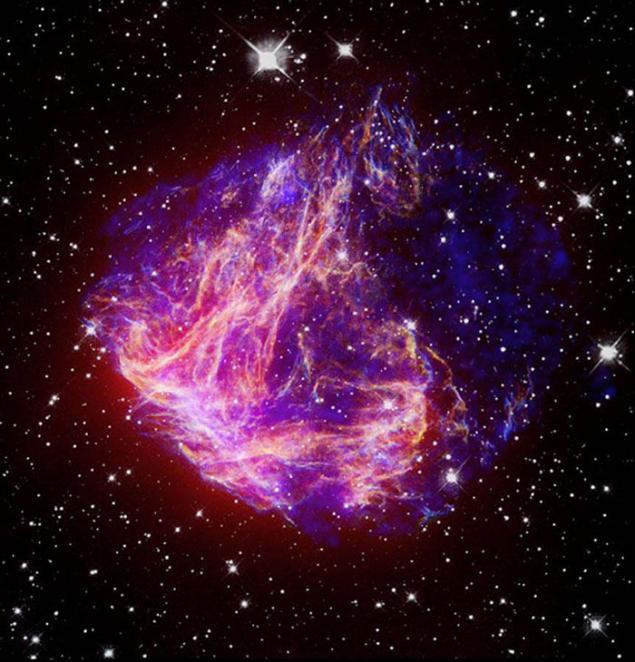

5. This composite image of Chandra and Spitzer shows us the brightest supernova remnant in the "Large Magellanic Cloud." Image X-ray telescope Chandra X-ray (blue) reveals gas heated to millions of degrees in the center and in the outer parts shown cooler gas in the infrared (red), produced by the telescope Spitzer.

6. These intensely moving galaxy took the form of a giant mask. Icy blue eyes - is the core of two merging galaxies, NGC 2207 with the names and IC 2163, and the mask itself - its spiral peripherals. False-color image consists of infrared data of X-ray telescope Spitzer (red) and visible to our eyes the data space telescope Hubble (blue and green).

7. One of the most recent images captured with the help of space telescope Hubble, shows us the galaxy Antennae, is more powerful and harsh in this pair of merging galaxies. As a result of the collapse will be formed billions of new stars. The brightest and most compact of these areas of the birth of new stars are called "super-star cluster" (super star clusters). This image allows astronomers to better distinguish between the stars and super star clusters created in the collision of two spiral galaxies.
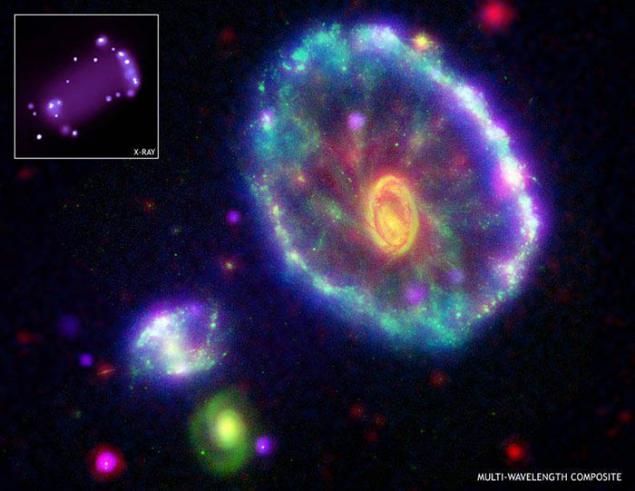
8. The unusual shape of the galaxy from the ridiculous to the Russian ear the name "Cartwheel" (Cartwheel galaxy) turned out, probably by a collision with another, smaller galaxy of several hundred million years ago.
On the left you can see from above, it looks like "Cartwheel" X-ray Spitzer's infrared.
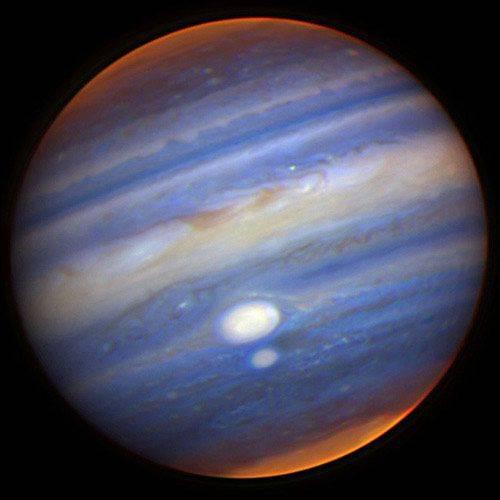

9. Two massive storm on the largest gas giant of the Solar System - Jupiter taken with telescopes from Earth. Two oval-shaped storm (so-called "red spots") appear white in this image, because it shows us in the infrared range, not in the traditional wavelengths perceived by the human eye (I would call it 'human-eye wavelenght').

10. Swirls of gas and dust in the formation of new stars, shot space telescope Hubble. This krasotischa called LH 95 is located in "the Large Magellanic Cloud," she shows us the field of "low mass" - infant stars, as well as some of their more massive neighbors. The image was taken in March 2006 with the camera "Hubble Advanced Camera" telescope Hubble.

11. Philip Jones (Phillip Jones) caught a rare and exciting moment - Mercury attempt to outshine the sun. The photo was taken November 15, 2006.

12. This image, obtained with the apparatus "Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter", shows us the crater "Victoria" located near the equator of Mars. The diameter of the crater about 800 meters. It has toothed form-induced erosion and the movement of the material that makes up the wall of the crater. The surface area of the crater takes amazing dunes.
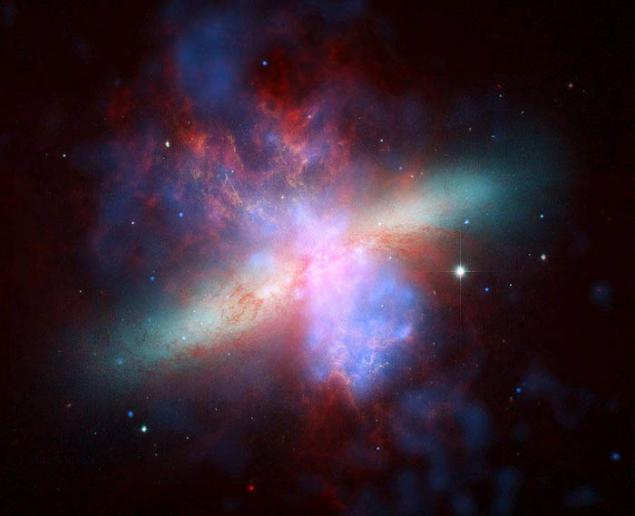

13. Spitzer, Hubble, and Chandra Observatory have teamed up to create this multivolnovoe, false-color image of the galaxy M82. The photo was taken in the sixteenth day of the telescope Hubble, 24 April 2006.
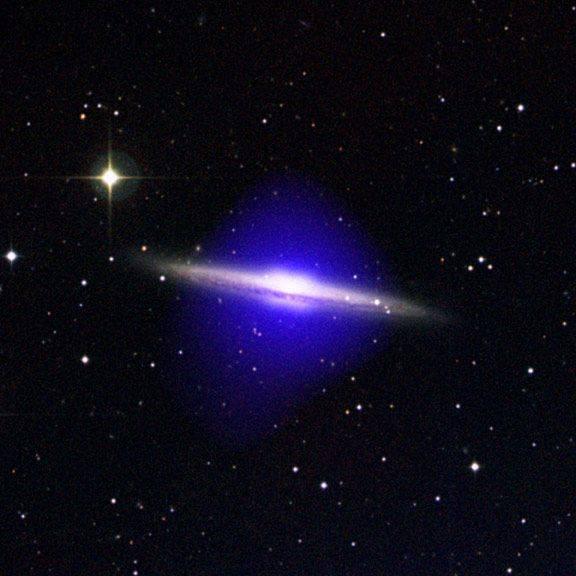

14. Chandra Observatory image of a massive spiral galaxy NGC 5746 shows us an enormous halo of hot gas (blue) surrounded by the optical disk of the galaxy (white). Halo is expanding by more than 60 000 light years in all directions of the galaxy.
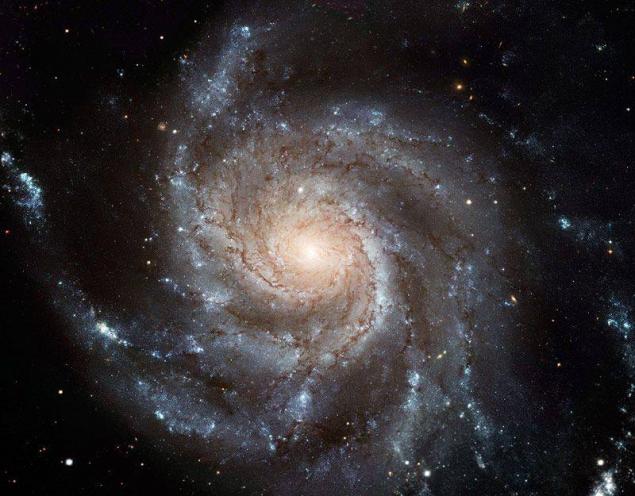

15. Giant telescope Hubble galaxy to assemble a whole day. In the picture shown facing the "face to us" spiral galaxy Messier 101 (M101), and it is the most detailed photo of a spiral galaxy ever made telescope Hubble.

16. This large, bubble-like mass of interstellar dust clouds called N44 superbubble complex. It has a length of 325 light-years away in the apogee (the point of maximum extension), and a hole in the center was formed due to the strong solar winds from massive stars that literally "blew" the middle of the bubble.
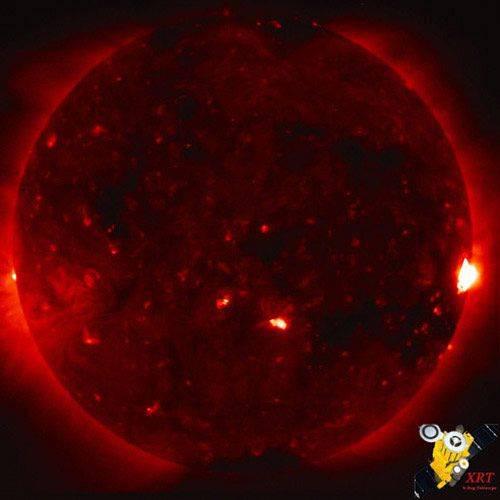

17. The infrared portrait of the Sun, made in Japanese observatory Hinode. This image obtained by X-ray telescope Hinode, which is one of the three watched the sun instruments satellite Hinode, launched into orbit in September 2006. Before the telescope called Solar-B, and was renamed after it went into orbit. Currently, Hinode is an X-ray telescope with the highest resolution ever launched into space.
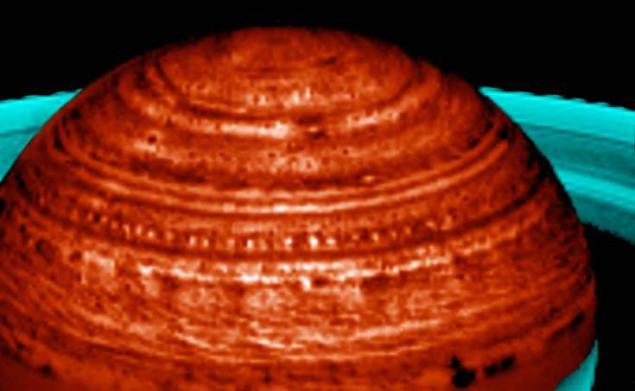
18. This image shows Saturn's lovely weather, like a "string of pearls", covering more than 60,000 kilometers. The image is made with the help of visual and infrared mapping spectrometer, located on the probe Cassini. Pearls are clearing deep in Saturn's cloud system.
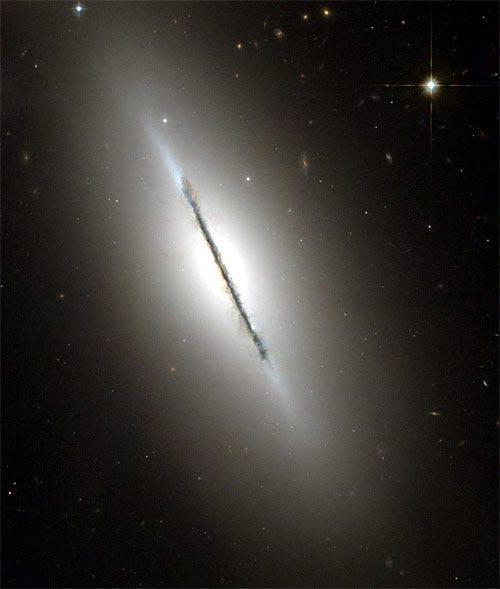

19. This is a unique image of the disk galaxy NGC 5866. Hubble Space Telescope Eagle Eye shows us a fresh bunch of dust, dividing the galaxy into two halves.
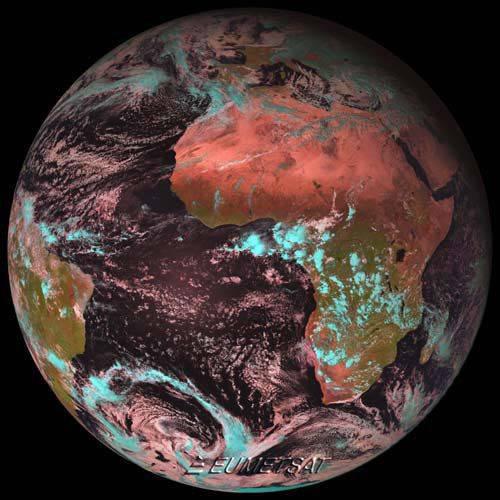
20. Earth, presented in a reddish tinge - the result of the opening of the European satellite MSG-2 (Meteosat Second Generation 2). A recorded January 25, 2006, the picture of our home planet - the first image made satellite launched in December 2005.
Taken from rykun
























