739
10 amazing galactic phenomena
Astronomers often face in their observations to the phenomena, which is not something that is difficult to explain and impossible to describe. The farther we look into space, the more such events we find.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with ten of some of the most interesting galactic phenomena and oddities, collected over years of painstaking contemplation of the cosmos.
The Triangulum galaxy IIis Located near the edge of the milky Way, the Triangulum galaxy II has already managed to impress many astronomers their incredibly fast stars. Our small galactic neighbor contains a very low number of them — only about 1,000 (in the milky Way, for example, 100 billion). However, in Triangulum II hides a tremendous mass.
Taking the observation of this galaxy, a large telescope, Keck, is located on the Hawaiian volcano of Mauna Kea, noticed six stars, which move much faster than expected. The fact that the galaxy is so dark that the telescope could see only the six stars. However, with even these stars, the researchers were able to calculate the gravitational forces Triangulum II and its total weight. It turned out that the galaxy is more massive than the combined mass of all its stars.
Scientists have discovered that this galaxy contains the highest among all studied up to this concentration of galaxies is dark matter. Nevertheless, the French astronomers from the University of Strasbourg believe that the reason for the strong scattering of stars and the dim galaxy is the effect of the gravitational forces of neighbouring Triangulum galaxies II.
Such a high concentration of dark matter in the Triangulum II gives scientists the unprecedented opportunity to try to explore this strange substance, which accounts for 24 percent of the entire mass of the Universe. Due to the fact that this galaxy contains very few stars, it produces virtually no gamma radiation, thereby providing a chance to detect the x-ray power from the interaction of dark matter. Since the galaxy is in fact dead, these signals should be recorded clearly, virtually without any distortion from many cosmic sources of energy that are present in a more "lively" areas.
Mysterious galactic ring American, and Hungarian astronomers have recently stumbled into space to a structure that has been so huge that it is difficult to believe in its existence. This structure turned out to be a cluster of galaxies that formed a kind of ring, which extends nearly 5 billion light-years. This object is so huge that in the night sky in the optical range, he would have looked 70 times larger than the full disk of the moon.
Astronomers were able to calculate the estimated size of this outer ring due to the affinity of seven of the observed bursts of gamma radiation- one of the biggest phenomena of the energy of an explosive nature in space. Bursts of gamma rays typically occur at a time when the star becomes a supernova sviryanki, and then turns into a black hole.
As observed bursts were from each other almost at the same distance, astronomers speculated that they are part of the same space mega structure. Of course, to discard the probability of chance is not worth it. The existence of galactic ring of this size is contrary to our cosmological models describing the limit of the size of the largest objects in the Universe, which is, according to these models, about 1.2 billion light years.
And even if this ring does exist, then why is it so big? The answer to this question is nobody knows. However, there are suggestions that the establishment of such space objects of incredible size one way or another, to meet the same mysterious dark matter.
Galaxy Lin
By combining the power of space telescopes "Hubble" and "Spitzer, astronomers have discovered one of the most remote from us the objects in the Universe. While scientists believe that this object appeared after 400 million years after the Big Bang. That is, he still is one of the oldest objects in the Universe. This object is barely visible and extremely faded galaxy, called Lin that the South American dialect means "first born". At the moment, scientists have discovered 22 similar to the "firstborn" of the galaxy, originating soon after the Big Bang.
For the detection of galaxy Lin took the forces of the two best space telescopes and mankind big help from the galaxy cluster MACS J0416.1-2403, is located about four billion light years from us. Weighing in quadrillion Suns, this galactic cluster attracts an incredible amount of light creating a gravitational lens and allowing you to look at Lin, who in fact is behind it. Telescope named James Webb, who is going to be sent into space in 2018, will allow us a better look at this galaxy and provide much more detail about this representative of the first galactic objects in the Universe.
Galactic babysitter
Astronomers are unsure about your knowledge about how galaxies are born. It is generally accepted that all the required substance for its education galaxy is taken from the intergalactic medium. However, there are other assumptions. According to one view, the initial formation of galaxies originates from dense clusters of dark matter, around which begin to accumulate clouds of hydrogen and other gases drawn by gravitational forces. According to another theory, galaxies are formed from matter a specific source. The first option is too long, so it can be checked on the basis of observed data. For a second no one ever watched.
At least until recently. Researchers from the California Institute of technology using the Cosmic Web Imager instrument mounted on the Hale telescope at Palomar Observatory, discovered protogalactical drive (very young, newly formed galaxy, located 10 billion light-years away. It consists of hot gas, whose volume increases due to cold gas, which young galaxy gets from the threads of the so-called Cosmic web, which the galaxy formed. Scientists believe that this is the first direct proof of the existence of the Cosmic web that unites everything in the Universe.
Due to the random location of the two quasars in this region of space, the part of the thread of a web which delivers the gas to start-UPS the galaxy, warmed up, allowing scientists to detect its presence.
"Large Magellanic lawlessness"
The large Magellanic cloud (LMC) and its dwarf companion called the Small Magellanic cloud (SMC) are our nearest neighboring galaxies, situated about 160 000 and 200 000 light-years. Being the largest of the dwarf galaxies located near the Milky Way, they can easily be seen in the southern hemisphere night sky.
Scientists say that with BMO's something strange going on. In the tarantula nebula, which is part of the LMC, astronomers have discovered a veritable incubator of star formation. But as it turned out, the stars here produced is much less than it seems at first glance.
The fact that about 5 percent of 5900 studied large and very large stars located in the LMC, belong to this galaxy. BMO actually stole them, IMO. To such conclusion scientists came after he discovered that these stars go in the opposite direction, compared to the rest. Moreover, the chemical composition of these stars is not like the one that is usually characteristic of the stars of the LMC. These stars contain more heavy elements such as iron and calcium. Scientists believe that this fertility the tarantula nebula, is largely due to the fact that BMO is stealing the stars IMO. In addition, BMO did not scruple to eat up and gas from its outer neighbor. The gas in this case accelerates so much that "ignites the residual gases between the two galaxies.
Galaxy Hercules A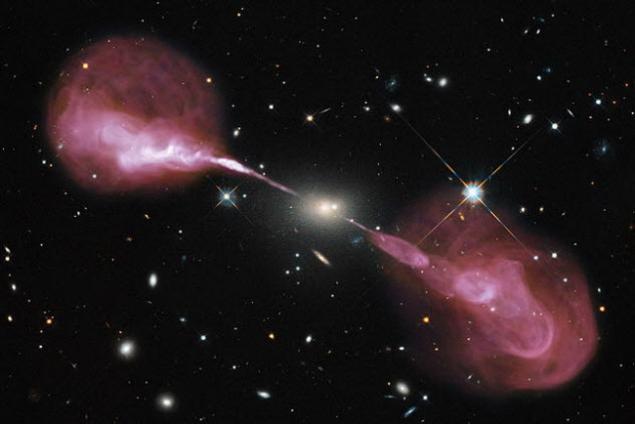
In the center of the galaxy Hercules A (3C 348), a gigantic black hole with a mass of 2.5 billion Suns! It is 1000 times more massive than the black hole of the milky Way and produces two giant jets of plasma, which obscure almost the entire galaxy in which they reside. Moreover, extending to 1.5 million light years, these streams of plasma a dim and other galaxies, including the milky Way, which in diameter 15 times less. The amount of energy it is very difficult to describe. The output impact of the black hole at the centre of radio waves equivalent to one billion times that of our Sun.
This is enough to consider the Hercules And one of the brightest ever observed sources of radio waves. Pink-red beam on the image above is a plasma of atomic particles and magnetic fields, accelerated to relativistic velocities (nearly the speed of light). Volumetric globular clusters at the edges, most likely, talking about many of the early incredible volume of emissions.
Unfortunately, all this is invisible to the naked sight, that is, is only a representation of the artist. The image created on the basis of optical data from the camera Wide Field Camera 3 of the Hubble space telescope, as well as observations of the radio telescope Very Large Array (Corbella Antenna array).
The ancient white dwarfs in the milky Way Our galaxy is very old. She is almost as old as the universe itself. Watching the Central rib of the milky Way, astronomers have discovered a cluster of 70 white dwarfs — dense and compact stars with mass of the Sun (or even more), but it is not the size of the Earth.
Of course, the jumper is a lot more stars, but scientists are interested in a certain group, located in the relative openness of space dust and located about 25 000 light years from Earth.
Now these stars are nothing short of astronomical relics, however, according to scientists, they can tell us about how came our galaxy. It is believed that the age of some of the white dwarfs is more than 12 billion years. In addition, scientists think that these white dwarfs were one of those stars that once "planted" our galaxy. With them began the history of the milky Way. Millions of stars at the end of their life cycle, followed their example, leaving 100 000 light years the matter.
Incredibly bright galaxy
Space telescope WISE space Agency NASA has detected the brightest ever found the galaxy. Its brightness is equivalent to a brightness of more than 300 trillion Suns. Photons galaxy WISE J224607.57-052635.0, in question, had to overcome a 12.5 billion years to leave us your message and give us an idea of how the universe looked in fact at the dawn of its birth.
This galaxy is so bright that it is difficult even to see her full image in the view of the artist, which you can see above. But its brightness it owes not to the stars. Galaxy is so bright thanks to its black hole. It is so massive that even to some extent casts doubt on our understanding of physics.
Scientists are surprised that the early universe could be a haven for such space objects. Usually black holes are limited in their "gluttony", and elapsed time would not be enough so she swallowed the entire galaxy. However, this black hole could somehow overcome the limits of their gluttony" until you reached the weight that it is now. She "ate" so that now frees up (burps) a huge amount of energy that is literally going up in here a giant cocoon of gas, which eventually begins to light up with a dazzling aura.
Tiny galaxy with a giant black hole
Ultra-compact dwarf galaxy M60-UCD1 may change our understanding of black holes and the notion of dwarf galaxies in General. Its size is only 300 light years, which is only 0.2 percent of the size of the milky Way. However, this galaxy is a black hole with a mass equivalent to 21 million Suns. For comparison, the black hole at the center of the milky Way is much larger in size but has a mass of 4 million Suns.
Until recently it was believed that the size of galaxies and the size of black holes linked. However, this opening has questioned this model and suggests that the sizes of these two space objects can be completely disproportionate. And scientists have explanation for this.
The fact is that M60-UCD1 was not always a dwarf galaxy. Astronomers from the University of Utah (USA) believe that once this galaxy was the dwelling place of the 10 billion stars. However, she gets too close to the larger galactic neighbour, which is actually robbed her. As a result, in the galaxy there are only about 140 million stars. This makes M60-UCD1 in the end, one of the smallest galaxies with a massive black hole in the center. However, the same researchers suggests other questions. Whether dwarf galaxies "failed" a large or all of them at some point in their history they became victims of their larger neighbors?
Galaxy EGS8p7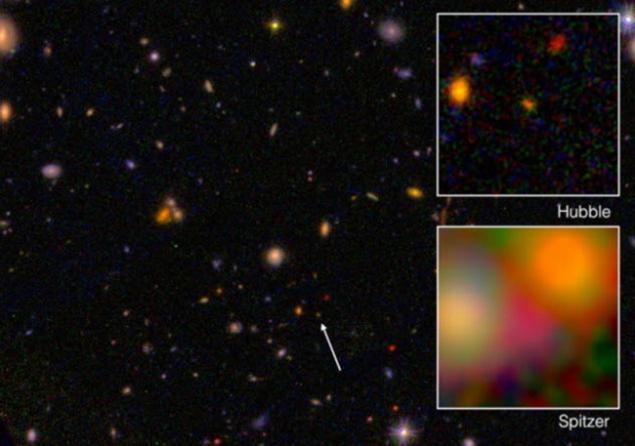
Galaxy EGS8p7 age of 13.2 billion years is so ancient that we can't see her. After the Big Bang, the universe for some time was a hot cluster of protons and electrons. After a cooling period of a particle connected to the neutral hydrogen. The point is that in this case, our telescopes would not be able to detect the early light of the Universe, because he would be in this case had to go through a lot of different distortions.
The emergence of galaxies and other sources of energy in the Universe, they were neionizirovanne the gas dissipated its dense cluster and paved the way for the light. However, this happened already about a billion years later, so EGS8p7 is too far from us so we can see it. And yet astronomers somehow say that could catch a line of the Lyman-alpha galaxy, which is kind of her barcode. It appears when a relatively young star begins to radiate ultraviolet light into the surrounding gas, leaving a heat signature. This signature was detected by the spectrometer MOSFIRE installed in the Observatory Keck in Hawaii.
And yet the line Lyman-alpha galaxy EGS8p7 had to stay hidden early opaque neutral hydrogen. Astronomers are unsure about how light EGS8p7 manage to break through this barrier. There is speculation that radiation from the local star is so powerful that it has neionizirovanne part of the Universe much earlier than other galaxies.
Bonus: Ring Of Andromeda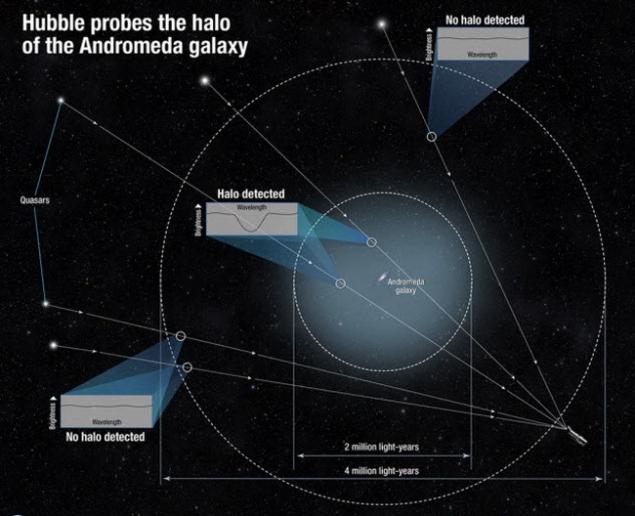
Our closest neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy (M31) surrounded by a giant ring (or halo). Andromeda itself is twice the milky Way and extends more than 200,000 light-years. Her halo takes up the space of about 2 million light years. It acts as a beacon to astronomers who are looking for quasars. Under the scientific instruments of the space telescope "Hubble" ultra-violet light filed the scientists an idea of around how Andromeda could have formed such a huge ring of gas.
Part of the galactic gas ring is a kind of huge repository of matter for the future and have already formed stars. It is rich and heavy elements produced by a supernova, located on the borders of Andromeda and emitted outside. Unfortunately, the ring itself is invisible to the human eye, but in the night sky it would be 100 times larger than the diameter of the full moon.published
Author: Nicholas Khizhnyak
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: hi-news.ru/space/10-udivitelnyx-galakticheskix-yavlenij.html
We offer you to familiarize yourself with ten of some of the most interesting galactic phenomena and oddities, collected over years of painstaking contemplation of the cosmos.
The Triangulum galaxy IIis Located near the edge of the milky Way, the Triangulum galaxy II has already managed to impress many astronomers their incredibly fast stars. Our small galactic neighbor contains a very low number of them — only about 1,000 (in the milky Way, for example, 100 billion). However, in Triangulum II hides a tremendous mass.
Taking the observation of this galaxy, a large telescope, Keck, is located on the Hawaiian volcano of Mauna Kea, noticed six stars, which move much faster than expected. The fact that the galaxy is so dark that the telescope could see only the six stars. However, with even these stars, the researchers were able to calculate the gravitational forces Triangulum II and its total weight. It turned out that the galaxy is more massive than the combined mass of all its stars.
Scientists have discovered that this galaxy contains the highest among all studied up to this concentration of galaxies is dark matter. Nevertheless, the French astronomers from the University of Strasbourg believe that the reason for the strong scattering of stars and the dim galaxy is the effect of the gravitational forces of neighbouring Triangulum galaxies II.
Such a high concentration of dark matter in the Triangulum II gives scientists the unprecedented opportunity to try to explore this strange substance, which accounts for 24 percent of the entire mass of the Universe. Due to the fact that this galaxy contains very few stars, it produces virtually no gamma radiation, thereby providing a chance to detect the x-ray power from the interaction of dark matter. Since the galaxy is in fact dead, these signals should be recorded clearly, virtually without any distortion from many cosmic sources of energy that are present in a more "lively" areas.
Mysterious galactic ring American, and Hungarian astronomers have recently stumbled into space to a structure that has been so huge that it is difficult to believe in its existence. This structure turned out to be a cluster of galaxies that formed a kind of ring, which extends nearly 5 billion light-years. This object is so huge that in the night sky in the optical range, he would have looked 70 times larger than the full disk of the moon.
Astronomers were able to calculate the estimated size of this outer ring due to the affinity of seven of the observed bursts of gamma radiation- one of the biggest phenomena of the energy of an explosive nature in space. Bursts of gamma rays typically occur at a time when the star becomes a supernova sviryanki, and then turns into a black hole.
As observed bursts were from each other almost at the same distance, astronomers speculated that they are part of the same space mega structure. Of course, to discard the probability of chance is not worth it. The existence of galactic ring of this size is contrary to our cosmological models describing the limit of the size of the largest objects in the Universe, which is, according to these models, about 1.2 billion light years.
And even if this ring does exist, then why is it so big? The answer to this question is nobody knows. However, there are suggestions that the establishment of such space objects of incredible size one way or another, to meet the same mysterious dark matter.
Galaxy Lin
By combining the power of space telescopes "Hubble" and "Spitzer, astronomers have discovered one of the most remote from us the objects in the Universe. While scientists believe that this object appeared after 400 million years after the Big Bang. That is, he still is one of the oldest objects in the Universe. This object is barely visible and extremely faded galaxy, called Lin that the South American dialect means "first born". At the moment, scientists have discovered 22 similar to the "firstborn" of the galaxy, originating soon after the Big Bang.
For the detection of galaxy Lin took the forces of the two best space telescopes and mankind big help from the galaxy cluster MACS J0416.1-2403, is located about four billion light years from us. Weighing in quadrillion Suns, this galactic cluster attracts an incredible amount of light creating a gravitational lens and allowing you to look at Lin, who in fact is behind it. Telescope named James Webb, who is going to be sent into space in 2018, will allow us a better look at this galaxy and provide much more detail about this representative of the first galactic objects in the Universe.
Galactic babysitter
Astronomers are unsure about your knowledge about how galaxies are born. It is generally accepted that all the required substance for its education galaxy is taken from the intergalactic medium. However, there are other assumptions. According to one view, the initial formation of galaxies originates from dense clusters of dark matter, around which begin to accumulate clouds of hydrogen and other gases drawn by gravitational forces. According to another theory, galaxies are formed from matter a specific source. The first option is too long, so it can be checked on the basis of observed data. For a second no one ever watched.
At least until recently. Researchers from the California Institute of technology using the Cosmic Web Imager instrument mounted on the Hale telescope at Palomar Observatory, discovered protogalactical drive (very young, newly formed galaxy, located 10 billion light-years away. It consists of hot gas, whose volume increases due to cold gas, which young galaxy gets from the threads of the so-called Cosmic web, which the galaxy formed. Scientists believe that this is the first direct proof of the existence of the Cosmic web that unites everything in the Universe.
Due to the random location of the two quasars in this region of space, the part of the thread of a web which delivers the gas to start-UPS the galaxy, warmed up, allowing scientists to detect its presence.
"Large Magellanic lawlessness"

The large Magellanic cloud (LMC) and its dwarf companion called the Small Magellanic cloud (SMC) are our nearest neighboring galaxies, situated about 160 000 and 200 000 light-years. Being the largest of the dwarf galaxies located near the Milky Way, they can easily be seen in the southern hemisphere night sky.
Scientists say that with BMO's something strange going on. In the tarantula nebula, which is part of the LMC, astronomers have discovered a veritable incubator of star formation. But as it turned out, the stars here produced is much less than it seems at first glance.
The fact that about 5 percent of 5900 studied large and very large stars located in the LMC, belong to this galaxy. BMO actually stole them, IMO. To such conclusion scientists came after he discovered that these stars go in the opposite direction, compared to the rest. Moreover, the chemical composition of these stars is not like the one that is usually characteristic of the stars of the LMC. These stars contain more heavy elements such as iron and calcium. Scientists believe that this fertility the tarantula nebula, is largely due to the fact that BMO is stealing the stars IMO. In addition, BMO did not scruple to eat up and gas from its outer neighbor. The gas in this case accelerates so much that "ignites the residual gases between the two galaxies.
Galaxy Hercules A

In the center of the galaxy Hercules A (3C 348), a gigantic black hole with a mass of 2.5 billion Suns! It is 1000 times more massive than the black hole of the milky Way and produces two giant jets of plasma, which obscure almost the entire galaxy in which they reside. Moreover, extending to 1.5 million light years, these streams of plasma a dim and other galaxies, including the milky Way, which in diameter 15 times less. The amount of energy it is very difficult to describe. The output impact of the black hole at the centre of radio waves equivalent to one billion times that of our Sun.
This is enough to consider the Hercules And one of the brightest ever observed sources of radio waves. Pink-red beam on the image above is a plasma of atomic particles and magnetic fields, accelerated to relativistic velocities (nearly the speed of light). Volumetric globular clusters at the edges, most likely, talking about many of the early incredible volume of emissions.
Unfortunately, all this is invisible to the naked sight, that is, is only a representation of the artist. The image created on the basis of optical data from the camera Wide Field Camera 3 of the Hubble space telescope, as well as observations of the radio telescope Very Large Array (Corbella Antenna array).
The ancient white dwarfs in the milky Way Our galaxy is very old. She is almost as old as the universe itself. Watching the Central rib of the milky Way, astronomers have discovered a cluster of 70 white dwarfs — dense and compact stars with mass of the Sun (or even more), but it is not the size of the Earth.
Of course, the jumper is a lot more stars, but scientists are interested in a certain group, located in the relative openness of space dust and located about 25 000 light years from Earth.
Now these stars are nothing short of astronomical relics, however, according to scientists, they can tell us about how came our galaxy. It is believed that the age of some of the white dwarfs is more than 12 billion years. In addition, scientists think that these white dwarfs were one of those stars that once "planted" our galaxy. With them began the history of the milky Way. Millions of stars at the end of their life cycle, followed their example, leaving 100 000 light years the matter.
Incredibly bright galaxy

Space telescope WISE space Agency NASA has detected the brightest ever found the galaxy. Its brightness is equivalent to a brightness of more than 300 trillion Suns. Photons galaxy WISE J224607.57-052635.0, in question, had to overcome a 12.5 billion years to leave us your message and give us an idea of how the universe looked in fact at the dawn of its birth.
This galaxy is so bright that it is difficult even to see her full image in the view of the artist, which you can see above. But its brightness it owes not to the stars. Galaxy is so bright thanks to its black hole. It is so massive that even to some extent casts doubt on our understanding of physics.
Scientists are surprised that the early universe could be a haven for such space objects. Usually black holes are limited in their "gluttony", and elapsed time would not be enough so she swallowed the entire galaxy. However, this black hole could somehow overcome the limits of their gluttony" until you reached the weight that it is now. She "ate" so that now frees up (burps) a huge amount of energy that is literally going up in here a giant cocoon of gas, which eventually begins to light up with a dazzling aura.
Tiny galaxy with a giant black hole

Ultra-compact dwarf galaxy M60-UCD1 may change our understanding of black holes and the notion of dwarf galaxies in General. Its size is only 300 light years, which is only 0.2 percent of the size of the milky Way. However, this galaxy is a black hole with a mass equivalent to 21 million Suns. For comparison, the black hole at the center of the milky Way is much larger in size but has a mass of 4 million Suns.
Until recently it was believed that the size of galaxies and the size of black holes linked. However, this opening has questioned this model and suggests that the sizes of these two space objects can be completely disproportionate. And scientists have explanation for this.
The fact is that M60-UCD1 was not always a dwarf galaxy. Astronomers from the University of Utah (USA) believe that once this galaxy was the dwelling place of the 10 billion stars. However, she gets too close to the larger galactic neighbour, which is actually robbed her. As a result, in the galaxy there are only about 140 million stars. This makes M60-UCD1 in the end, one of the smallest galaxies with a massive black hole in the center. However, the same researchers suggests other questions. Whether dwarf galaxies "failed" a large or all of them at some point in their history they became victims of their larger neighbors?
Galaxy EGS8p7

Galaxy EGS8p7 age of 13.2 billion years is so ancient that we can't see her. After the Big Bang, the universe for some time was a hot cluster of protons and electrons. After a cooling period of a particle connected to the neutral hydrogen. The point is that in this case, our telescopes would not be able to detect the early light of the Universe, because he would be in this case had to go through a lot of different distortions.
The emergence of galaxies and other sources of energy in the Universe, they were neionizirovanne the gas dissipated its dense cluster and paved the way for the light. However, this happened already about a billion years later, so EGS8p7 is too far from us so we can see it. And yet astronomers somehow say that could catch a line of the Lyman-alpha galaxy, which is kind of her barcode. It appears when a relatively young star begins to radiate ultraviolet light into the surrounding gas, leaving a heat signature. This signature was detected by the spectrometer MOSFIRE installed in the Observatory Keck in Hawaii.
And yet the line Lyman-alpha galaxy EGS8p7 had to stay hidden early opaque neutral hydrogen. Astronomers are unsure about how light EGS8p7 manage to break through this barrier. There is speculation that radiation from the local star is so powerful that it has neionizirovanne part of the Universe much earlier than other galaxies.
Bonus: Ring Of Andromeda

Our closest neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy (M31) surrounded by a giant ring (or halo). Andromeda itself is twice the milky Way and extends more than 200,000 light-years. Her halo takes up the space of about 2 million light years. It acts as a beacon to astronomers who are looking for quasars. Under the scientific instruments of the space telescope "Hubble" ultra-violet light filed the scientists an idea of around how Andromeda could have formed such a huge ring of gas.
Part of the galactic gas ring is a kind of huge repository of matter for the future and have already formed stars. It is rich and heavy elements produced by a supernova, located on the borders of Andromeda and emitted outside. Unfortunately, the ring itself is invisible to the human eye, but in the night sky it would be 100 times larger than the diameter of the full moon.published
Author: Nicholas Khizhnyak
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: hi-news.ru/space/10-udivitelnyx-galakticheskix-yavlenij.html