999
Hubble discovered the most distant galaxies known previously
An international team of astronomers led by researchers from Yale University and the University of California, pushed the boundaries of space exploration, сообщает NASA. Now we can see one of the earliest state of the universe - the team found galaxies light age of 13 billion years. Such precise data were obtained through the use of bundles of telescopes "Habll», «Спитцер» and a pair of mirror telescopes in the обсерватории Keck in Hawaii. The measurements confirmed that the scientists were able to find the most distant galaxy ever recorded.
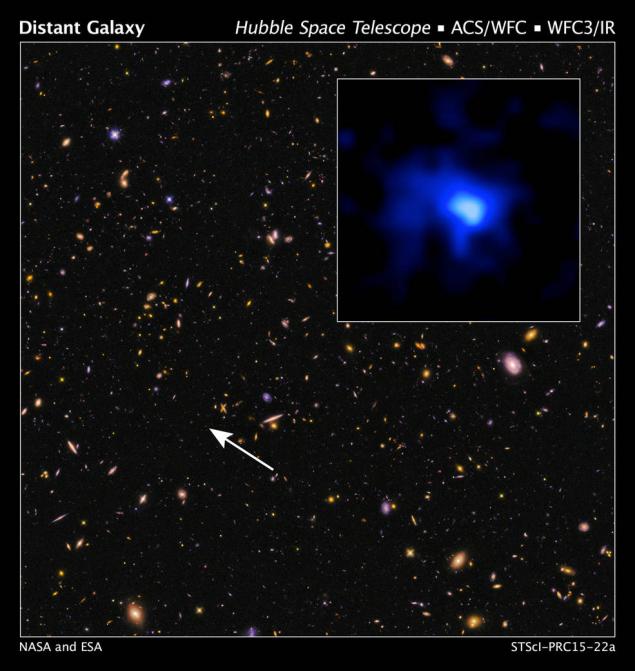

This image was taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, which spectral analysis confirmed the presence of the observed object. Galaxy was also discovered and Spitzer. Keck Observatory helped to define the size of the spectroscopic красного offset (r - 7, 7), which is also a new record observations. Found a light source is the most distant known galaxy and the brightest and most massive object of this type and age. The galaxy whose light has been discovered by scientists, there were more than 13 billion years ago, during the age of the universe at 13.8 billion years. Insert in the photo is a combination of light in the visible and infrared spectrum. / NASA, ESA, P. Oesch (Yale U.) I>
Galaxy EGS-zs8-1 was found in the analysis of specific colors in an image obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer and is one of the brightest and most massive objects of the early universe. "Observed the galaxy mass is already 15% more modern of the Milky Way," says Pascal Oysh, lead researcher from Yale University, Connecticut. "It took just 670 million years, when the Universe was still young." New data on distant galaxies enabled astronomers to determine that EGS-zs8-1 was on the stage is very active star formation about 80 times faster than the processes taking place in today's Milky Way (our galaxy to figure equals one star per year).
Today, such precise data on the distance from us there are only a handful of galaxies of the early Universe. "Each new proof (of the existence of such objects) adds another piece to the puzzle of how galaxies formed the first generation of our universe," says Peter van Dokkum, another researcher from Yale University. "Only the most powerful telescopes sensitive enough to look that far." This discovery was only possible thanks to the relatively new spectrometer «MOSFIRE» Keck Observatory, which allowed astronomers to study several galaxies at the same time.
New data obtained by the Hubble, Spitzer and the Keck Observatory, give rise to a number of questions. They confirm that massive galaxies existed in the early Universe, but their physical properties are very different from what we see today. Now, thanks to the peculiar world of early galaxies, the data which were obtained by Spitzer, astronomers have strong evidence that they held very rapid formation of massive young stars, the building blocks of which is the primary gas.
These observations also highlight the very interesting discovery, detailed studies are planned with the commissioning of the телескопа James Webb in 2018. The new equipment will push the boundaries of the observable universe even further and allow for a more detailed spectral analysis of galaxy EGS-zs8-1. So far, Spitzer astronomers provide information to better understand the properties of the gas of an open object. "Our current research shows that the James Webb telescope, we will be much easier to determine the distance to these galaxies," said a researcher at the University of California at Santa Cruz. "The aim of future measurements Webb will ensure a more complete picture of galaxy formation in the early days of the universe.»
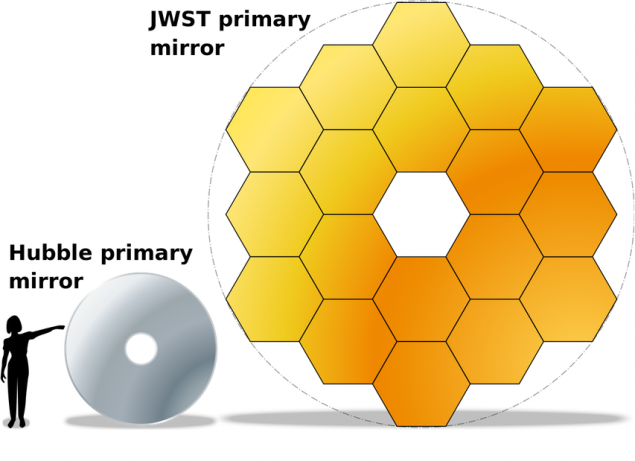
is sufficiently well known and clear comparison of the size of the Hubble telescope mirrors and James Webb. I>
In the meantime, "workhorse" Hubble astronomers is that for space exploration simultaneously use NASA , European Space Agency (ESA), a number of institutions and scientific associations. Managed by the Hubble from the Mission Control Center at NASA's Goddard .
Source: geektimes.ru/post/250058/

This image was taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, which spectral analysis confirmed the presence of the observed object. Galaxy was also discovered and Spitzer. Keck Observatory helped to define the size of the spectroscopic красного offset (r - 7, 7), which is also a new record observations. Found a light source is the most distant known galaxy and the brightest and most massive object of this type and age. The galaxy whose light has been discovered by scientists, there were more than 13 billion years ago, during the age of the universe at 13.8 billion years. Insert in the photo is a combination of light in the visible and infrared spectrum. / NASA, ESA, P. Oesch (Yale U.) I>
Galaxy EGS-zs8-1 was found in the analysis of specific colors in an image obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer and is one of the brightest and most massive objects of the early universe. "Observed the galaxy mass is already 15% more modern of the Milky Way," says Pascal Oysh, lead researcher from Yale University, Connecticut. "It took just 670 million years, when the Universe was still young." New data on distant galaxies enabled astronomers to determine that EGS-zs8-1 was on the stage is very active star formation about 80 times faster than the processes taking place in today's Milky Way (our galaxy to figure equals one star per year).
Today, such precise data on the distance from us there are only a handful of galaxies of the early Universe. "Each new proof (of the existence of such objects) adds another piece to the puzzle of how galaxies formed the first generation of our universe," says Peter van Dokkum, another researcher from Yale University. "Only the most powerful telescopes sensitive enough to look that far." This discovery was only possible thanks to the relatively new spectrometer «MOSFIRE» Keck Observatory, which allowed astronomers to study several galaxies at the same time.
New data obtained by the Hubble, Spitzer and the Keck Observatory, give rise to a number of questions. They confirm that massive galaxies existed in the early Universe, but their physical properties are very different from what we see today. Now, thanks to the peculiar world of early galaxies, the data which were obtained by Spitzer, astronomers have strong evidence that they held very rapid formation of massive young stars, the building blocks of which is the primary gas.
These observations also highlight the very interesting discovery, detailed studies are planned with the commissioning of the телескопа James Webb in 2018. The new equipment will push the boundaries of the observable universe even further and allow for a more detailed spectral analysis of galaxy EGS-zs8-1. So far, Spitzer astronomers provide information to better understand the properties of the gas of an open object. "Our current research shows that the James Webb telescope, we will be much easier to determine the distance to these galaxies," said a researcher at the University of California at Santa Cruz. "The aim of future measurements Webb will ensure a more complete picture of galaxy formation in the early days of the universe.»

is sufficiently well known and clear comparison of the size of the Hubble telescope mirrors and James Webb. I>
In the meantime, "workhorse" Hubble astronomers is that for space exploration simultaneously use NASA , European Space Agency (ESA), a number of institutions and scientific associations. Managed by the Hubble from the Mission Control Center at NASA's Goddard .
Source: geektimes.ru/post/250058/
Why not come out Windows 9? Joe Belfiore hinted at an answer using a binary code on his T-shirt
Tesla received 38,000 pre-orders for home battery system PowerWall