697
Little scientific data on galaxies
First post hurt do not hurt))
* Galaxy - is a giant cluster of stars, gas and dust held together by the force of gravity.
* Galaxy revolve around a central point.
* In the universe of billions of galaxies, each one to tens of billions of stars.
* Galaxy in groups, forming clusters of hundreds or thousands of galaxies.

10 ph will
The diversity of the observed shapes of galaxies has caused astronomers desire to unite similar objects in the galaxy and defeat a series of classes on their appearance.
Galaxies are divided into several main classes: elliptic (E), spiral (S) lenticular (S0) and irregular (Irr).
E-galaxies appear as elliptical or oval spots are not too stretched, within which the brightness gradually decreases with distance from the center.

The spiral (S) galaxies stands central concentration of stars - "bulge" and extended stellar disk, which (unless he turned to the viewer, "edge") observed the spiral arms.
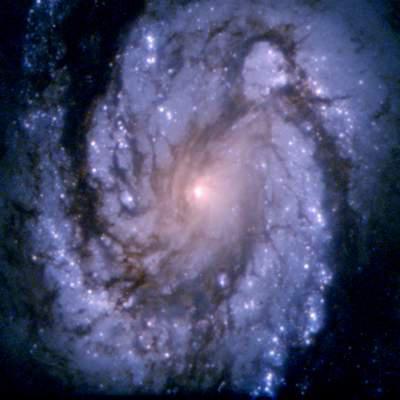

Between the types E and S is the type of lenticular galaxies (S0). As and S-galaxies, they have a stellar disk and bulge, but they have no spiral arms (although the bar can be). It is believed that this galaxy, which in the past was the spiral, but by now almost completely "lost" or used up interstellar gas, and with it - and the ability to form a bright spiral arms.

Irr-galaxies do not have an ordered structure, they do not have spiral arms, even though they contain within themselves the bright areas of different sizes (usually a region of intense star formation). Bulge in these galaxies are very small or absent.

To the naked eye is available in all three of the galaxy - Andromeda in the northern hemisphere and the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds - in the south. Magellanic Clouds are the closest galaxies to us: the distance to them approx. 150 thousand. St. let.Galaktika Andromeda - it's the closest to our own Milky Way from the giant galaxies. Most likely our Galaxy looks about the same as the Andromeda Galaxy. These two galaxies dominate the Local Group of galaxies. Hundreds of billions of stars that make up the galaxy Andromeda, together give a visible diffuse glow. Some stars in the image are actually stars in our galaxy located much closer to the remote object.

Large Magellanic Cloud
Explanation: Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) - it is the brightest galaxy visible from our own galaxy - the Milky Way. Watch LMC may advantageously be in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. LMC is one of eleven known dwarf galaxies today, orbiting our galaxy, and is the second distance from our galaxy after the Small Magellanic Cloud. LMC is an irregular galaxy, consisting of a field of old red stars, clouds of younger blue stars and a bright red star forming region visible at the top of the image called the Tarantula Nebula.
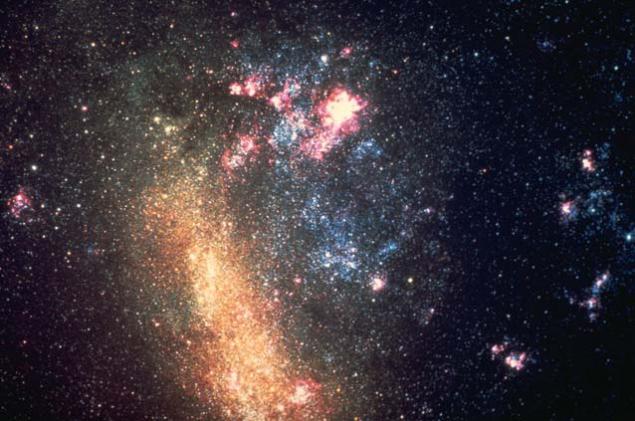

Small Magellanic Cloud

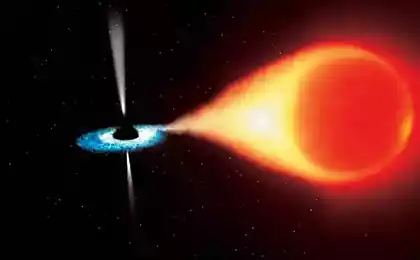
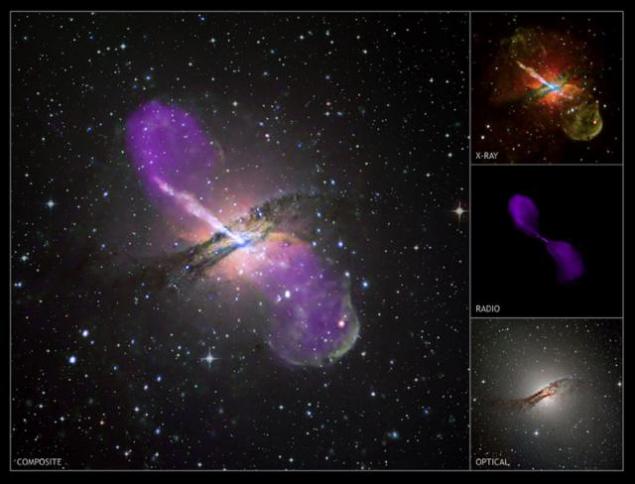
The giant elliptical galaxy Centaurus A, located at a distance of 11 million light-years - is the closest active galaxy to Earth. In visible light, the central region of Centaurus A - is a jumble of gas, dust and stars, however, and X-ray and radio telescopes show a wonderful stream of high-energy particles ejected from the nucleus of the galaxy. The energy source for this cosmic particle accelerator is a black hole whose mass is nearly ten million times the mass of the sun. On the X-ray image is visible as a bright spot in the center of the galaxy.

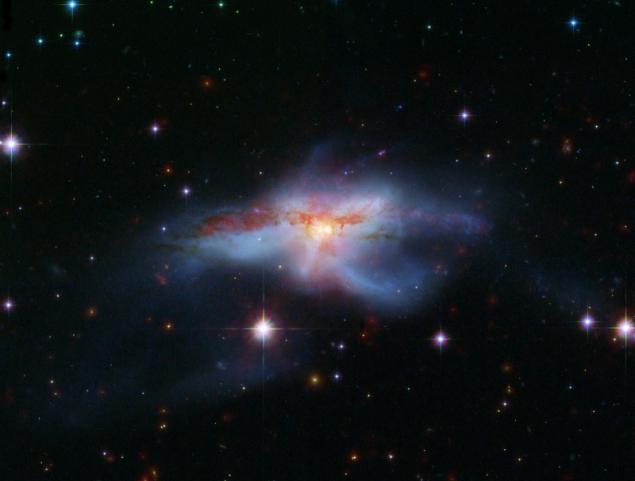
NGC 6240 is a rare opportunity to see the final stages of a cosmic catastrophe. The grand collision of two galaxies occurs only 400 million light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. Merging galaxies are one of the brightest sources in the infrared sky. They spew distorted tidal tails of stars, gas and dust in which there are powerful bursts of star formation. Two supermassive black holes that were formerly in the nuclei of galaxies, have in the future to merge into a single, more massive black hole. After the collision, there will be only one giant galaxy.
Dobavleno1 in [mergetime] 1273150046 [/ mergetime]
Well, that's all,

Source:
* Galaxy - is a giant cluster of stars, gas and dust held together by the force of gravity.
* Galaxy revolve around a central point.
* In the universe of billions of galaxies, each one to tens of billions of stars.
* Galaxy in groups, forming clusters of hundreds or thousands of galaxies.

10 ph will
The diversity of the observed shapes of galaxies has caused astronomers desire to unite similar objects in the galaxy and defeat a series of classes on their appearance.
Galaxies are divided into several main classes: elliptic (E), spiral (S) lenticular (S0) and irregular (Irr).
E-galaxies appear as elliptical or oval spots are not too stretched, within which the brightness gradually decreases with distance from the center.

The spiral (S) galaxies stands central concentration of stars - "bulge" and extended stellar disk, which (unless he turned to the viewer, "edge") observed the spiral arms.

Between the types E and S is the type of lenticular galaxies (S0). As and S-galaxies, they have a stellar disk and bulge, but they have no spiral arms (although the bar can be). It is believed that this galaxy, which in the past was the spiral, but by now almost completely "lost" or used up interstellar gas, and with it - and the ability to form a bright spiral arms.

Irr-galaxies do not have an ordered structure, they do not have spiral arms, even though they contain within themselves the bright areas of different sizes (usually a region of intense star formation). Bulge in these galaxies are very small or absent.

To the naked eye is available in all three of the galaxy - Andromeda in the northern hemisphere and the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds - in the south. Magellanic Clouds are the closest galaxies to us: the distance to them approx. 150 thousand. St. let.Galaktika Andromeda - it's the closest to our own Milky Way from the giant galaxies. Most likely our Galaxy looks about the same as the Andromeda Galaxy. These two galaxies dominate the Local Group of galaxies. Hundreds of billions of stars that make up the galaxy Andromeda, together give a visible diffuse glow. Some stars in the image are actually stars in our galaxy located much closer to the remote object.

Large Magellanic Cloud
Explanation: Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) - it is the brightest galaxy visible from our own galaxy - the Milky Way. Watch LMC may advantageously be in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. LMC is one of eleven known dwarf galaxies today, orbiting our galaxy, and is the second distance from our galaxy after the Small Magellanic Cloud. LMC is an irregular galaxy, consisting of a field of old red stars, clouds of younger blue stars and a bright red star forming region visible at the top of the image called the Tarantula Nebula.

Small Magellanic Cloud

The giant elliptical galaxy Centaurus A, located at a distance of 11 million light-years - is the closest active galaxy to Earth. In visible light, the central region of Centaurus A - is a jumble of gas, dust and stars, however, and X-ray and radio telescopes show a wonderful stream of high-energy particles ejected from the nucleus of the galaxy. The energy source for this cosmic particle accelerator is a black hole whose mass is nearly ten million times the mass of the sun. On the X-ray image is visible as a bright spot in the center of the galaxy.

NGC 6240 is a rare opportunity to see the final stages of a cosmic catastrophe. The grand collision of two galaxies occurs only 400 million light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. Merging galaxies are one of the brightest sources in the infrared sky. They spew distorted tidal tails of stars, gas and dust in which there are powerful bursts of star formation. Two supermassive black holes that were formerly in the nuclei of galaxies, have in the future to merge into a single, more massive black hole. After the collision, there will be only one giant galaxy.
Dobavleno1 in [mergetime] 1273150046 [/ mergetime]
Well, that's all,

Source: