1741
Theory two singularities in black holes
On the evolution of galaxies to date, little is known. Under evolution is meant a change in its characteristics (color, spectrum, chemical composition, velocity) in time. Models of the evolution of galaxies and agree that their changes affect not only internal processes, but also the external environment. For example, the merger of galaxies:
Figure 1: Merging Whirlpool Galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici with satellite galaxies i>
In the photograph the process of merging spiral galaxy with a satellite galaxy located at the end of one of her arms. The center of mass of galaxies are mutually attracted, but their motion vectors are not aligned at each time, and the directions lying in the same plane, is rotation around a common center of mass, the gravitational interaction between two objects is the process in the plane, as shown by the equation for two gravitating objects:
where r ^ 2 tells about the process in the plane, there is a product of the two metrics.
According to general relativity, gravitational interactions caused not force interaction of bodies and fields located in space-time, and the deformation of the space-time in the presence of mass-energy. This strain has a definite place in space-time and is manifested in the form of the galactic arm. Galactic sleeve characterized by enhanced star formation, because the matter inside the sleeves have more opportunities to contract, compared to the matter in space-time, which appear only own around deformation of matter in the space between the arms, for example. This is a manifestation of the tidal force for that part of the sleeve, which is stretched in the direction of the satellite galaxies. Manifestation of all arms of the Galaxy is also associated with the processes of deformation of space-time, and their origin lies in the central supermassive black hole. As is known, gravity occurs only in the interaction and the second object is needed to induce a curvature in the form of sleeves. This object is located within the same supermassive black hole, the first. During the event horizon is not a singularity, but two. Sleeve is gravitational waves, which emits a double system. The figure below - model merging two strongly magnetized stars:
![]()
Fig. 2: Computer model of the merger of two highly magnetized neutron stars (DANIEL PRICE, UNIVERSITY OF EXETER, STEPHAN ROSSWOG INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY, BREMEN) i>
Such gravitational waves, according to the general theory of relativity, emits any dual system, and their intensity depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. Sleeves in spiral galaxies look similar to:
Fig. 3: The spiral galaxy M74 in the constellation of Pisces i>
In the evolution of galaxies often merge, and merge their central black holes, they have a common event horizon and the singularity inside form a binary system. This applies to spiral galaxies. There are several types of galaxies: elliptical, lenticular, spiral and irregular.
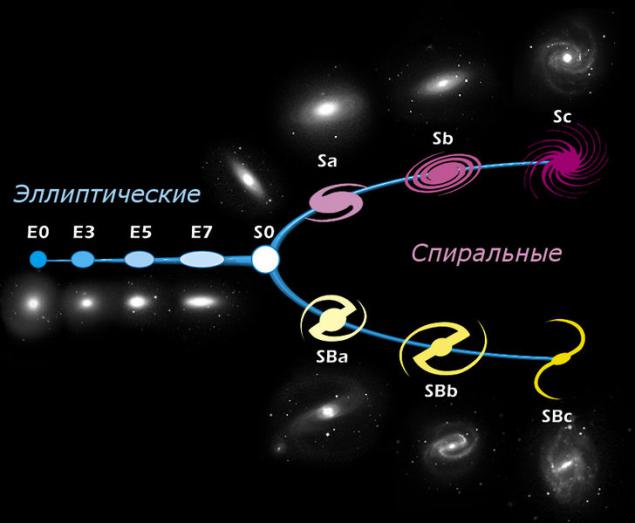
Fig. 4: The Hubble Tuning Fork i>
Irregular galaxies have no rotational symmetry and the active nucleus is the initial stage of the evolution of galaxies. Elliptical galaxies are ellipsoidal structure and decreases from the center to the edges of the luminosity, the second phase of evolution. Lenticular - an intermediate stage between elliptical and spiral, a disk galaxy, it is considered that they have spent or lost their stocks of dust, but the disk is its significant reserves, the sleeves are absent because of such galaxies in the black hole singularity one. After the merger of the two lenticular galaxies formed spiral galaxies, star formation processes are using the galactic arms - gravitational waves from the center, where there is a system of singular. There is evidence the Milky Way's collision with another galaxy in the past - it was possible to detect a ring consisting of hundreds of millions of stars that are extremely old and, according to some, are different in chemical composition of stars in our galaxy. The diameter of the ring of St. 120.000. years. The diameter of the Milky Way without a ring - 100,000 St. years.
Fig. 5: Ring around the Milky Way i>
According to the law of recession of galaxies (Hubble, Linda), implies the accelerated expansion of the universe in the distant future, all galaxies will be at such a distance from each other, and will be removed with the acceleration of that light will lose the opportunity to overcome the distance from one galaxy to another. And the recession is not simply removing the galaxies apart, does not come from a point location which may establish and, according to the general theory of relativity, the recession is the dynamic change of the space-time.
Galaxies are by some oscillatory processes, they rotate around the center, and one day when every galaxy will cease to influence external factors will be damped oscillatory processes. Will stabilize the system singularities, by the time of the galaxy will be only the central supermassive black hole. All galaxies will be very far from each other, and are stabilized to varying degrees, depending on the individual characteristics of each galaxy, these may include factors weight, dimensions, mass of the central black hole, the rotation speed of the black hole, matter and sleeves. The rotational speed of the singularity is also associated with the speed of rotation of the sleeves, but for the event horizon there is a high degree of curvature of space-time in which time is different, therefore, a system of singular rotates with unknown speed inside the black hole, and with the speed of the galactic arms, on our sites observation. In a space-time system rotates faster than one revolution in 250 million years, as the rotating sleeve (according to various sources from 225 to 250, is the rotational speed of corotation zone of our galaxy). The lifetime of the binary system of singularities inside the spiral galaxies also depends on the initial structure of the galaxy and is relative elapsed time inside and outside the event horizon will differ significantly. The process of rotation of a black hole is not eternal, once the singularity will fall on each other. When two neutron stars collide, energy is released more than in the supernova explosion. A collision of two supermassive singularities rationally assumed energy release comparable to the Big Bang, in a completely black space.
© abbr>
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/217311/
Figure 1: Merging Whirlpool Galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici with satellite galaxies i>
In the photograph the process of merging spiral galaxy with a satellite galaxy located at the end of one of her arms. The center of mass of galaxies are mutually attracted, but their motion vectors are not aligned at each time, and the directions lying in the same plane, is rotation around a common center of mass, the gravitational interaction between two objects is the process in the plane, as shown by the equation for two gravitating objects:
where r ^ 2 tells about the process in the plane, there is a product of the two metrics.
According to general relativity, gravitational interactions caused not force interaction of bodies and fields located in space-time, and the deformation of the space-time in the presence of mass-energy. This strain has a definite place in space-time and is manifested in the form of the galactic arm. Galactic sleeve characterized by enhanced star formation, because the matter inside the sleeves have more opportunities to contract, compared to the matter in space-time, which appear only own around deformation of matter in the space between the arms, for example. This is a manifestation of the tidal force for that part of the sleeve, which is stretched in the direction of the satellite galaxies. Manifestation of all arms of the Galaxy is also associated with the processes of deformation of space-time, and their origin lies in the central supermassive black hole. As is known, gravity occurs only in the interaction and the second object is needed to induce a curvature in the form of sleeves. This object is located within the same supermassive black hole, the first. During the event horizon is not a singularity, but two. Sleeve is gravitational waves, which emits a double system. The figure below - model merging two strongly magnetized stars:
Fig. 2: Computer model of the merger of two highly magnetized neutron stars (DANIEL PRICE, UNIVERSITY OF EXETER, STEPHAN ROSSWOG INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY, BREMEN) i>
Such gravitational waves, according to the general theory of relativity, emits any dual system, and their intensity depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. Sleeves in spiral galaxies look similar to:
Fig. 3: The spiral galaxy M74 in the constellation of Pisces i>
In the evolution of galaxies often merge, and merge their central black holes, they have a common event horizon and the singularity inside form a binary system. This applies to spiral galaxies. There are several types of galaxies: elliptical, lenticular, spiral and irregular.

Fig. 4: The Hubble Tuning Fork i>
Irregular galaxies have no rotational symmetry and the active nucleus is the initial stage of the evolution of galaxies. Elliptical galaxies are ellipsoidal structure and decreases from the center to the edges of the luminosity, the second phase of evolution. Lenticular - an intermediate stage between elliptical and spiral, a disk galaxy, it is considered that they have spent or lost their stocks of dust, but the disk is its significant reserves, the sleeves are absent because of such galaxies in the black hole singularity one. After the merger of the two lenticular galaxies formed spiral galaxies, star formation processes are using the galactic arms - gravitational waves from the center, where there is a system of singular. There is evidence the Milky Way's collision with another galaxy in the past - it was possible to detect a ring consisting of hundreds of millions of stars that are extremely old and, according to some, are different in chemical composition of stars in our galaxy. The diameter of the ring of St. 120.000. years. The diameter of the Milky Way without a ring - 100,000 St. years.
Fig. 5: Ring around the Milky Way i>
According to the law of recession of galaxies (Hubble, Linda), implies the accelerated expansion of the universe in the distant future, all galaxies will be at such a distance from each other, and will be removed with the acceleration of that light will lose the opportunity to overcome the distance from one galaxy to another. And the recession is not simply removing the galaxies apart, does not come from a point location which may establish and, according to the general theory of relativity, the recession is the dynamic change of the space-time.
Galaxies are by some oscillatory processes, they rotate around the center, and one day when every galaxy will cease to influence external factors will be damped oscillatory processes. Will stabilize the system singularities, by the time of the galaxy will be only the central supermassive black hole. All galaxies will be very far from each other, and are stabilized to varying degrees, depending on the individual characteristics of each galaxy, these may include factors weight, dimensions, mass of the central black hole, the rotation speed of the black hole, matter and sleeves. The rotational speed of the singularity is also associated with the speed of rotation of the sleeves, but for the event horizon there is a high degree of curvature of space-time in which time is different, therefore, a system of singular rotates with unknown speed inside the black hole, and with the speed of the galactic arms, on our sites observation. In a space-time system rotates faster than one revolution in 250 million years, as the rotating sleeve (according to various sources from 225 to 250, is the rotational speed of corotation zone of our galaxy). The lifetime of the binary system of singularities inside the spiral galaxies also depends on the initial structure of the galaxy and is relative elapsed time inside and outside the event horizon will differ significantly. The process of rotation of a black hole is not eternal, once the singularity will fall on each other. When two neutron stars collide, energy is released more than in the supernova explosion. A collision of two supermassive singularities rationally assumed energy release comparable to the Big Bang, in a completely black space.
© abbr>
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/217311/