1075
Types of metal anchors and their applications
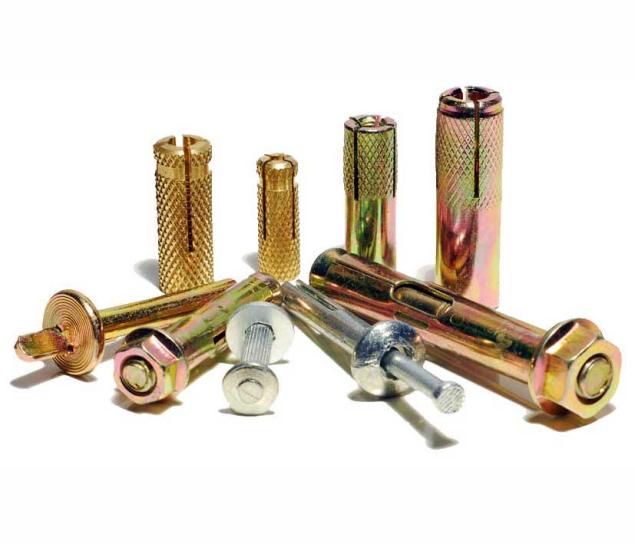

Metal anchors are an important element in construction and engineering systems, allowing you to fix and install structures safely and securely. They can be used in various areas such as walls, ceilings, columns and more. Metal anchors can withstand high loads, making them very popular in the construction industry.
Definition and working principle
Metal anchors are components used to fix and install structures in buildings and engineering systems. They serve to strengthen and protect structures, increasing their reliability and safety.
The principle of operation of metal anchors is based on the principle of friction resistance. They are installed in holes in concrete or other materials and then secured to prevent movement of the structure. Metal anchors can withstand high loads and further strengthen the structure, making them ideal for the installation and fixing of large structures.

Types of metal anchors and their application
Metal anchors can be divided into three main types: stud anchors, conical anchors and straight anchors.
- Stud anchors are used for installation in hard materials such as concrete or brick.
- Conical anchors are used for installation in wooden surfaces.
- Straight anchors are used to install into holes in metal surfaces.
Materials and parameters of metal anchors
Metal anchors can be made from various materials such as steel, aluminium, stainless steel and others. The choice of material depends on the conditions in which the installation and use of the anchor will take place.
In addition, an important parameter of metal anchors is their length, diameter and shape. These parameters must be matched to the installation conditions to ensure a secure fit. You should also consider the maximum load that the anchor must withstand.
Certain types of metal anchors, such as stud or screw anchors, also require special surface treatment to ensure good contact with the surface and maximum fastening effect.

Few people will remember why the Soviet man beat the doors with dermatine
Reverse osmosis water systems: types, principles of operation, advantages and technical difficulties























