686
Glass frog
Glass frog (lat. Centrolenidae) is a family of tailless amphibians consists of 12 genera including 60 species.
The first who discovered and described these amphibians was a Spanish zoologist Marcos Jimenez de La Espada. In 50-70–ies of the 20th century has been described frogs that live in Central America (Costa Rica and Panama), a bit later in the Andes in Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Peru. Some species live in areas of the rivers Amazon and Orinoco.
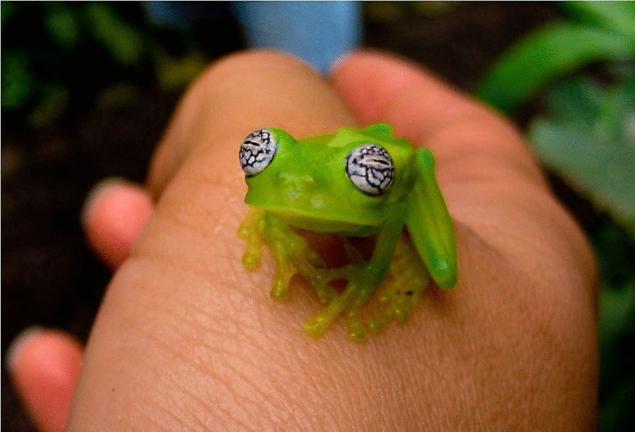

According to scientists, a glass frog originally lived only in the northwestern part of South America, and then greatly expanded the area of their habitat. Glass frogs live in trees in tropical and semi-deciduous forests. Closer to the water they move only during the breeding season.
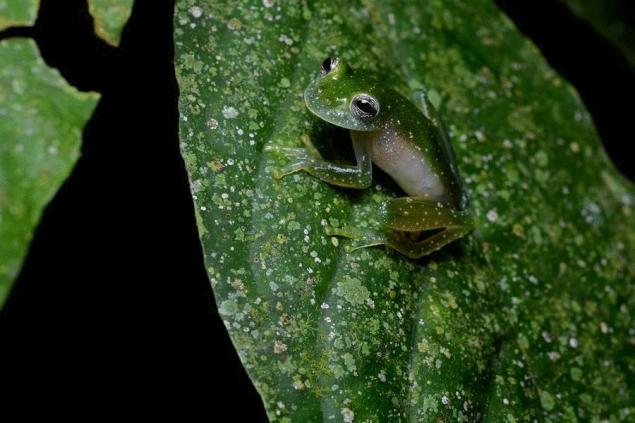

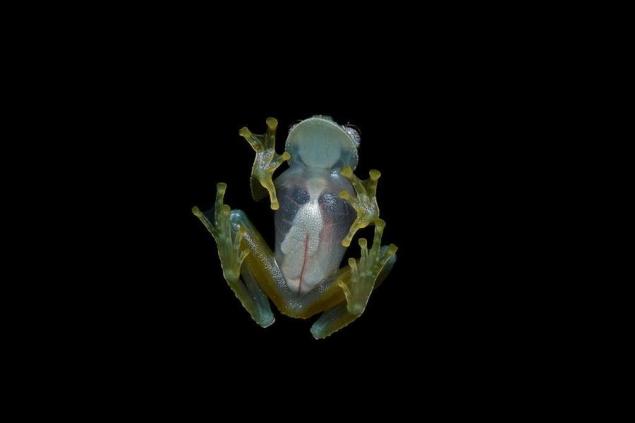
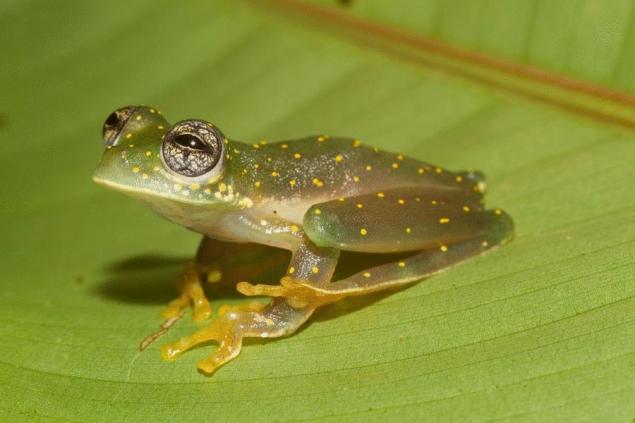
The skin on the belly of this frog is illuminated and through it you can see the internal organs of a frog – the liver, heart, gastrointestinal tract, and sometimes even the eggs of females. For this reason, the frog and got the name of glass. If you don't count the transparent skin on the belly, the frog looks quite normal.
Externally, the glass frog are somewhat similar to a tree frog from the family tree frogs, but it is distinguished by the eye. The arboreal frog eyes looking in different directions, and the glass forward. In addition, some species of glass frogs on the heel is a kind of cartilage. The size of glass frogs are small, from 3 to 7.5 centimeters. Certain parts of the body, such as legs, are almost completely transparent. Frogs lay their eggs on the leaves of shrubs and trees located above flowing rivers and streams.

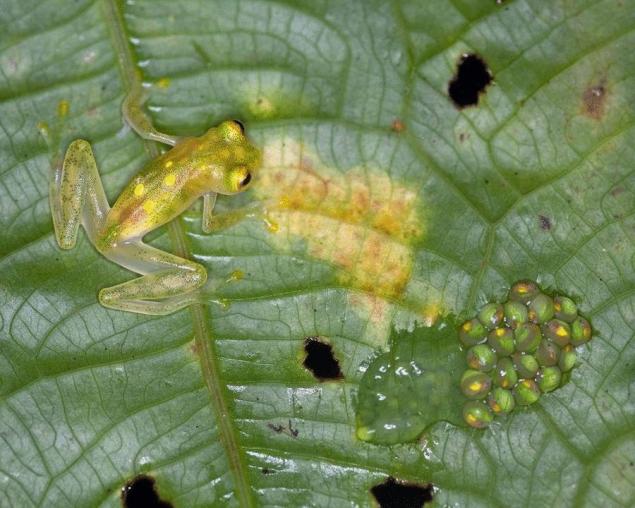
One species lays eggs on rocks near waterfalls. After maturation and birth, the tadpoles have to jump into the water. Strong current, into the arms which they fall, is not a serious obstacle. Thanks to a powerful tail and lower fins they can easily cope with it.

The choice of such an unusual place to lay their eggs brings its advantages. Glass frogs thus increase the chances of survival, as to her calf predatory fish will not reach. Although, when the tadpoles fall into the water, they can also become easy prey for fish.

Source: /users/104
The first who discovered and described these amphibians was a Spanish zoologist Marcos Jimenez de La Espada. In 50-70–ies of the 20th century has been described frogs that live in Central America (Costa Rica and Panama), a bit later in the Andes in Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Peru. Some species live in areas of the rivers Amazon and Orinoco.

According to scientists, a glass frog originally lived only in the northwestern part of South America, and then greatly expanded the area of their habitat. Glass frogs live in trees in tropical and semi-deciduous forests. Closer to the water they move only during the breeding season.

The skin on the belly of this frog is illuminated and through it you can see the internal organs of a frog – the liver, heart, gastrointestinal tract, and sometimes even the eggs of females. For this reason, the frog and got the name of glass. If you don't count the transparent skin on the belly, the frog looks quite normal.
Externally, the glass frog are somewhat similar to a tree frog from the family tree frogs, but it is distinguished by the eye. The arboreal frog eyes looking in different directions, and the glass forward. In addition, some species of glass frogs on the heel is a kind of cartilage. The size of glass frogs are small, from 3 to 7.5 centimeters. Certain parts of the body, such as legs, are almost completely transparent. Frogs lay their eggs on the leaves of shrubs and trees located above flowing rivers and streams.

One species lays eggs on rocks near waterfalls. After maturation and birth, the tadpoles have to jump into the water. Strong current, into the arms which they fall, is not a serious obstacle. Thanks to a powerful tail and lower fins they can easily cope with it.

The choice of such an unusual place to lay their eggs brings its advantages. Glass frogs thus increase the chances of survival, as to her calf predatory fish will not reach. Although, when the tadpoles fall into the water, they can also become easy prey for fish.

Source: /users/104