431
The researchers space and time like a superfluid
In 1905 Einstein special theory of relativity first suggested that space and time can be linked. The term "space-time" was coined three years later by mathematician Hermann Minkowski.
According to the tenets of Einstein, the speed of light (300 million meters per second) is the same for all observers in all systems moving with constant velocity will experience the same physical laws.
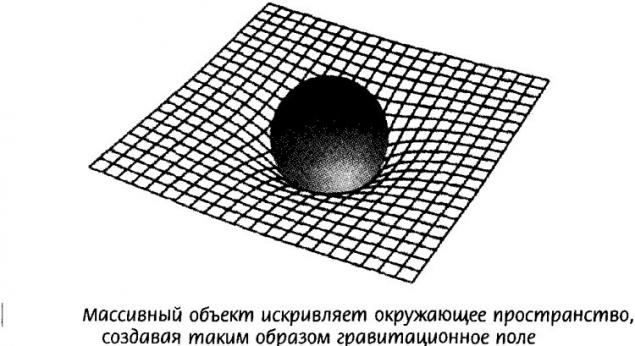
But if we move in space or to be in the gravitational field of a large mass, the time in the system will flow at a slower speed due to the deformation of space-time.
The idea that space-time behaves like a liquid, not an entirely new theory "superfluid vacuum" (SVT) was proposed half a century ago.
But researchers Stefano Liberati, Professor International school for advanced studies (SISSA) and Luca Maccione, researcher at the Ludwig-Maximilian University in Munich, first wondered about the viscosity of the liquid.
One of the biggest challenges in understanding the Universe is figuring out how things move in space. For example — wave propagates through the water, using it as a "medium" through which it can move. In General, energy transfer requires a medium — for example, the sound passes through air or heat through metal.
But as electromagnetic waves, photons, etc. move in space, where it is thought there is nothing?
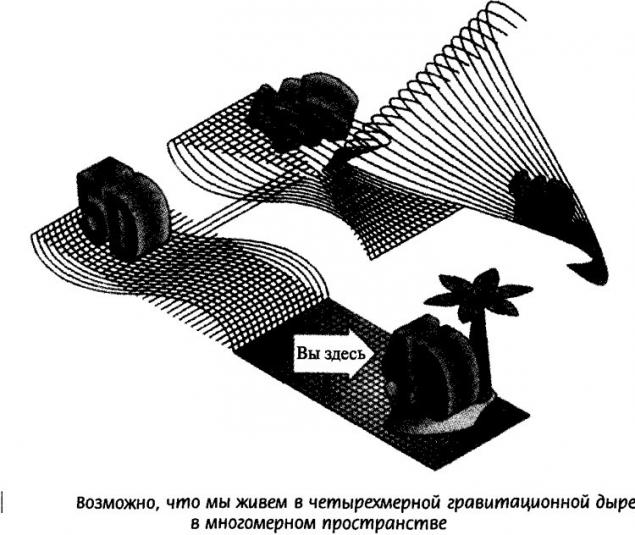
Consider how we perceive water – it seems to us that the fluid flows, but in reality it is the movement of the mass of H2O molecules. Space-time, say the researchers, consists of its own H20 molecules — though they are unknown.
Liberati and Maccione believe that the most likely model for quantum gravity is the model of a superfluid space – fluid with zero viscosity acting as a single unit. The key point of evidence for their theory revolves around the four fundamental forces of the Universe — electromagnetism, weak interaction, strong interaction and gravity.

A superfluid is a fluid that can flow endlessly without losing energy. This is the phase of matter that move liquids or gases when they are cooled to certain temperatures near absolute zero. However, their atoms begin to occupy the same "quantum state".
This means that the atoms lose their individual properties, and behave like single super-atom. Helium, for example, exhibits superfluid properties at 2 Kelvin (about -271,15 C).
From superfluid liquids have several unique properties. They can, for example, to climb the walls and open the vessel to escape from it.
It is impossible to heat — they are extremely good heat transfer – superfluid liquid when heated, will simply evaporate.
Scientists also predict other weak dissipative effects, which could be identified in future astrophysical observations.
Source: brainswork.ru
According to the tenets of Einstein, the speed of light (300 million meters per second) is the same for all observers in all systems moving with constant velocity will experience the same physical laws.
But if we move in space or to be in the gravitational field of a large mass, the time in the system will flow at a slower speed due to the deformation of space-time.
The idea that space-time behaves like a liquid, not an entirely new theory "superfluid vacuum" (SVT) was proposed half a century ago.
But researchers Stefano Liberati, Professor International school for advanced studies (SISSA) and Luca Maccione, researcher at the Ludwig-Maximilian University in Munich, first wondered about the viscosity of the liquid.
One of the biggest challenges in understanding the Universe is figuring out how things move in space. For example — wave propagates through the water, using it as a "medium" through which it can move. In General, energy transfer requires a medium — for example, the sound passes through air or heat through metal.

But as electromagnetic waves, photons, etc. move in space, where it is thought there is nothing?
Consider how we perceive water – it seems to us that the fluid flows, but in reality it is the movement of the mass of H2O molecules. Space-time, say the researchers, consists of its own H20 molecules — though they are unknown.
Liberati and Maccione believe that the most likely model for quantum gravity is the model of a superfluid space – fluid with zero viscosity acting as a single unit. The key point of evidence for their theory revolves around the four fundamental forces of the Universe — electromagnetism, weak interaction, strong interaction and gravity.

A superfluid is a fluid that can flow endlessly without losing energy. This is the phase of matter that move liquids or gases when they are cooled to certain temperatures near absolute zero. However, their atoms begin to occupy the same "quantum state".
This means that the atoms lose their individual properties, and behave like single super-atom. Helium, for example, exhibits superfluid properties at 2 Kelvin (about -271,15 C).
From superfluid liquids have several unique properties. They can, for example, to climb the walls and open the vessel to escape from it.
It is impossible to heat — they are extremely good heat transfer – superfluid liquid when heated, will simply evaporate.
Scientists also predict other weak dissipative effects, which could be identified in future astrophysical observations.
Source: brainswork.ru
Scientists Monday is not the most difficult day of the week
The A3 E-Tron – rechargeable concept hybrid from Audi