440
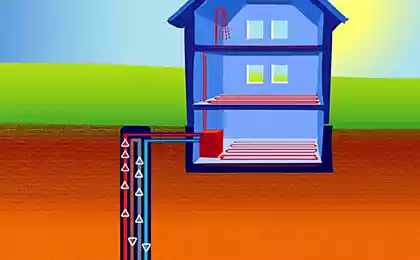
Buried pipe allows to save on heating and cooling the house
The surface layer of the soil of the Earth is a natural heat accumulator. The main source of thermal energy in the upper layers of the Earth — solar radiation. At a depth of about 3 m and more (below freezing) the soil temperature during the year does not change and is approximately equal to the average annual outside air temperature. At a depth of 1.5-3.2 m in winter the temperature ranges from +5 to + 7 ° C and in summer from +10 to + 12 ° C. This heat can in the winter to prevent freezing house, and in the summer not to let it overheat above 18-20 ° C
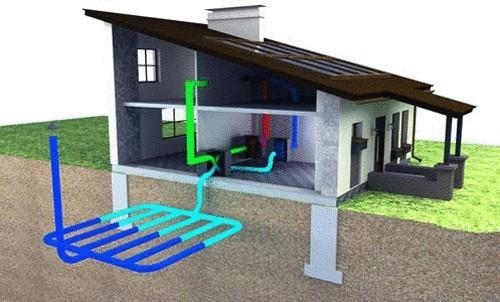
The simplest way to use the earth's heat is the use of a soil heat exchanger (PHE). Underground, below the level of soil freezing, fit the air duct system, which perform the function of a heat exchanger between the earth and the air which passes through these ducts. In the winter the incoming cold air that enters the house and passes through the pipes is heated and in summer cooled. When correct placement of the ducts can be selected from the soil a considerable amount of heat energy with a small electric power consumption.
You can use an heat exchanger "pipe in pipe". Internal ducts made of stainless steel appear here as recuperators.
Cooling in the summer
In warm season soil heat exchanger provides cooling of the supply air. Ambient air is drawn through the air intake device in the subterranean heat exchanger where it is cooled by the ground. Then cooled air is supplied by ducts in the supply and installation of exhaust, which in the summer is the heat exchanger installed summer insert. Thanks to this solution, a decrease in the temperature in the building, improving the microclimate in the house, reduced the cost of electricity for air conditioning.
The work in the offseason
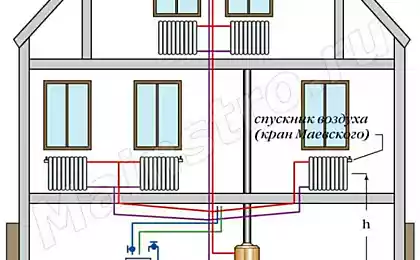
When the difference between ambient and internal air is small, the supply of fresh air possible through the intake grille located on the wall of a house in aerial parts. In the period when the difference is significant, the supply of fresh air can be supplied through the PTO, ensuring that heating / cooling the supply air.
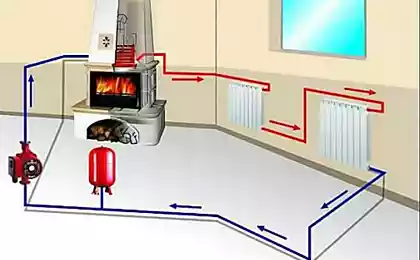
Savings in winter
In the cold season, outdoor air enters through the air intake device to the PTO, where it is heated and then enters the air handling unit for heating in the heat exchanger. Preheating of the air in the PTO reduces the chance of icing of the heat exchanger air handling units, increasing the effective usage time of recovery and minimizes the cost of additional heating of the air in the water / electric heater.
How to calculate the cost of heating and cooling of air
You can pre-calculate the cost of heating the air in winter to areas where the air comes in at the standard of 300 m3 / hour. In winter the average temperature for 80 days, is -5 ° C — it needs to be warmed up to + 20 ° C. To heat this amount of air must be expended by 2.55 kWh (without heat recovery system). When you use a geothermal system is heating outside air up to +5 and then heating up the incoming air to a comfortable out of 1.02 kW. Even better situation when using the recovery — we need to spend only 0,714 kW. Over a period of 80 days will be spent accordingly 2448 kWh of thermal energy, and geothermal system will reduce the cost of 1175 or 685 kWh.
In the offseason, within 180 days, the average daily temperature is + 5 ° C — it needs to be warmed up to + 20 ° C. Routine costs account for 3305 kWh, and the geothermal system will reduce costs or 1102 1322 kWh.
In the summer, within 60 days, the average daily temperature is around + 20 ° C, but within 8 hours it is in the range of + 26 ° C. the Costs for cooling will amount to 206 kWh, and a geothermal system will reduce the costs of 137 kWh.
During the year the work of such a geothermal system was evaluated using factor — SPF (the factor of seasonal power), which is defined as the ratio of received thermal energy to the amount of the consumed electric adjusted for seasonal changes in air temperature/soil.
To obtain the extraction of 2634 kWh thermal energy per year ventilation system is 635 kWh of electricity. SPF = 2634/635 = 4,14.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.ecology.md

The simplest way to use the earth's heat is the use of a soil heat exchanger (PHE). Underground, below the level of soil freezing, fit the air duct system, which perform the function of a heat exchanger between the earth and the air which passes through these ducts. In the winter the incoming cold air that enters the house and passes through the pipes is heated and in summer cooled. When correct placement of the ducts can be selected from the soil a considerable amount of heat energy with a small electric power consumption.
You can use an heat exchanger "pipe in pipe". Internal ducts made of stainless steel appear here as recuperators.
Cooling in the summer
In warm season soil heat exchanger provides cooling of the supply air. Ambient air is drawn through the air intake device in the subterranean heat exchanger where it is cooled by the ground. Then cooled air is supplied by ducts in the supply and installation of exhaust, which in the summer is the heat exchanger installed summer insert. Thanks to this solution, a decrease in the temperature in the building, improving the microclimate in the house, reduced the cost of electricity for air conditioning.
The work in the offseason
When the difference between ambient and internal air is small, the supply of fresh air possible through the intake grille located on the wall of a house in aerial parts. In the period when the difference is significant, the supply of fresh air can be supplied through the PTO, ensuring that heating / cooling the supply air.
Savings in winter
In the cold season, outdoor air enters through the air intake device to the PTO, where it is heated and then enters the air handling unit for heating in the heat exchanger. Preheating of the air in the PTO reduces the chance of icing of the heat exchanger air handling units, increasing the effective usage time of recovery and minimizes the cost of additional heating of the air in the water / electric heater.
How to calculate the cost of heating and cooling of air
You can pre-calculate the cost of heating the air in winter to areas where the air comes in at the standard of 300 m3 / hour. In winter the average temperature for 80 days, is -5 ° C — it needs to be warmed up to + 20 ° C. To heat this amount of air must be expended by 2.55 kWh (without heat recovery system). When you use a geothermal system is heating outside air up to +5 and then heating up the incoming air to a comfortable out of 1.02 kW. Even better situation when using the recovery — we need to spend only 0,714 kW. Over a period of 80 days will be spent accordingly 2448 kWh of thermal energy, and geothermal system will reduce the cost of 1175 or 685 kWh.
In the offseason, within 180 days, the average daily temperature is + 5 ° C — it needs to be warmed up to + 20 ° C. Routine costs account for 3305 kWh, and the geothermal system will reduce costs or 1102 1322 kWh.
In the summer, within 60 days, the average daily temperature is around + 20 ° C, but within 8 hours it is in the range of + 26 ° C. the Costs for cooling will amount to 206 kWh, and a geothermal system will reduce the costs of 137 kWh.
During the year the work of such a geothermal system was evaluated using factor — SPF (the factor of seasonal power), which is defined as the ratio of received thermal energy to the amount of the consumed electric adjusted for seasonal changes in air temperature/soil.
To obtain the extraction of 2634 kWh thermal energy per year ventilation system is 635 kWh of electricity. SPF = 2634/635 = 4,14.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.ecology.md