447
The Germans were faced with the problem of disposal of obsolete wind turbines
Today, Germany is the European pioneer in the use and generation of renewable energy. However, the Germans came close to an unusual problem with a rapidly ageing wind turbines. The old wind turbines is disadvantageous to maintain and use, worse is that they are expensive to dismantle with the aim of recycling – and we have not definitively resolved the question of how they will be disposed of.

Germany has begun to install wind turbines in the mid 90-ies. After the disaster at the nuclear plant Fukushima-1 in 2011, and the related emergence of the next wave of panic before atomic energy, the rapid transition to green energy is even more intensified.
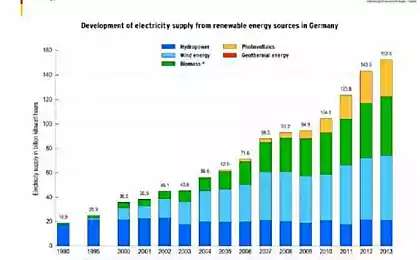
Today, Germany employs more than 25 thousand wind turbines. In four years, closed 5 nuclear power plants, and currently in Germany only 15 percent of all energy consumed is produced by nuclear power plants. But "green" energy, as it turned out, has its own difficulties.
First, the pace of transition on wind energy goes too quickly, so that Germany is exporting surplus energy to neighboring countries. This increases the risk of blackouts in the event of disruption to the grid.
Second, the oldest German wind turbines for more than twenty years. And local laws, such turbines are subject to dismantling and recycling. In 2016, 7 thousand working windmills will be for 15 years.
Plays a role and the fact that over the last decade, the technology of energy production from the wind has taken a big step forward, and one modern wind turbine can produce energy as much as 4-7 of his predecessors. Today turbine replacement new in lieu of repair or upgrading old looks more profitable. However, the repair of old wind turbines is disadvantageous for other reasons.
Production of renewable energy in Germany is subsidized by the state. To generate electricity are fixed rates – high enough to ensure that the wind turbine can quickly be recouped. After twenty years of use of the wind turbine subsidies are suspended, after which the maintenance of the turbines is unprofitable.
The problem is that the output of one windmill down, its dismantling and recycling costs 30 thousand euros. Most wind turbines are gigantic, they had to be disassembled using two 150-ton cranes. There are those owners who unthinkingly bring down the huge turbines on land, but in this case they are more difficult to dispose of or sell on the secondary market.
A number of windmills, is the construction of 150 meters high, it is possible to put in the Metalworking. Also, the wind turbines of German production there is a demand in the secondary markets in Eastern Europe. However, the complexity of the problem of disposal of heavy and high structures as the increase in their number is growing rapidly.
In 2025 will become outdated coastal wind turbines, which stand in the sea – they began to establish in 2010 alone, and no one thinks about how design to dismantle.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: zeleneet.com

Germany has begun to install wind turbines in the mid 90-ies. After the disaster at the nuclear plant Fukushima-1 in 2011, and the related emergence of the next wave of panic before atomic energy, the rapid transition to green energy is even more intensified.
Today, Germany employs more than 25 thousand wind turbines. In four years, closed 5 nuclear power plants, and currently in Germany only 15 percent of all energy consumed is produced by nuclear power plants. But "green" energy, as it turned out, has its own difficulties.
First, the pace of transition on wind energy goes too quickly, so that Germany is exporting surplus energy to neighboring countries. This increases the risk of blackouts in the event of disruption to the grid.
Second, the oldest German wind turbines for more than twenty years. And local laws, such turbines are subject to dismantling and recycling. In 2016, 7 thousand working windmills will be for 15 years.
Plays a role and the fact that over the last decade, the technology of energy production from the wind has taken a big step forward, and one modern wind turbine can produce energy as much as 4-7 of his predecessors. Today turbine replacement new in lieu of repair or upgrading old looks more profitable. However, the repair of old wind turbines is disadvantageous for other reasons.
Production of renewable energy in Germany is subsidized by the state. To generate electricity are fixed rates – high enough to ensure that the wind turbine can quickly be recouped. After twenty years of use of the wind turbine subsidies are suspended, after which the maintenance of the turbines is unprofitable.
The problem is that the output of one windmill down, its dismantling and recycling costs 30 thousand euros. Most wind turbines are gigantic, they had to be disassembled using two 150-ton cranes. There are those owners who unthinkingly bring down the huge turbines on land, but in this case they are more difficult to dispose of or sell on the secondary market.
A number of windmills, is the construction of 150 meters high, it is possible to put in the Metalworking. Also, the wind turbines of German production there is a demand in the secondary markets in Eastern Europe. However, the complexity of the problem of disposal of heavy and high structures as the increase in their number is growing rapidly.
In 2025 will become outdated coastal wind turbines, which stand in the sea – they began to establish in 2010 alone, and no one thinks about how design to dismantle.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: zeleneet.com
How to replace the button helped the company to increase revenues by $300 million a year
Mango, orange and ginger, and Your morning smoothie above all praise!