685
The circle of fifths: music in simple words
The circle of fifths keys (or Kurtovo the circle of fourths) is a graphical diagram used by musicians for the visualization of relations between keys. In other words, it is a convenient way of organizing the twelve notes of the chromatic scale.
For the first time kvantovo-the circle of fifths was described in the book "the Idea of grammar musicescu" from 1679, the Russian-Ukrainian composer Nikolai Diletsky.

Page from the book "the Idea of grammar musikiysky", which depicts the circle of fifths
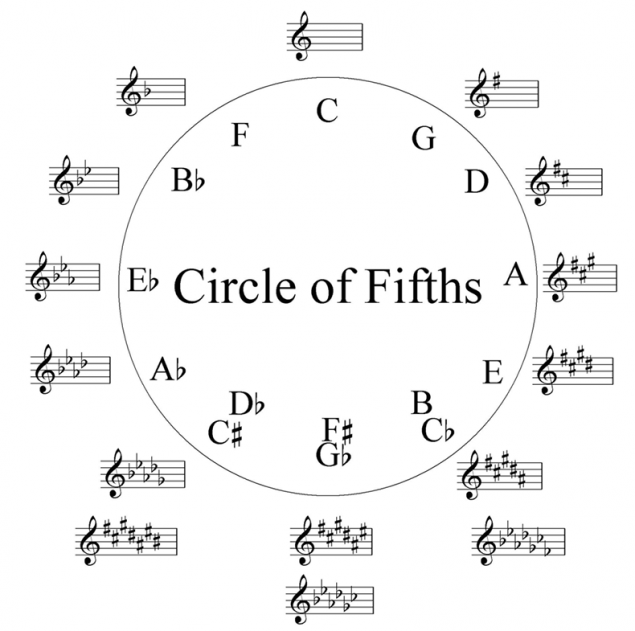
Begin to build the circle is possible with any notes, for example. Then, moving in the direction of increasing pitch, piled up one fifth (five steps or 3.5 tones). The first Quint – it's up to Sol, so for the key of C major the tone should be g major. Then add one fifth, and the resulting Sol-re. D major is the third tone. Repeating this process 12 times, we, in the end, back to the key of C major.
The circle of fifths is called kvantovo-Quintum because it is possible to build and use a quart. If you take note to and lowering it to 2.5 tones, we also get a G.
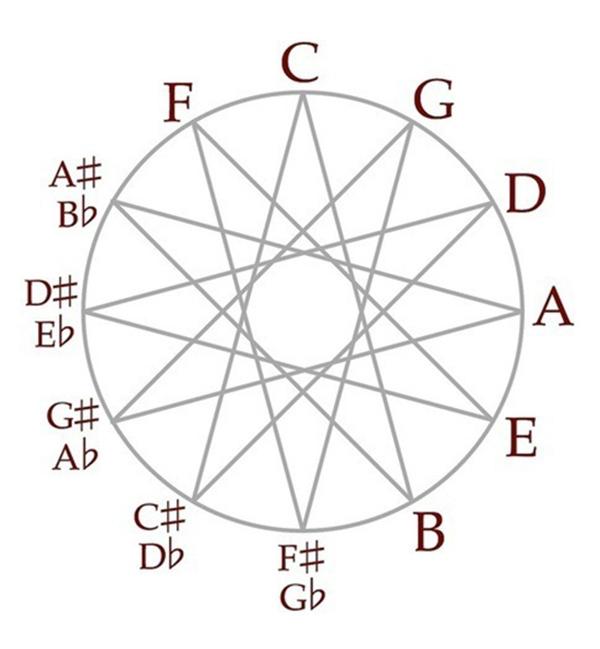
Lines linked notes, the distance between which is equal to the half tones
Gail grace (Gayle Grace) notes that the circle of fifths allows you to calculate the number of characters in the key of a particular key. Each time, counting a 5-speed and moving along the circle of fifths clockwise, we get the key and the number of signs sharp in which on one more than the previous. The tonality of C major doesn't contain any accidentals. In the key of g major, one sharp, in the key of C sharp major has seven.
To calculate the number of characters in b flat in the key should move in the opposite direction, i.e. counterclockwise. For example, starting from before and he counted a fifth down, you will come to the key of f major, in which one character flat. The next tone will be b flat major, in which two characters in a flat key, and so on.
As for the minor, the minor scales, major is identical to the number of characters in the key, is parallel to the (major) key. To define them simply, only need to build each tonic minor third (1.5 tone) down. For example, the parallel minor tonality to C major is a minor.
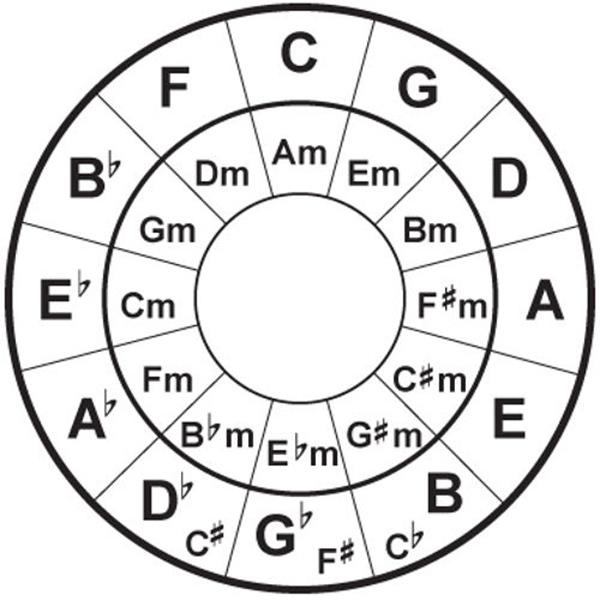
Very often on the outer part of the circle of fifths major scales are represented and the internal minor
Ethan Hein (Ethan Hein), Professor of music at the State University of the city of Montclair, said that the circle helps to understand the structure of Western music of different styles: classic rock, folk-rock, pop-rock and jazz.
"Tonality and the chords on the circle of fifths are located close to each other, most Western listeners will be considered a consonant. The key of a major and d major are composed of six equal notes, so the transition from one to another is smooth and does not cause feelings of dissonance. La major and e flat major are only one note, so the transition from one tone to another will sound strange or even unpleasant," explains Ethan.
It turns out that with each step on the circle of fifths in the initial scheme C major one of the tones is substituted for another. For example, the transition from to the major to a neighboring g major leads to the replacement of only one tone, and move five steps from to the major to C major leads to the replacement of the five tones in primary colours.
Thus, the closer to each other are two set the tone, the closer the degree of kinship. On the system of Rimsky-Korsakov, if between keys, the distance of one step is the first degree of kinship, step two – second, three – third. To keys first-degree relatives (or simply related) are those majors and minors that differ from the original tone to one character.
To the second degree of kinship are key that are related to related keys. Similarly, the tonalities of the third degree of relationship are key first-degree relatives to the tonalities of the second degree.
With the degree of kinship is the reason that these two sequences of chords are frequently used in pop music and jazz:
"In jazz the basic tone is often replaced in a clockwise direction, and in rock, folk and country – against," says Ethan. The appearance of the circle of fifths was due to the fact that the musicians needed a universal scheme, which would allow you to quickly identify the correspondence of the keys and chords. "If You understand the working principle of the circle of fifths, you can easily play the selected tone – You don't have to painfully pick up the right notes," concludes Gail grace.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: geektimes.ru/company/audiomania/blog/270562/

For the first time kvantovo-the circle of fifths was described in the book "the Idea of grammar musicescu" from 1679, the Russian-Ukrainian composer Nikolai Diletsky.

Page from the book "the Idea of grammar musikiysky", which depicts the circle of fifths
Begin to build the circle is possible with any notes, for example. Then, moving in the direction of increasing pitch, piled up one fifth (five steps or 3.5 tones). The first Quint – it's up to Sol, so for the key of C major the tone should be g major. Then add one fifth, and the resulting Sol-re. D major is the third tone. Repeating this process 12 times, we, in the end, back to the key of C major.
The circle of fifths is called kvantovo-Quintum because it is possible to build and use a quart. If you take note to and lowering it to 2.5 tones, we also get a G.

Lines linked notes, the distance between which is equal to the half tones
Gail grace (Gayle Grace) notes that the circle of fifths allows you to calculate the number of characters in the key of a particular key. Each time, counting a 5-speed and moving along the circle of fifths clockwise, we get the key and the number of signs sharp in which on one more than the previous. The tonality of C major doesn't contain any accidentals. In the key of g major, one sharp, in the key of C sharp major has seven.
To calculate the number of characters in b flat in the key should move in the opposite direction, i.e. counterclockwise. For example, starting from before and he counted a fifth down, you will come to the key of f major, in which one character flat. The next tone will be b flat major, in which two characters in a flat key, and so on.
As for the minor, the minor scales, major is identical to the number of characters in the key, is parallel to the (major) key. To define them simply, only need to build each tonic minor third (1.5 tone) down. For example, the parallel minor tonality to C major is a minor.

Very often on the outer part of the circle of fifths major scales are represented and the internal minor
Ethan Hein (Ethan Hein), Professor of music at the State University of the city of Montclair, said that the circle helps to understand the structure of Western music of different styles: classic rock, folk-rock, pop-rock and jazz.
"Tonality and the chords on the circle of fifths are located close to each other, most Western listeners will be considered a consonant. The key of a major and d major are composed of six equal notes, so the transition from one to another is smooth and does not cause feelings of dissonance. La major and e flat major are only one note, so the transition from one tone to another will sound strange or even unpleasant," explains Ethan.
It turns out that with each step on the circle of fifths in the initial scheme C major one of the tones is substituted for another. For example, the transition from to the major to a neighboring g major leads to the replacement of only one tone, and move five steps from to the major to C major leads to the replacement of the five tones in primary colours.
Thus, the closer to each other are two set the tone, the closer the degree of kinship. On the system of Rimsky-Korsakov, if between keys, the distance of one step is the first degree of kinship, step two – second, three – third. To keys first-degree relatives (or simply related) are those majors and minors that differ from the original tone to one character.
To the second degree of kinship are key that are related to related keys. Similarly, the tonalities of the third degree of relationship are key first-degree relatives to the tonalities of the second degree.
With the degree of kinship is the reason that these two sequences of chords are frequently used in pop music and jazz:
- E7, A7, D7, G7, C
"In jazz the basic tone is often replaced in a clockwise direction, and in rock, folk and country – against," says Ethan. The appearance of the circle of fifths was due to the fact that the musicians needed a universal scheme, which would allow you to quickly identify the correspondence of the keys and chords. "If You understand the working principle of the circle of fifths, you can easily play the selected tone – You don't have to painfully pick up the right notes," concludes Gail grace.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: geektimes.ru/company/audiomania/blog/270562/