864
How to help psoas muscle: 3 exercises to relieve pain syndrome
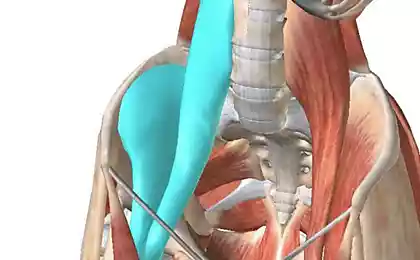
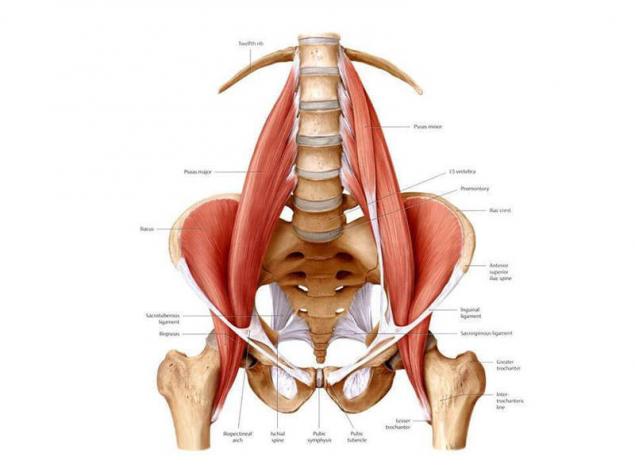
Misunderstanding of the role of the lumbar muscles is not surprising. The process of naming these muscles that connect the upper body with the lower part contains a number of errors spanning four centuries.
Long before Hippocrates began using the modern Latin term "psoa"- lumbar (muscle), anatomists Ancient Greeks called these muscles "the womb to the kidneys" because the physical relationship with these bodies.
In the 17th century the French anatomist Silanus (Riolanus) made a grammatical error, which exists to this day, referring to the two psoas muscles, one "psoas" instead of the proper Latin "psoai" (Diab, 1999).
This might affect our perception of muscles as team players, not as individual muscles are adapting to our asymmetrical habits.
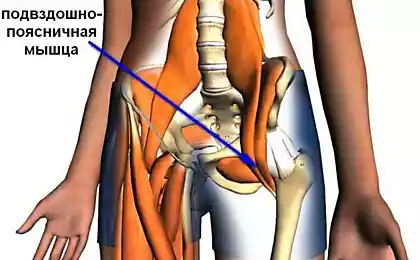
Dr. John Basmajian (John Basmajian), the father of electromyography (EMG) science, has contributed to a misunderstanding of the assertion that the lumbar and iliac muscle function are inseparable, because they have a common lower anchorage. His opinion has led to a proliferation of the term "iliopsoas" (ilio-lumbar), depriving each of the muscle individual characteristics, and triggered the precedent to measure EMG iliac muscles, not the deeper and more hard-to-reach psoas muscle.
All this history helps to understand the causes of the prevalence of misconceptions about the actual role of the psoas muscle.
Mechanics of lumbar muscles
In the light of information about the points of attachment questions arise: whether flexes the lumbar muscle of the thigh? Or it moves the spine? Maybe she does both?
Biomechanics are always trying to build a picture based on "alleged" actions, taking into account the health of joints, levers and produce the effort.
Put LIKES and share with your FRIENDS!
www.youtube.com/channel/UCXd71u0w04qcwk32c8kY2BA/videos
Subscribe -https://www.facebook.com//
Multiple connections with the spine imply that the primary role of psoas is to ensure that somehow the movements of the spine. But testing this hypothesis shows that the angles of attachments not provide sufficient force to tilt to the side.
Remember sit-UPS, lying to school (old school!) from National Fitness Testing program (currently known as the President's Challenge Program)? When driving, similar to the elevation of the trunk (which, oddly enough, still included in the Protocol), psoas muscle simultaneously extends the upper vertebrae and flexes the lower vertebrae, creating a shearing force in the lumbar vertebrae (one vertebra slips relative to another), and creates substantial compressive loads (Bogduk, Pearcy & Hadfield, 1992) is an undesirable move for the long-term health of the back.
Studies show that the psoas muscle plays an active role in hip flexion, but compared with the iliac muscle psoas stabilizes the spine more (not allowing the vertebrae to rotate in the frontal plane) than it produces foot traffic (Hu et al. 2011). Finally, multiple attachment creates the need for sufficient capacity to lengthening psoas muscles to allow the spine, pelvis and hips free, natural movement without pain and injury.
A sedentary lifestyle and psoas muscle
If you ever seen a triathlete transition from bike to run leg of the race, you can imagine how long stay lumbar muscles in a shortened condition affects your ability to walk upright.
In a less extreme situation: hours (and hours) spent sitting, affect the ability of the lumbar muscles to stretch to its maximum length, which allows you exactly stand and what is probably more important to stretch when walking.
If you calculate the number of patients that are moving from eight hours of sitting on workplace for "fitness" activity, which further predisposes to lumbar muscle shortening (stationary bike, trainer-stairs, exercise in the gym, sitting), you will not be surprised that people performing exercises there are so many problems with the lower back, pelvis and hips.
How does the shortening of the psoas muscles?
Experts notice excessive curvature of the lumbar spine, often make a conclusion about the tilt of the pelvis forward by the client.
This form of postural assessment is erroneous, as not supported by the objective data of the position of the skeleton, in particular, the origin of the curve.
Excessive extension of the spine or tilt the pelvis forward is not necessarily evidence of a shortened psoas muscle. Instead there is a special curve that is created by the displacement of the upper lumbar spine in combination with extension and flexion offset and lower vertebrae. It's like excessive bending, with one exception – skeletal symptom: thorax.
Assessment of lumbar muscle
Due to the fact that the psoas muscle can shift the spine forward, is very common to see "protruding ribs" by shortening the muscles.
To appreciate it in the standing position difficult, as many people compensate for shortening of the lumbar muscle small flexion of the hip joints and knees, "weakening the lumbar line." For objective assessment of the use position, lying on his back.
Start with the patient in the sitting position with straight legs. The quadriceps muscles should be completely relaxed, and the rear surface of the thighs touch the floor. Stop the patient when tilting back, when the bottom surface of the thighs is lifted from the floor.
At this point, support your patient under the head and shoulder, leaving space for lowering of the ribs on the floor. The height of the support depends on the strain of lumbar muscles.
Ideally, the patient should be in a lying position on the floor with a "neutral" position of the skeleton. A shortened psoas muscle will lift the thigh or lower ribs off the floor. This assessment – corrective position. In case of detection of elevated lumbar muscle of the ribs, ask the patient to relax while the bottom edge will not be on the floor. In the future, should gradually reduce the height or position at which support is needed.
To test the iliopsoas muscle (MRP), ask the patient to sit on the edge of the bed. Stand beside the patient and place one hand on the thigh of a patient just above his knee.
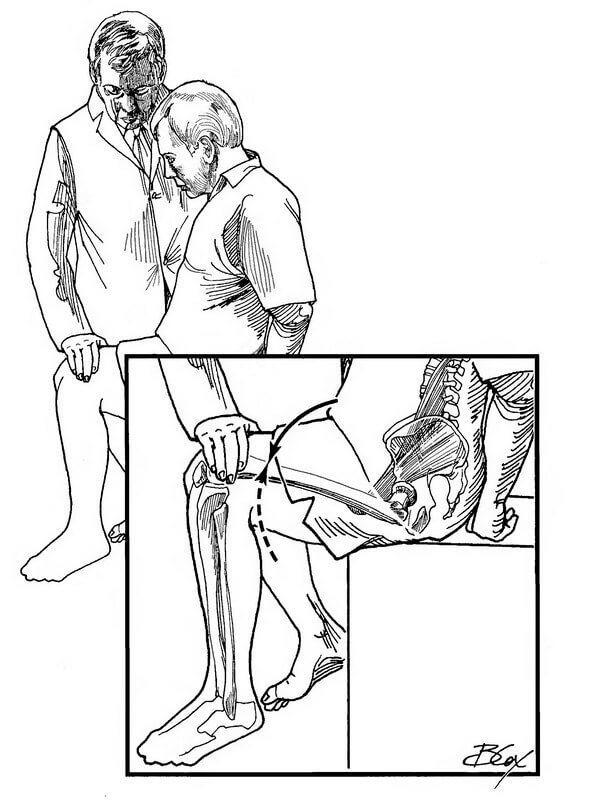
Put your other hand on the shoulder of the patient. Ask the patient to raise the knee against resistance of your hand. Operating force MRP then compare with the stress the same muscles on the other leg.
Postisometric relaxation of muscles
All joints of the human body surrounded by systems of muscles and are driven by their abbreviations. The reduction of some muscle groups and timely relaxation of the others were the smooth performance of body movements. When pathological displacements in the joints of the effect of pronounced irritation of the receptors of the tendons, muscle fibers. This leads to a reduction in as small groups periarticular muscles, fixing abnormal position of a joint, large muscle-fascial complexes, leading to changes in the biomechanics of the entire body.
Treatment of these complex disorders should be to return the causal joint in normal position and range of motion. Unfortunately, pronounced periarticular muscle tension hinders the body holding self-correction.
To help the body get back on the path to healing it is necessary to spend the relaxation of muscles.
It is known that in the phase of normal muscle contraction is the depletion of domestic energy resources of the muscles, followed by relaxation phase. In the case of pathologically tense muscles alternating activation of different groups of fibers, which allows muscle long-term is in a stressed condition. If we consciously increase the force of muscle contraction in response to applied from the outside resistance, and will involve all groups of muscle fibers, leading to their subsequent relaxation and will provide an opportunity to stretch the tense muscles, to release pathologically displaced joint.
The basic rules of a postisometric relaxation of muscles:
1. Before the beginning of the exercise need to be joint in the direction of constraints to achieve maximum tension and tension is pathologically shortened muscles. The preparatory movement is performed until the gain level of pain manifestations. It is a barrier restricting movement.
2. Motion carried to increase muscle reduction, should be performed in the direction of maximum pain and a to comply with the direction prior to the muscle contraction (the opposite barrier restrictions).
3. The additional contraction of the muscles is 30% of maximum and should not increase pain symptoms.
4. Resistance to muscle contraction should be sufficient to hold the limb or body move in space. Muscle needs to strain, but do not produce movement, held by the resistance.
5. Time additional muscle tension for 5-7 seconds.
6. After the voltage is aged 3 second pause – the muscle relaxes.
7. After the pause is stretching the muscles in the side of the barrier to limit the appearance of pain syndrome. This is a new barrier restrictions.
8. Running 3-4 passes with a gradual increase in freedom of movement and relaxation of muscles.
Exercise 1.
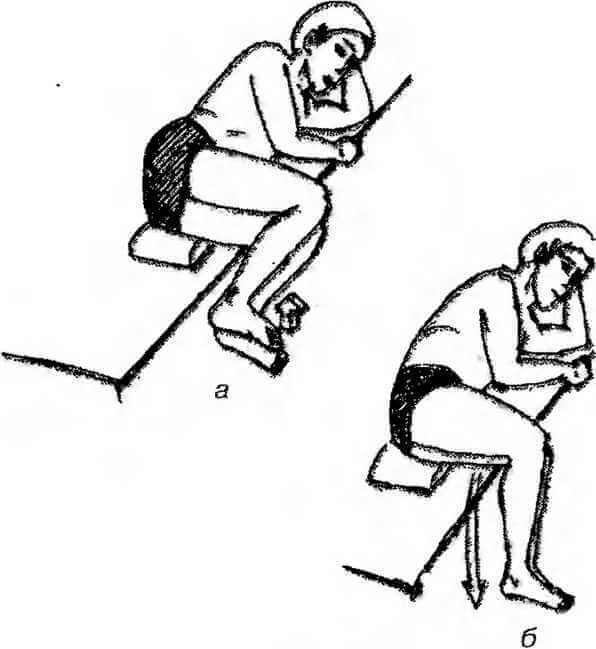
I. p. — lying on the edge of the bed on the healthy side, under pelvis and lower back can put a small pillow. Both legs bent at the knee and hip joints, leg and foot hanging over the edge of the bed. Due to the weight of the legs when relaxation happens the tilt of the pelvis and overlying the side feel a stretch.
Lift the foot and lower leg to a horizontal position, hold the tension for 5-10 seconds (a). Movement to perform better on the exhale.
Then take a deep breath, relax and stretch. The legs will drop and your weight will stretch the square of the loin muscles and the intrinsic muscles of the spine (b). The motion is repeated 3-4 times with an increase in the amplitude while stretching.
If conditions permit, you can "top" with your hand to grab the headboard. In this case, the stretching is palpable and will capture the widest muscle of the back.
Exercise 2.
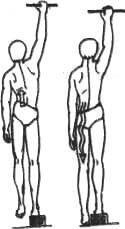
Allows you to stretch those muscles and relieve the joints and discs of the spine. It is more suitable for those who have pain in the evening. To run it put next to the closet pile of books the height of 15-20 centimeters. If your house has a crossbar, it is better to use it, although suitable and the door, or at least just the wall, on which to build.
I. p. — standing with one foot on a stack of books, the other hangs freely without touching the supports, hands stretched up to the maximum, fix the position, holding for support. On the exhale, pull up hanging leg-up ("pull" his leg in the body), as shown in Fig..
Holding this position for 10 seconds, breathe, relax and shake a leg hanging down, trying to touch the foot of the floor (Fig.b). Normal should feel the stretch of muscles in the lumbar region on the side dangling his feet. Repeat the movement 3-4 times for each leg.
After completing this exercise, you need to go and lie down for hours, so it is best to do before bedtime.
Welcome PERM will be more effective if it is carried out from the position of visa on the bar on one hand. And if on the right, then pull left foot should be and Vice versa. This option is ideal for athletes and anyone who could do it, having hung on the crossbar for 2-3 minutes, holding on with one hand.
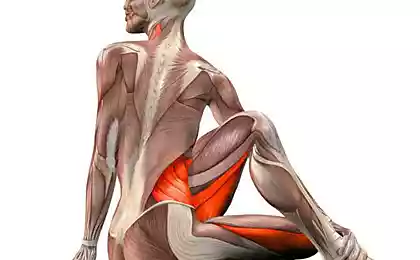
Exercise 3.
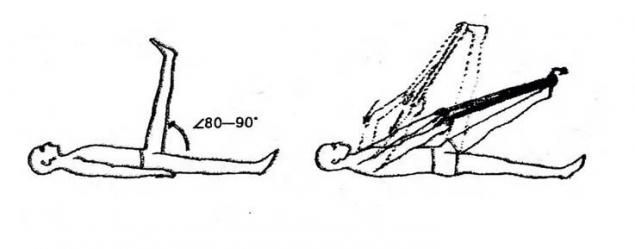
I. p. — lying on your back, legs straight. On the foot (near the toes) wear a long towel, like a stirrup. The ends hold it in my hands and pull the call. The leg will begin to rise, as we have said, are normal at 80-90°, that is released in a vertical position. If the angle of elevation is smaller and, for example, after the 30° appeared nagging pain at the back of the thigh, behind the knee or in the tibia, it is the same (hidden) spasm of the muscles that must be eliminated, otherwise it will sooner or later manifest themselves clearly in the form of an exacerbation. To eliminate this spasm is used PERM.
First, slightly loosen the tension of the towel and set it back to a painless position of the feet. Then take a calm breath and press down with toes on a towel, as the pedal You will feel how tense the muscles in the back of his legs. Your effort should be moderate in intensity. Hold the muscle tension for 7-15 seconds (and preferably hold breath). Exhale, slowly relax the muscles in the legs and hands pull the towel on yourself.
If done correctly, effortlessly and jerks, that leg will rise above the original level and overcome the initial pain barrier.
Next, stretch the muscles to a new "threshold" — in our case, for example, from 30 to 50° to 70°. And as soon as already familiar tugging sensation, re-apply pressure with your fingers on a towel, hold the tension on the inhale, and stretch. Now the angle of elevation may reach 80-90°.
So, for 2-3 cycles of spasm the vast majority is eliminated.
Often there is an opinion that similar pain associated with the inflammation of the sciatic nerve, but the exercise proves a muscular origin of pain, which is often possible to stop an easy stretch.
Possible difficulties with this exercise:
1. Tight muscles are susceptible to stretching, or it triggers the pain. In this case, try increasing the delay voltage to 20 seconds, and the stretching movement of produce in small amplitudes is 5-10°.
2. Perhaps, for one such cycle to normal muscles do not stretch. So the classes should be repeated for several days, sometimes 2 times a day. It is important to note that if after this exercise the volume of traffic has increased at least 5-10°, then you are on the right track and it will go.
3. If the movement has "stalled" before reaching the standards you should look for persistent changes in the muscles or in the hip joint. This situation is often observed in long-term suffering from osteoarthritis, after trauma, in patients with osteoporosis. In this case, do not try to increase the flexion up to 90°. Perhaps your individual rate is smaller and is, for example, 45°. But in this case, after the admission of PERM you will definitely feel relief.
The exercises PERM are key for proper position of all upstream parts of the spine. In addition, they increase the reserve of the musculoskeletal system due to growth and the normalisation of traffic in two major joints — knee and hip. Now they will put them to perform range of motion and relieve the spine, and therefore, the risk of recurrent exacerbations of lumbar pain will be reduced.
Also interesting: How to relieve the pain in the supraspinatus muscle
How to stop neck pain for 6 minutes
If you perform these exercises regularly, then after a week or two you will notice that the legs are bent and unbent in full and without holding FIRM. In this case we can restrict the test 1 time per week using the same techniques, and the deviation from the norm to conduct stretching exercises.
Recall that the main criterion of correctness of the techniques PERM are not degrees, and your feelings. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: xn--80ajkvbglie5k.com.ua/?p=170
Long before Hippocrates began using the modern Latin term "psoa"- lumbar (muscle), anatomists Ancient Greeks called these muscles "the womb to the kidneys" because the physical relationship with these bodies.
In the 17th century the French anatomist Silanus (Riolanus) made a grammatical error, which exists to this day, referring to the two psoas muscles, one "psoas" instead of the proper Latin "psoai" (Diab, 1999).

This might affect our perception of muscles as team players, not as individual muscles are adapting to our asymmetrical habits.
Dr. John Basmajian (John Basmajian), the father of electromyography (EMG) science, has contributed to a misunderstanding of the assertion that the lumbar and iliac muscle function are inseparable, because they have a common lower anchorage. His opinion has led to a proliferation of the term "iliopsoas" (ilio-lumbar), depriving each of the muscle individual characteristics, and triggered the precedent to measure EMG iliac muscles, not the deeper and more hard-to-reach psoas muscle.
All this history helps to understand the causes of the prevalence of misconceptions about the actual role of the psoas muscle.
Mechanics of lumbar muscles
In the light of information about the points of attachment questions arise: whether flexes the lumbar muscle of the thigh? Or it moves the spine? Maybe she does both?
Biomechanics are always trying to build a picture based on "alleged" actions, taking into account the health of joints, levers and produce the effort.
Put LIKES and share with your FRIENDS!
www.youtube.com/channel/UCXd71u0w04qcwk32c8kY2BA/videos
Subscribe -https://www.facebook.com//
Multiple connections with the spine imply that the primary role of psoas is to ensure that somehow the movements of the spine. But testing this hypothesis shows that the angles of attachments not provide sufficient force to tilt to the side.
Remember sit-UPS, lying to school (old school!) from National Fitness Testing program (currently known as the President's Challenge Program)? When driving, similar to the elevation of the trunk (which, oddly enough, still included in the Protocol), psoas muscle simultaneously extends the upper vertebrae and flexes the lower vertebrae, creating a shearing force in the lumbar vertebrae (one vertebra slips relative to another), and creates substantial compressive loads (Bogduk, Pearcy & Hadfield, 1992) is an undesirable move for the long-term health of the back.
Studies show that the psoas muscle plays an active role in hip flexion, but compared with the iliac muscle psoas stabilizes the spine more (not allowing the vertebrae to rotate in the frontal plane) than it produces foot traffic (Hu et al. 2011). Finally, multiple attachment creates the need for sufficient capacity to lengthening psoas muscles to allow the spine, pelvis and hips free, natural movement without pain and injury.
A sedentary lifestyle and psoas muscle
If you ever seen a triathlete transition from bike to run leg of the race, you can imagine how long stay lumbar muscles in a shortened condition affects your ability to walk upright.
In a less extreme situation: hours (and hours) spent sitting, affect the ability of the lumbar muscles to stretch to its maximum length, which allows you exactly stand and what is probably more important to stretch when walking.
If you calculate the number of patients that are moving from eight hours of sitting on workplace for "fitness" activity, which further predisposes to lumbar muscle shortening (stationary bike, trainer-stairs, exercise in the gym, sitting), you will not be surprised that people performing exercises there are so many problems with the lower back, pelvis and hips.
How does the shortening of the psoas muscles?
Experts notice excessive curvature of the lumbar spine, often make a conclusion about the tilt of the pelvis forward by the client.
This form of postural assessment is erroneous, as not supported by the objective data of the position of the skeleton, in particular, the origin of the curve.
Excessive extension of the spine or tilt the pelvis forward is not necessarily evidence of a shortened psoas muscle. Instead there is a special curve that is created by the displacement of the upper lumbar spine in combination with extension and flexion offset and lower vertebrae. It's like excessive bending, with one exception – skeletal symptom: thorax.
Assessment of lumbar muscle
Due to the fact that the psoas muscle can shift the spine forward, is very common to see "protruding ribs" by shortening the muscles.
To appreciate it in the standing position difficult, as many people compensate for shortening of the lumbar muscle small flexion of the hip joints and knees, "weakening the lumbar line." For objective assessment of the use position, lying on his back.
Start with the patient in the sitting position with straight legs. The quadriceps muscles should be completely relaxed, and the rear surface of the thighs touch the floor. Stop the patient when tilting back, when the bottom surface of the thighs is lifted from the floor.
At this point, support your patient under the head and shoulder, leaving space for lowering of the ribs on the floor. The height of the support depends on the strain of lumbar muscles.
Ideally, the patient should be in a lying position on the floor with a "neutral" position of the skeleton. A shortened psoas muscle will lift the thigh or lower ribs off the floor. This assessment – corrective position. In case of detection of elevated lumbar muscle of the ribs, ask the patient to relax while the bottom edge will not be on the floor. In the future, should gradually reduce the height or position at which support is needed.
To test the iliopsoas muscle (MRP), ask the patient to sit on the edge of the bed. Stand beside the patient and place one hand on the thigh of a patient just above his knee.

Put your other hand on the shoulder of the patient. Ask the patient to raise the knee against resistance of your hand. Operating force MRP then compare with the stress the same muscles on the other leg.
Postisometric relaxation of muscles
All joints of the human body surrounded by systems of muscles and are driven by their abbreviations. The reduction of some muscle groups and timely relaxation of the others were the smooth performance of body movements. When pathological displacements in the joints of the effect of pronounced irritation of the receptors of the tendons, muscle fibers. This leads to a reduction in as small groups periarticular muscles, fixing abnormal position of a joint, large muscle-fascial complexes, leading to changes in the biomechanics of the entire body.
Treatment of these complex disorders should be to return the causal joint in normal position and range of motion. Unfortunately, pronounced periarticular muscle tension hinders the body holding self-correction.
To help the body get back on the path to healing it is necessary to spend the relaxation of muscles.
It is known that in the phase of normal muscle contraction is the depletion of domestic energy resources of the muscles, followed by relaxation phase. In the case of pathologically tense muscles alternating activation of different groups of fibers, which allows muscle long-term is in a stressed condition. If we consciously increase the force of muscle contraction in response to applied from the outside resistance, and will involve all groups of muscle fibers, leading to their subsequent relaxation and will provide an opportunity to stretch the tense muscles, to release pathologically displaced joint.
The basic rules of a postisometric relaxation of muscles:
1. Before the beginning of the exercise need to be joint in the direction of constraints to achieve maximum tension and tension is pathologically shortened muscles. The preparatory movement is performed until the gain level of pain manifestations. It is a barrier restricting movement.
2. Motion carried to increase muscle reduction, should be performed in the direction of maximum pain and a to comply with the direction prior to the muscle contraction (the opposite barrier restrictions).
3. The additional contraction of the muscles is 30% of maximum and should not increase pain symptoms.
4. Resistance to muscle contraction should be sufficient to hold the limb or body move in space. Muscle needs to strain, but do not produce movement, held by the resistance.
5. Time additional muscle tension for 5-7 seconds.
6. After the voltage is aged 3 second pause – the muscle relaxes.
7. After the pause is stretching the muscles in the side of the barrier to limit the appearance of pain syndrome. This is a new barrier restrictions.
8. Running 3-4 passes with a gradual increase in freedom of movement and relaxation of muscles.
Exercise 1.

I. p. — lying on the edge of the bed on the healthy side, under pelvis and lower back can put a small pillow. Both legs bent at the knee and hip joints, leg and foot hanging over the edge of the bed. Due to the weight of the legs when relaxation happens the tilt of the pelvis and overlying the side feel a stretch.
Lift the foot and lower leg to a horizontal position, hold the tension for 5-10 seconds (a). Movement to perform better on the exhale.
Then take a deep breath, relax and stretch. The legs will drop and your weight will stretch the square of the loin muscles and the intrinsic muscles of the spine (b). The motion is repeated 3-4 times with an increase in the amplitude while stretching.
If conditions permit, you can "top" with your hand to grab the headboard. In this case, the stretching is palpable and will capture the widest muscle of the back.
Exercise 2.

Allows you to stretch those muscles and relieve the joints and discs of the spine. It is more suitable for those who have pain in the evening. To run it put next to the closet pile of books the height of 15-20 centimeters. If your house has a crossbar, it is better to use it, although suitable and the door, or at least just the wall, on which to build.
I. p. — standing with one foot on a stack of books, the other hangs freely without touching the supports, hands stretched up to the maximum, fix the position, holding for support. On the exhale, pull up hanging leg-up ("pull" his leg in the body), as shown in Fig..
Holding this position for 10 seconds, breathe, relax and shake a leg hanging down, trying to touch the foot of the floor (Fig.b). Normal should feel the stretch of muscles in the lumbar region on the side dangling his feet. Repeat the movement 3-4 times for each leg.
After completing this exercise, you need to go and lie down for hours, so it is best to do before bedtime.
Welcome PERM will be more effective if it is carried out from the position of visa on the bar on one hand. And if on the right, then pull left foot should be and Vice versa. This option is ideal for athletes and anyone who could do it, having hung on the crossbar for 2-3 minutes, holding on with one hand.
Exercise 3.

I. p. — lying on your back, legs straight. On the foot (near the toes) wear a long towel, like a stirrup. The ends hold it in my hands and pull the call. The leg will begin to rise, as we have said, are normal at 80-90°, that is released in a vertical position. If the angle of elevation is smaller and, for example, after the 30° appeared nagging pain at the back of the thigh, behind the knee or in the tibia, it is the same (hidden) spasm of the muscles that must be eliminated, otherwise it will sooner or later manifest themselves clearly in the form of an exacerbation. To eliminate this spasm is used PERM.
First, slightly loosen the tension of the towel and set it back to a painless position of the feet. Then take a calm breath and press down with toes on a towel, as the pedal You will feel how tense the muscles in the back of his legs. Your effort should be moderate in intensity. Hold the muscle tension for 7-15 seconds (and preferably hold breath). Exhale, slowly relax the muscles in the legs and hands pull the towel on yourself.
If done correctly, effortlessly and jerks, that leg will rise above the original level and overcome the initial pain barrier.
Next, stretch the muscles to a new "threshold" — in our case, for example, from 30 to 50° to 70°. And as soon as already familiar tugging sensation, re-apply pressure with your fingers on a towel, hold the tension on the inhale, and stretch. Now the angle of elevation may reach 80-90°.
So, for 2-3 cycles of spasm the vast majority is eliminated.
Often there is an opinion that similar pain associated with the inflammation of the sciatic nerve, but the exercise proves a muscular origin of pain, which is often possible to stop an easy stretch.
Possible difficulties with this exercise:
1. Tight muscles are susceptible to stretching, or it triggers the pain. In this case, try increasing the delay voltage to 20 seconds, and the stretching movement of produce in small amplitudes is 5-10°.
2. Perhaps, for one such cycle to normal muscles do not stretch. So the classes should be repeated for several days, sometimes 2 times a day. It is important to note that if after this exercise the volume of traffic has increased at least 5-10°, then you are on the right track and it will go.
3. If the movement has "stalled" before reaching the standards you should look for persistent changes in the muscles or in the hip joint. This situation is often observed in long-term suffering from osteoarthritis, after trauma, in patients with osteoporosis. In this case, do not try to increase the flexion up to 90°. Perhaps your individual rate is smaller and is, for example, 45°. But in this case, after the admission of PERM you will definitely feel relief.
The exercises PERM are key for proper position of all upstream parts of the spine. In addition, they increase the reserve of the musculoskeletal system due to growth and the normalisation of traffic in two major joints — knee and hip. Now they will put them to perform range of motion and relieve the spine, and therefore, the risk of recurrent exacerbations of lumbar pain will be reduced.
Also interesting: How to relieve the pain in the supraspinatus muscle
How to stop neck pain for 6 minutes
If you perform these exercises regularly, then after a week or two you will notice that the legs are bent and unbent in full and without holding FIRM. In this case we can restrict the test 1 time per week using the same techniques, and the deviation from the norm to conduct stretching exercises.
Recall that the main criterion of correctness of the techniques PERM are not degrees, and your feelings. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: xn--80ajkvbglie5k.com.ua/?p=170