2435
Intel has talked about the Core of the fifth generation
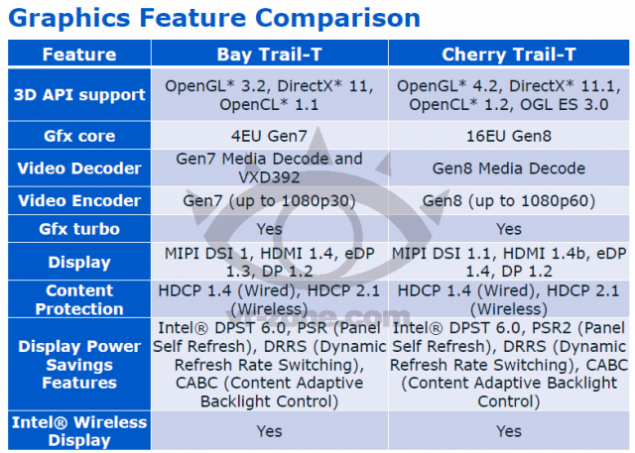
Were begun delivery SoC Cherry Trail
Representatives of Intel говорили, that in early 2015 will see more microprocessors on the new architecture Broadwell, and they kept their promise.
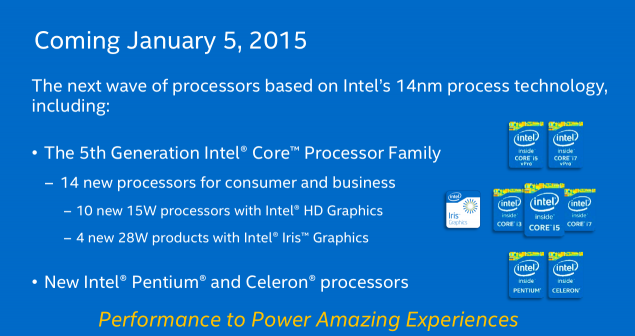
5 January at the International Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas was announced 17 new dual-core processors at once - from expensive Core i7 to more affordable Pentium and Celeron. This should be expected - have passed six months after the announcement of the first Core M chips with 14-nanometer process technology.
Typically, Intel is initially expensive models, and later by reducing costs establishes release cheaper solutions. But in the case of Broadwell we somehow decided to show the first dual-core microprocessors for inexpensive devices, and is faster and requires more power quad-core chips will not be until the summer.
So, what we got yesterday, and what to expect in the future.

Intel remains faithful to the development strategy of "tick-tock". "Tick" - a reduction in process technology, "so" means a new architecture. Yesterday presented a novelty - a "tick».

Representatives of Intel говорили, that in early 2015 will see more microprocessors on the new architecture Broadwell, and they kept their promise.
5 January at the International Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas was announced 17 new dual-core processors at once - from expensive Core i7 to more affordable Pentium and Celeron. This should be expected - have passed six months after the announcement of the first Core M chips with 14-nanometer process technology.
Typically, Intel is initially expensive models, and later by reducing costs establishes release cheaper solutions. But in the case of Broadwell we somehow decided to show the first dual-core microprocessors for inexpensive devices, and is faster and requires more power quad-core chips will not be until the summer.
So, what we got yesterday, and what to expect in the future.

Intel remains faithful to the development strategy of "tick-tock". "Tick" - a reduction in process technology, "so" means a new architecture. Yesterday presented a novelty - a "tick».
| Year th> | microarchitecture code name th> | TechProcess th> | Branding th> | «Tick" or "wrong" th> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Westmere | 32 nm | Core i3 / i5 / i7 < «Tick» | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | Sandy Bridge | 32 nm | The second generation i3 / i5 / i7 | «So» | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | Ivy Bridge | 22 nm < The third generation i3 / i5 / i7 | «Tick» | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | Haswell | 22 nm | The fourth generation i3 / i5 / i7 | «So» | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014-2015 | Broadwell | 14 nm | The fifth generation i3 / i5 / i7, Core M | «Tick» | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
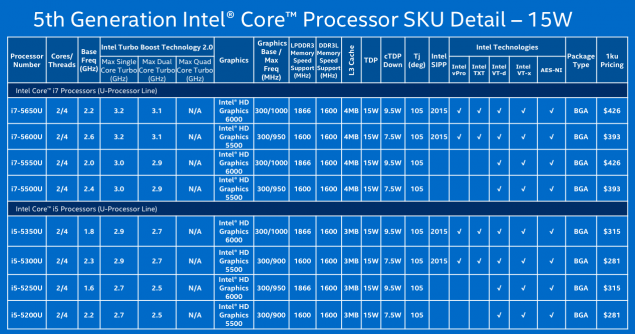
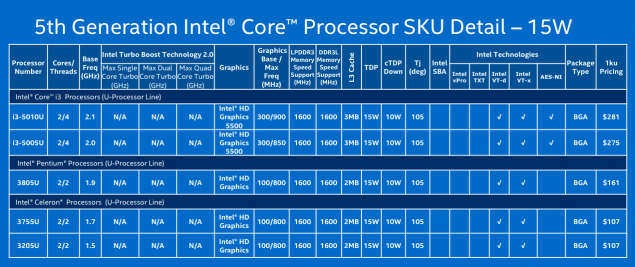
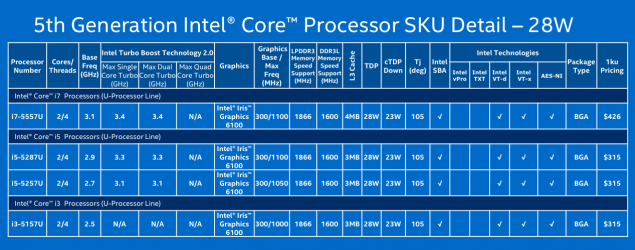
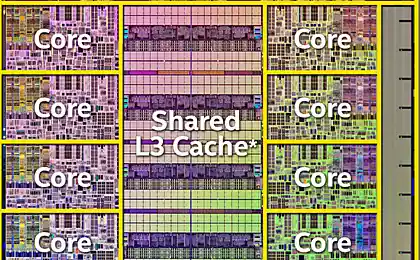
| 2015? | Skylake | 14 nm | - | «So» first from brodvellov were several models of Core M last year. These microprocessors have the letter 'Y' in the title, and this is not the flagship Intel, weaker than them unless the "atoms". Announced yesterday microprocessors - is a powerful U-series. Most of the new products is the heat 15 watts, although there are versions of the productive capacity of 28 watts. Haswell has a similar performance. Intel notes that the producers at the unwillingness to create a new system from scratch will be able to use microprocessors in systems for Broadwell Haswell. The most common chips are 15-watt i3, i5 and i7, which will most often appear in Ultrabooks, and even desktop computers, where size and weight are important. Pentium and Celeron processors will be used in a more cost solutions. One such Celeron already lit a ThinkPad from Lenovo. But the new microprocessors for desktop systems - those with more than 45 watts of heat - will be shown until mid-2015. The crystal size is reduced by 37%, while at the same time it umeshaetsya 35% more transistors. Intel promises that the new items microarchitecture Broadwell can increase the battery life of one and a half hours (from 45 minutes to 2 hours) with respect to its predecessor Haswell. However, for the consumer, this may mean a new round of the race for the thick, not longer working electronics. 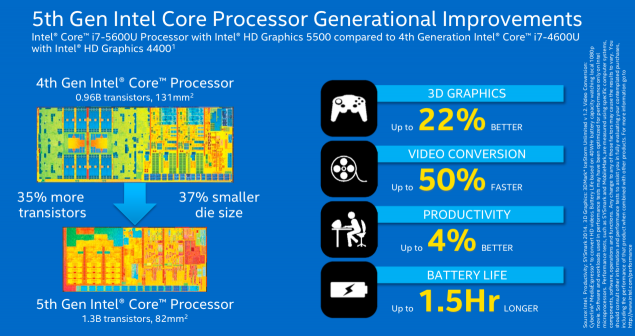 Several performance improvements. For example, the frequency of i7-5600U is 2, 4 GHz at i7-4600U this parameter is 1, 8 GHz and 2 GHz i7-4610U. Below for effect compares Intel i5-520UM processor with novelty four years ago. This, in general, is correct - a typical consumer notebook changes every few years, and not with the advent of new microarchitecture. Such a step is necessary to go, because the performance of a relatively Haswell grew by only 4%, as shown on the slide above. And there is nothing strange - computing power mainly improves the "wrong" and not "tick». 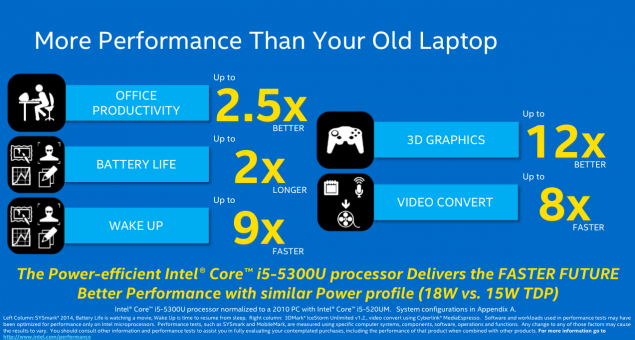 Much more interesting to improving the graphics. As can be seen from the illustration below, it takes almost two-thirds of the chip. The situation gradually changed with respect to the four or five years ago, when the gamer was foolish to rely on integrated graphics. 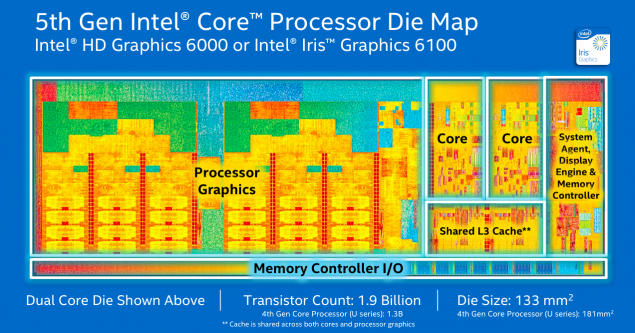
|
Scarlett Johansson to star in the film version of "Ghost in the Shell"
Falcon 9 launch v1.1 ® canceled