1830
What do astronauts eat?
Cosmic health products different from the usual food we eat, especially their composition, manufacture and packaging. In this review, you look like the best chefs and scientists are developing space food, space will see products from different countries and learn how many calories a day diet is a modern Russian cosmonaut.

A bit of history
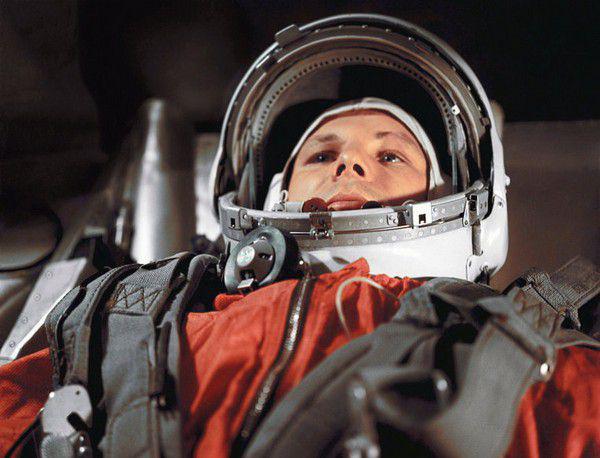
The first person who tried the food directly on the space orbit, of course, was Yuri Gagarin. Despite the fact that his flight took only 108 minutes and hungry astronaut had no time to plan the launch meant a meal.
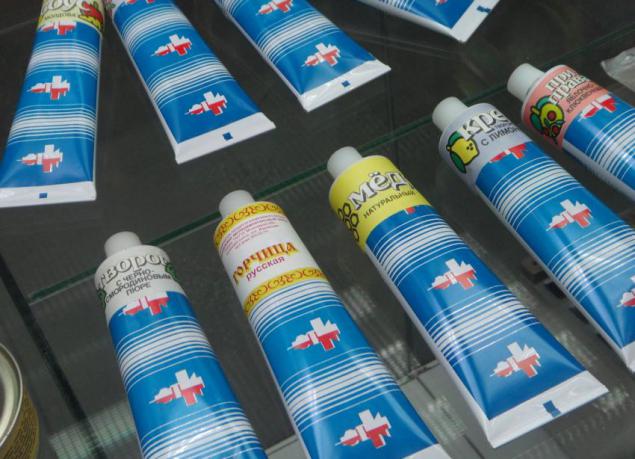
After all, it was the first manned mission to orbit the Earth, and scientists do not know whether the astronaut will be able to eat normally in zero gravity, the body will take any food. As for food packaging tubes have been used successfully tested before in aviation. Inside were the meat and chocolate.
Yuri Gagarin before the start.

Already German Titov during a 25-hour flight to fully eaten three times. His diet consisted of three courses - soup, pate and stewed fruit. But to return to Earth, he still complained of dizziness of hunger. So in the future of space food experts engaged in the development of specialty products, which are the most nutritious, effective and well absorbed by the body.
Tubes of the first Soviet space food.
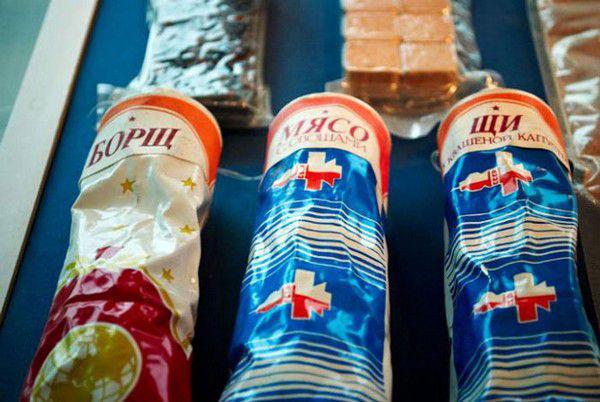

In 1963, the Institute of Biomedical Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences Laboratory will separate, fully occupied with the question of space food. There she still.
Members of the Soviet Apollo-Soyuz flight taking food.
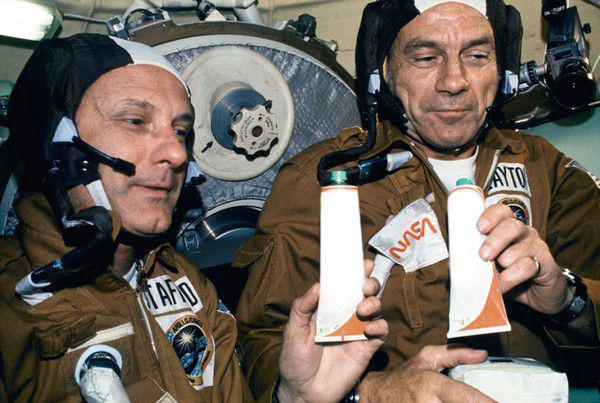

Americans during the first flight went the other way. The first US astronauts space food was a dried products, which had to be diluted with water. The quality of the food did not matter, so that seasoned space explorers have tried to smuggle in missiles with normal products.
The case when the astronaut John Young took a sandwich. But it has turned out to be in weightless conditions is extremely difficult. And the bread crumbs with pieces spacecraft, long turned the lives of the crew into a nightmare.
By the eighties the Soviet and American space food has become quite delicious and varied. In the USSR it was issued about three hundred names of products available to the astronauts in flight. Now this number has halved.
The first set of US space food.

Technology
Nowadays, hardly used the famous tubes of space food. Now the products are stored in vacuum-packed, passing in front of this process of freeze-drying.
This laborious process involves withdrawal from the frozen food moisture by special technology, which allows almost completely (95 per cent) saved in these nutrients, trace elements, vitamins, natural smell, taste, and even the original shape. In doing so, the food can be stored without compromising the quality of every kind to five years (!) Is a function of temperature and other storage conditions.
Scientists have learned how to dry this way almost any products, even cottage cheese. The latter, incidentally, is one of the most popular products at the International Space Station. Foreign cosmonauts in almost all lining up for the opportunity to taste this dish, included in the diet of Russian colleagues.
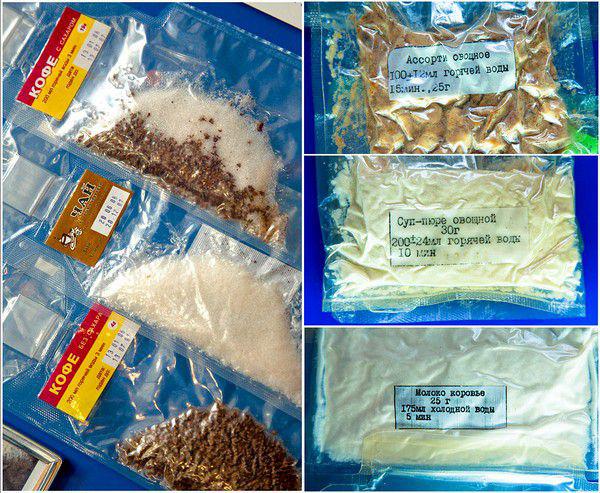
Modern Russian space food.
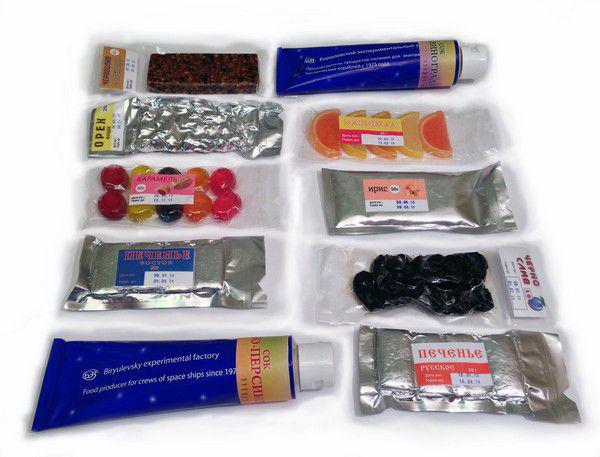

Russian space food
Daily ration of Russian cosmonaut 3200 calories, divided into four meals. Thus, the daily food of one man in orbit our space agency costs 18-20 thousand rubles. And it's not so much the cost of the products and their production, as in the high price for delivering cargoes into space (5-7 thousand dollars per kilogram of body weight).
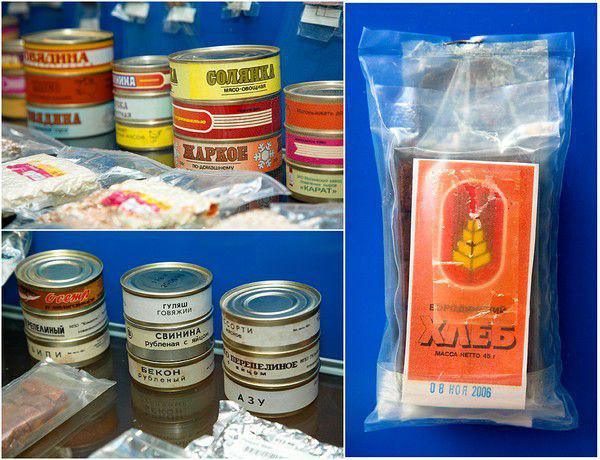

As mentioned above, in the eighties of the twentieth century, there were about three hundred names of Soviet space products. Now this list was reduced to one hundred and sixty. At the same time there are always new dishes and old are history. For example, in recent years, the diet of astronauts entered hodgepodge, mushroom soup, steamed vegetables with rice, salad of green beans, Greek salad, canned poultry meat, scrambled eggs with chicken liver, chicken with nutmeg and other products.
And from long-lived space dishes, which lasted to the present time since the sixties, may be mentioned Ukrainian borscht, chicken, steak, beef tongue and a special bread that does not crumble.
A significant drawback is the absence in the Russian part of the International Space Station refrigerators and microwaves. So our astronauts, unlike their foreign counterparts, are not available and frozen semi-finished products, including fresh fruits and vegetables.

The US space food
But there is a refrigerator in the American segment of the ISS, which makes them a diet rich and diverse. However, in recent years, Americans also began to move away from the semi-finished products to the sublimated. And if before their ratio was 70 to 30, is now 50 to 50.
Set meals for the crews of Space Space Shuttle.
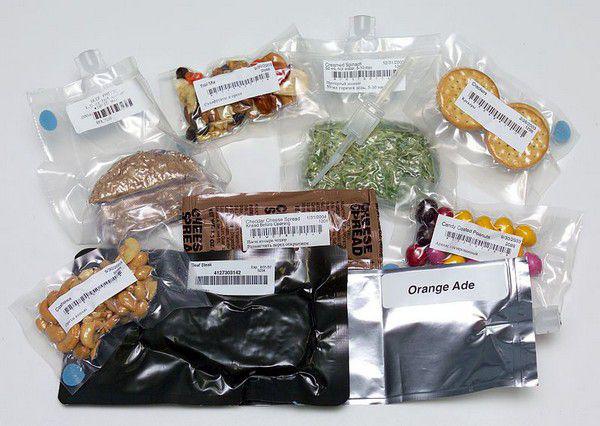

The Americans and the orbiting eat hamburgers.

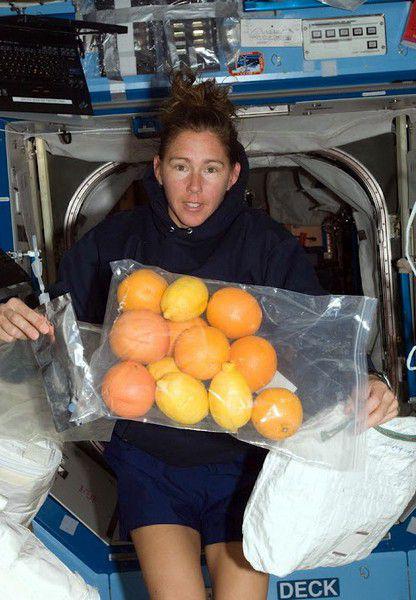
Aside from the possibility of using by-products, heating them in the microwave, the American space food is not much different from the Russian. The only difference is in the arrangement of dishes, and the main products are used are the same. But there are certain specifics. For example, Americans prefer the citrus fruit, while the Russians love apples and grapes.
Love American astronauts to the citrus.

Other countries
But for the astronauts from other countries of dietitians create space sometimes just too unusual for us, and even frankly exotic products. For example, the Japanese space explorers, even in orbit can not do without sushi, noodle soup, soy sauce and many kinds of green tea.
Chinese taykunavty, however, eat enough traditional food - pork, rice and chicken. And the greatest entertainer in terms of space diet considered French. They take with them into orbit, not only daily meal, but also delicacies, for example, mushrooms, truffles. A case where experts from Roscosmos refused French astronaut in the carriage by "Mir" blue cheese, fearing that it could disrupt the biological environment on the space station.
On a separate note, all space food have artificially increased levels of calcium. Living in conditions of weightlessness negative impact on its quantity in the human body, which promises significant problems with bones and musculoskeletal system as a whole. So nutritionists are trying to at least partially deal with this problem at the level of a special diet.
Korean woman astronaut in orbit dinner.

Space food future
In the foreseeable future, significant changes in the technology of preparation of space food are planned. Is that little will change the diet - there will be new dishes and will leave some of the old. Menu cosmonauts and astronauts will be formed on the needs and tastes of a particular person. And NASA has already stated that it is considering the possibility of creating a separate vegetarian menu for Mars mission members, the official start of which could begin in the next two decades.
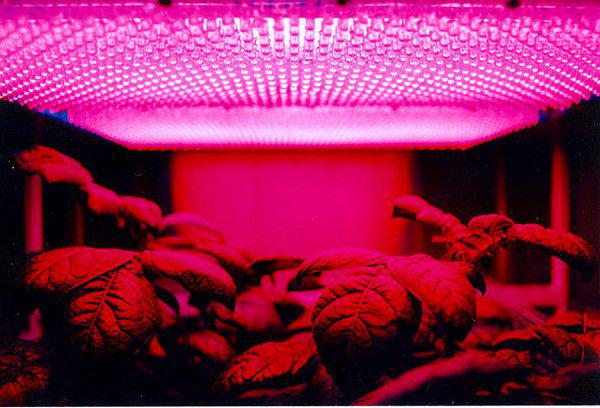
The mission of this, incidentally, involves not only the use of cooked food in the world of space, and growing food directly on board the ship. About such dreams for many decades scientists. And in the near future, their expectations are fulfilled. After all, the safety of milk and meat is not enough for a mission of a few years. And because the most logical way out is the appearance of the garden to grow fresh fruits and vegetables.
NASA's experimental farm growing potatoes.

Source: www.novate.ru

A bit of history
The first person who tried the food directly on the space orbit, of course, was Yuri Gagarin. Despite the fact that his flight took only 108 minutes and hungry astronaut had no time to plan the launch meant a meal.
After all, it was the first manned mission to orbit the Earth, and scientists do not know whether the astronaut will be able to eat normally in zero gravity, the body will take any food. As for food packaging tubes have been used successfully tested before in aviation. Inside were the meat and chocolate.
Yuri Gagarin before the start.

Already German Titov during a 25-hour flight to fully eaten three times. His diet consisted of three courses - soup, pate and stewed fruit. But to return to Earth, he still complained of dizziness of hunger. So in the future of space food experts engaged in the development of specialty products, which are the most nutritious, effective and well absorbed by the body.
Tubes of the first Soviet space food.

In 1963, the Institute of Biomedical Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences Laboratory will separate, fully occupied with the question of space food. There she still.
Members of the Soviet Apollo-Soyuz flight taking food.

Americans during the first flight went the other way. The first US astronauts space food was a dried products, which had to be diluted with water. The quality of the food did not matter, so that seasoned space explorers have tried to smuggle in missiles with normal products.
The case when the astronaut John Young took a sandwich. But it has turned out to be in weightless conditions is extremely difficult. And the bread crumbs with pieces spacecraft, long turned the lives of the crew into a nightmare.
By the eighties the Soviet and American space food has become quite delicious and varied. In the USSR it was issued about three hundred names of products available to the astronauts in flight. Now this number has halved.
The first set of US space food.

Technology
Nowadays, hardly used the famous tubes of space food. Now the products are stored in vacuum-packed, passing in front of this process of freeze-drying.
This laborious process involves withdrawal from the frozen food moisture by special technology, which allows almost completely (95 per cent) saved in these nutrients, trace elements, vitamins, natural smell, taste, and even the original shape. In doing so, the food can be stored without compromising the quality of every kind to five years (!) Is a function of temperature and other storage conditions.
Scientists have learned how to dry this way almost any products, even cottage cheese. The latter, incidentally, is one of the most popular products at the International Space Station. Foreign cosmonauts in almost all lining up for the opportunity to taste this dish, included in the diet of Russian colleagues.
Modern Russian space food.

Russian space food
Daily ration of Russian cosmonaut 3200 calories, divided into four meals. Thus, the daily food of one man in orbit our space agency costs 18-20 thousand rubles. And it's not so much the cost of the products and their production, as in the high price for delivering cargoes into space (5-7 thousand dollars per kilogram of body weight).

As mentioned above, in the eighties of the twentieth century, there were about three hundred names of Soviet space products. Now this list was reduced to one hundred and sixty. At the same time there are always new dishes and old are history. For example, in recent years, the diet of astronauts entered hodgepodge, mushroom soup, steamed vegetables with rice, salad of green beans, Greek salad, canned poultry meat, scrambled eggs with chicken liver, chicken with nutmeg and other products.
And from long-lived space dishes, which lasted to the present time since the sixties, may be mentioned Ukrainian borscht, chicken, steak, beef tongue and a special bread that does not crumble.
A significant drawback is the absence in the Russian part of the International Space Station refrigerators and microwaves. So our astronauts, unlike their foreign counterparts, are not available and frozen semi-finished products, including fresh fruits and vegetables.

The US space food
But there is a refrigerator in the American segment of the ISS, which makes them a diet rich and diverse. However, in recent years, Americans also began to move away from the semi-finished products to the sublimated. And if before their ratio was 70 to 30, is now 50 to 50.
Set meals for the crews of Space Space Shuttle.

The Americans and the orbiting eat hamburgers.

Aside from the possibility of using by-products, heating them in the microwave, the American space food is not much different from the Russian. The only difference is in the arrangement of dishes, and the main products are used are the same. But there are certain specifics. For example, Americans prefer the citrus fruit, while the Russians love apples and grapes.
Love American astronauts to the citrus.

Other countries
But for the astronauts from other countries of dietitians create space sometimes just too unusual for us, and even frankly exotic products. For example, the Japanese space explorers, even in orbit can not do without sushi, noodle soup, soy sauce and many kinds of green tea.
Chinese taykunavty, however, eat enough traditional food - pork, rice and chicken. And the greatest entertainer in terms of space diet considered French. They take with them into orbit, not only daily meal, but also delicacies, for example, mushrooms, truffles. A case where experts from Roscosmos refused French astronaut in the carriage by "Mir" blue cheese, fearing that it could disrupt the biological environment on the space station.
On a separate note, all space food have artificially increased levels of calcium. Living in conditions of weightlessness negative impact on its quantity in the human body, which promises significant problems with bones and musculoskeletal system as a whole. So nutritionists are trying to at least partially deal with this problem at the level of a special diet.
Korean woman astronaut in orbit dinner.

Space food future
In the foreseeable future, significant changes in the technology of preparation of space food are planned. Is that little will change the diet - there will be new dishes and will leave some of the old. Menu cosmonauts and astronauts will be formed on the needs and tastes of a particular person. And NASA has already stated that it is considering the possibility of creating a separate vegetarian menu for Mars mission members, the official start of which could begin in the next two decades.
The mission of this, incidentally, involves not only the use of cooked food in the world of space, and growing food directly on board the ship. About such dreams for many decades scientists. And in the near future, their expectations are fulfilled. After all, the safety of milk and meat is not enough for a mission of a few years. And because the most logical way out is the appearance of the garden to grow fresh fruits and vegetables.
NASA's experimental farm growing potatoes.

Source: www.novate.ru