1737
The problem of space debris

Each of us knows that humanity is incredibly dirtied their planet and every day continues to generate incredible kolichesvto debris. But few know that for a short period of space exploration, we managed to turn a small near-Earth space in the landfill of waste satellites. Here are two interactive visualizations that reflect the current situation.
The first visualization (author Alex Rasmussen ) reflects all known and track satellites and debris:
- green dots denote operational satellites.
- Gray - Inactive, but workable.
- Red - the failed satellites and their fragments. ul >
The European Space Agency установило, that now revolves around the Earth:
- about 29,000 debris larger than 10 cm,
- about 670,000 fragments of from 1 to 10 cm,
- 170 million over the wreckage from 1 mm to 1 cm.

link to the online version .
Over the past 50 years has been launched about 6600 satellites , 3600 of them are still orbiting the Earth, and in 1000 is in active mode.
How dangerous all this garbage? H4>
Presented visualization can enter our minds misleading because the dots denote a location i> the wreckage, but not the size, that is, the scale has not been respected. In reality, the near-Earth space is not a dump as it looks in the pictures. However, the space agencies of different countries anyway alert, because the cost of objects launched very high, and the potential damage from the loss of 1,000 active satellites now as a result of collisions with debris is estimated at 130 billion dollars.
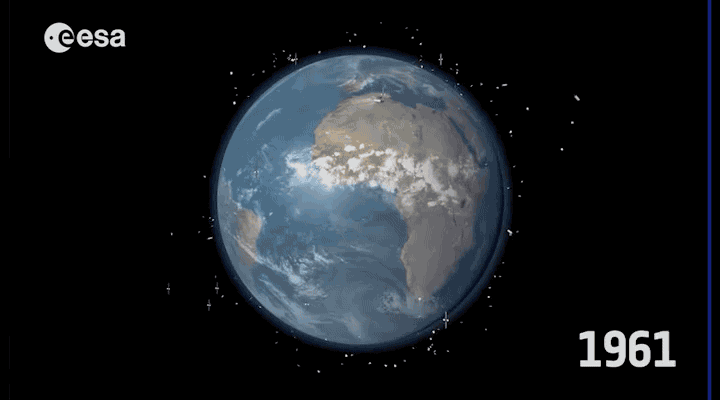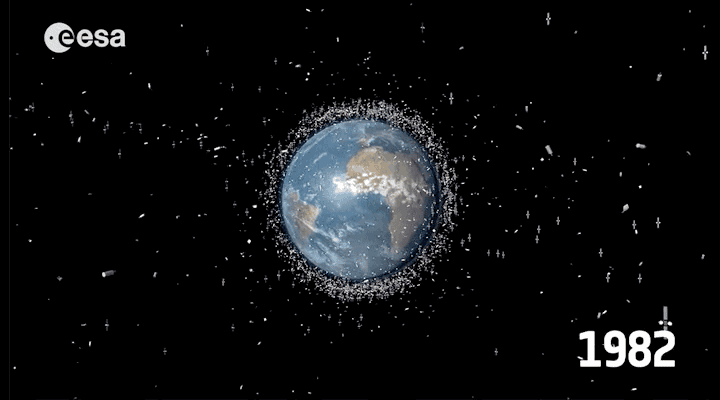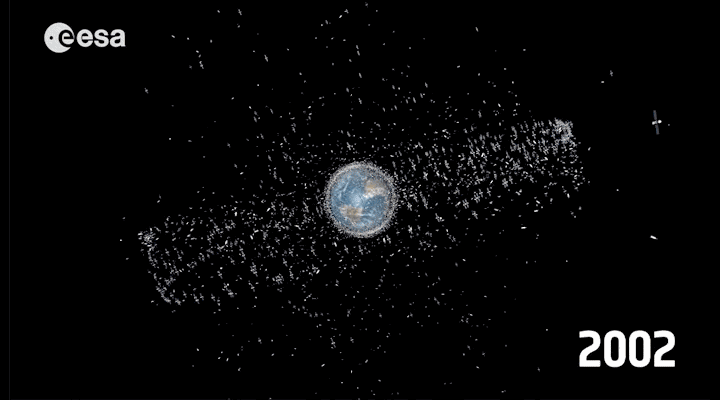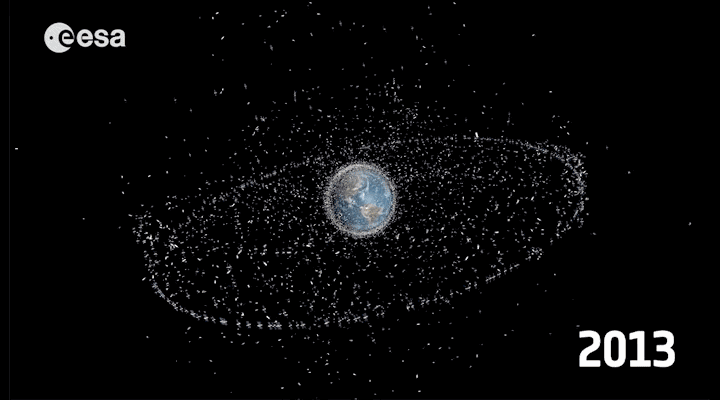
Every year the earth's atmosphere includes 100-150 tons of debris. The most remarkable has happened in recent years has become clash of German and American satellites , whose debris fell into the Bay of Bengal 2011. Astronauts in orbit and do not relax (hello "Gravity"). In 2012, ISS was переведена into a higher orbit to avoid a collision with debris from the Japanese satellite.
What should I do? H4>
Fortunately, the repetition in the life of the script in the image of "Gravity" is unlikely. In addition, инженеры provided a lot of remedies (ISS considered & quot; наиболее protected spacecraft in history & quot;). However, the speed of flight and the growing amount of debris are still a major threat. Scientists warn about the possibility of синдрома Kessler , when in orbit would be so much debris that the risk of destruction of any device will be launched very high. Such a chain reaction can, in fact, close to mankind access to space.
Today, scientists are looking for ways to keep track of debris and clearing space. One of the many ideas is to use special satellites that will capture debris and send to the planet's surface. Also consider the option of collecting more usable debris for recycling.
Whichever method is chosen in the future, one thing is certain: littering the nearest space will cost us dearly. If we want to continue to have access beyond their planet, have a modern satellite communications, surveillance and research, we need to already begin to explore possible ways of getting rid of orbital debris.


Coming in from the ссылке Original article can be estimated interactive visualization. Unfortunately, embed them in the post does not allow Habr, had to take screenshots.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/218257/




























