1020
Sorting and recycling facilities in Japan
In Japan, the problem of waste disposal is particularly relevant, since the Islands are not so much space to bury them. Largely for this reason, the Japanese have long developed a system of sorting and recycling rubbish, and came up with a special "zero-waste" philosophy.
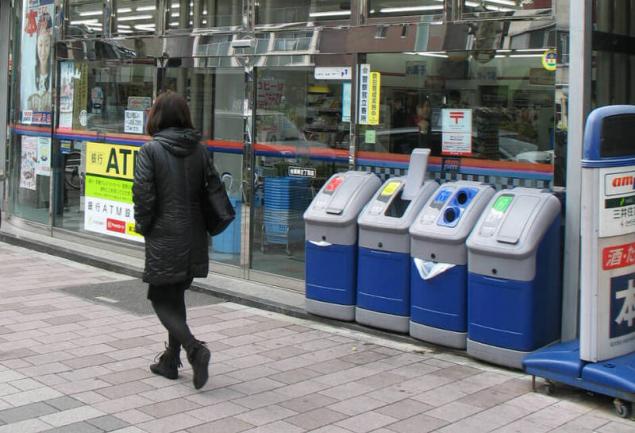

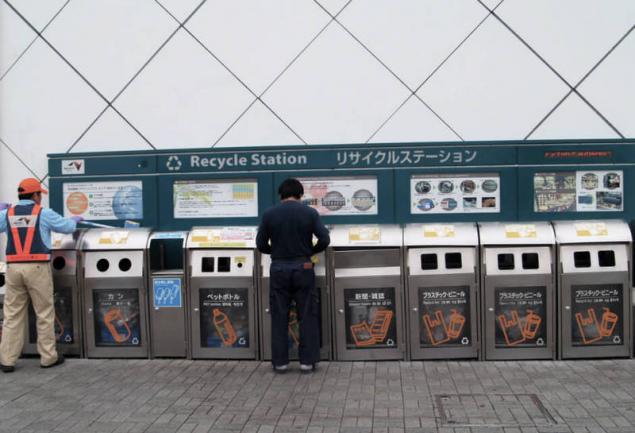
Four types of waste Principles of separating garbage in Japan depend on the area and requirements of municipal authorities, but most often waste is separated into four categories, which are slightly different from traditional separation.
Here in different pots, put a garbage non-combustible, combustible, recyclable and bulky. Moreover, for each type of waste there are special packages of a certain color and volume make it easier to distinguish the dregs of what type is in them.
For large items, which, of course, the packages do not fit, glued special sticker.
That everything was graded properly, keep working, serving the garbage truck. Machine garbage collection comes at a certain time.
By this time the inhabitants carried their bags, and since they are transparent, scavengers are able to trace the truth of sorted waste. If there are violations, the packages don't take
The garbage truck not only comes at certain hours, but on certain days. Each type of waste is deposited exactly at the appointed day of the week, which is set by the municipality.
So, in the city of kita-Kyushu on Tuesday and Friday, the export of combustible waste, into the environment — cans and bottles Thursday — packing plastic. If you make, say, Tuesday plastic trash, you simply will not accept. I'll try to leave packages at musorovozki — put up a fine whole housing cooperative.
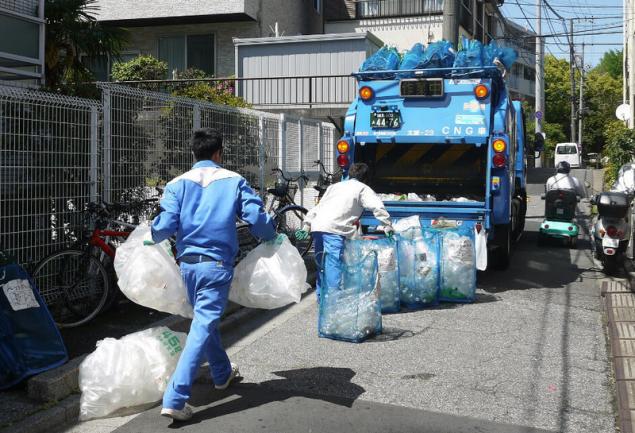

Fee for old equipment Day to dispose of large things is usually assigned separately: residents calling the company to collect garbage and make a request, there they were misleading, when the furniture will arrive the garbage truck.
For furniture, because household appliances to large debris does not apply. For its disposal need to pay separately.
This can be done in different ways. We can take her to the store where equipment was purchased, and to pay to the manufacturer for recycling.
Or you can pay in the store dispose of the goods in return for it will be given a special sticker. It can stick on the old equipment and bring to the garbage cans — the garbage truck will pick her up and take her to the scrap. This practice has led to good results: the recycling of household appliances, providing the country with more than 1 million tons of iron and 50 thousand tons of nonferrous metal per year.
Attempts to throw away unnecessary appliances and electronics without payment will result in penalties of several hundred dollars. But such cases, unconsciousness is not so much — discipline and love of order of the Japanese blood.

Trash-sorcery To guests of the country also abide by the rules of separate collection, the Japanese have found on the streets of the special ballot box: the holes in them are made so that anything other than what they are, there were not included.
If compartment boxes are designed for Tetrapak, you will not be able to squeeze back a glass bottle.
In order to make it clear which category of waste is one or the other trash, on all product packaging there are markings showing where to throw it.
For example, yogurt is specified that the cover should be discarded in plastic trash, and the Cup — combustible waste.
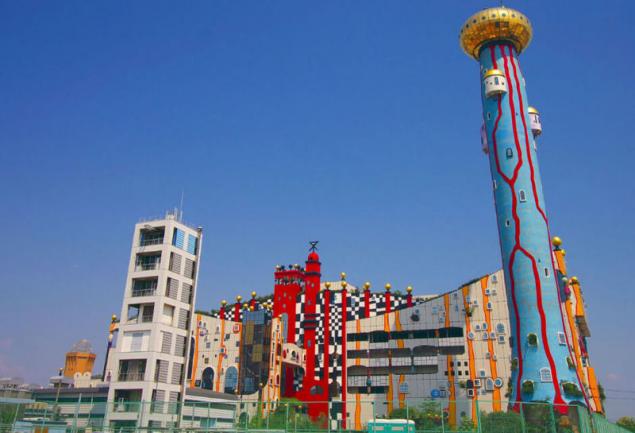

Burning of waste In combustible waste enters a lot. Even paper, 80% of which Japanese pass for processing, dispose only at 63%.
The rest — burned, like most of the other debris. Although all over the world MSW incineration is considered to be not environmentally friendly, Japan along with the USA is an exception, because in these countries, we use the most modern disposal technology — plasma gasification.
Solid waste in this technique, the processed plasma stream with temperature of 1200ºC and above. At this temperature the resin is not formed, and the toxic waste are destroyed. 30 tons of garbage are left with 6 tons of ash, which is then purified and used in construction. The plant not only destroys the waste but also generates electricity, which is provided with city houses, baths, swimming pools.
Generally in society formed the attitude to the waste recycling industry, in which this case gives rise to pleasant associations. So, near waste recycling plants break parks, and businesses themselves lead tours, they equip lecture halls for students.
Some of the objects of the waste recycling industry can be considered a real architectural treasure. For example, the plant Maishima in Osaka, designed by Viennese artist friedensreich Hundertwasser, the outside resembles an entertainment complex, and inside is decorated with paintings of the artist.
The plant not only recycles waste into electricity but also serves a social function — it has a rehabilitation centre for the disabled.
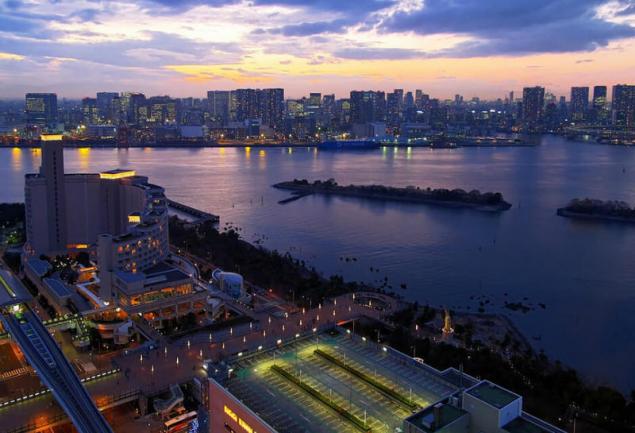

Islands of waste Slag from the combustion of waste used in construction. It is compressed in a huge briquettes, which later build buildings and even entire Islands.
The most famous of them — the artificial island of Odaiba in Tokyo Bay, which is a luxury residential complex. Generally, such Islands post anything: housing, parks, factories, airports — in General, increase the size of the state at the expense of the former debris.
Not all the trash is burning — 17-18% of waste in Japan recycled. For example, of glass make the new bottle, and turn broken glass into building materials, in particular glass dust is used for walls.
Of recycled plastic in Japan made sports uniforms, work clothing, carpet.

The philosophy of "mottainai" Japan recycles 90% of waste, but still concerned about their number. According to statistics, the average Japanese person produces about a kilogram of garbage.
Realizing that all rework is impossible, the Japanese decided to follow the example of other countries and introduce a program of "zero waste". Its essence is to minimize not only waste, but in General the materials used.
Society embraced the idea of a "mottainai", which reads: "don't kill the not yet fully".
In the town of Kamikatsu the government implements the idea of a complete abandonment of disposable products. In 2003, the municipality began to actively carry out special structural reform aimed at reducing the amount of disposable goods. The ultimate goal — by 2020 to make the city became totally "waste-free".
Now 60% of the population, Kamikatsu made their choice in favor of multiple use products that significantly reduce the amount of waste. By the way, every dealer shall submit an annual report that he had personally done to it less was purchased, for example, plastic bags.
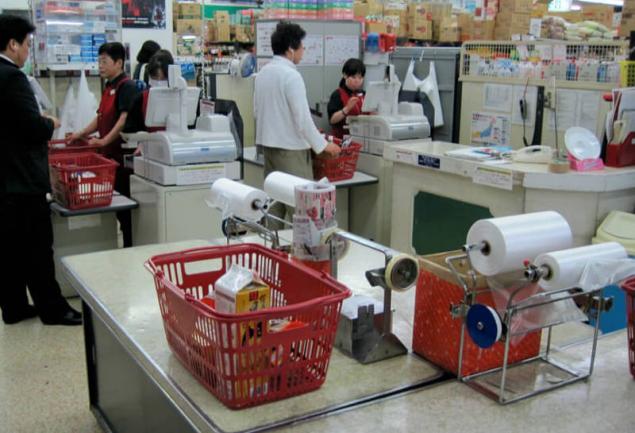

Green tokens as a sign of rejection of the package, Reducing consumption of plastic bags is one of the important directions of the movement "mottainai".
The fact that the Japanese are very fond of when each product, each product is Packed in an individual box or bag. Due to this feature, in Japan, annually use about 30 billion packages.
The government began to promote their economical use: now in stores do not give the default package, first ask whether he is the buyer. In some supermarkets the buyer to take special green token and put it in my shopping cart — so he will give the merchant to understand what's in the package is not needed.
The principle of "mottainai" applies not only to packaging but also all household goods. It also complies with the principles of Shintoism is the main religion of Japan. According to the concept of "mottainai", all the earthly blessings bestowed from above and to waste anything unnecessarily, to lose or throw away is a sin.
So those Japanese who don't want to ruin your karma, try careful with products and taught to this younger generation. published
Author: Asya Malyutina P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: recyclemag.ru/article/kak-sortiruyut-i-pererabatyivayut-musor-v-yaponii

Four types of waste Principles of separating garbage in Japan depend on the area and requirements of municipal authorities, but most often waste is separated into four categories, which are slightly different from traditional separation.
Here in different pots, put a garbage non-combustible, combustible, recyclable and bulky. Moreover, for each type of waste there are special packages of a certain color and volume make it easier to distinguish the dregs of what type is in them.
For large items, which, of course, the packages do not fit, glued special sticker.
That everything was graded properly, keep working, serving the garbage truck. Machine garbage collection comes at a certain time.
By this time the inhabitants carried their bags, and since they are transparent, scavengers are able to trace the truth of sorted waste. If there are violations, the packages don't take
The garbage truck not only comes at certain hours, but on certain days. Each type of waste is deposited exactly at the appointed day of the week, which is set by the municipality.
So, in the city of kita-Kyushu on Tuesday and Friday, the export of combustible waste, into the environment — cans and bottles Thursday — packing plastic. If you make, say, Tuesday plastic trash, you simply will not accept. I'll try to leave packages at musorovozki — put up a fine whole housing cooperative.

Fee for old equipment Day to dispose of large things is usually assigned separately: residents calling the company to collect garbage and make a request, there they were misleading, when the furniture will arrive the garbage truck.
For furniture, because household appliances to large debris does not apply. For its disposal need to pay separately.
This can be done in different ways. We can take her to the store where equipment was purchased, and to pay to the manufacturer for recycling.
Or you can pay in the store dispose of the goods in return for it will be given a special sticker. It can stick on the old equipment and bring to the garbage cans — the garbage truck will pick her up and take her to the scrap. This practice has led to good results: the recycling of household appliances, providing the country with more than 1 million tons of iron and 50 thousand tons of nonferrous metal per year.
Attempts to throw away unnecessary appliances and electronics without payment will result in penalties of several hundred dollars. But such cases, unconsciousness is not so much — discipline and love of order of the Japanese blood.

Trash-sorcery To guests of the country also abide by the rules of separate collection, the Japanese have found on the streets of the special ballot box: the holes in them are made so that anything other than what they are, there were not included.
If compartment boxes are designed for Tetrapak, you will not be able to squeeze back a glass bottle.
In order to make it clear which category of waste is one or the other trash, on all product packaging there are markings showing where to throw it.
For example, yogurt is specified that the cover should be discarded in plastic trash, and the Cup — combustible waste.

Burning of waste In combustible waste enters a lot. Even paper, 80% of which Japanese pass for processing, dispose only at 63%.
The rest — burned, like most of the other debris. Although all over the world MSW incineration is considered to be not environmentally friendly, Japan along with the USA is an exception, because in these countries, we use the most modern disposal technology — plasma gasification.
Solid waste in this technique, the processed plasma stream with temperature of 1200ºC and above. At this temperature the resin is not formed, and the toxic waste are destroyed. 30 tons of garbage are left with 6 tons of ash, which is then purified and used in construction. The plant not only destroys the waste but also generates electricity, which is provided with city houses, baths, swimming pools.
Generally in society formed the attitude to the waste recycling industry, in which this case gives rise to pleasant associations. So, near waste recycling plants break parks, and businesses themselves lead tours, they equip lecture halls for students.
Some of the objects of the waste recycling industry can be considered a real architectural treasure. For example, the plant Maishima in Osaka, designed by Viennese artist friedensreich Hundertwasser, the outside resembles an entertainment complex, and inside is decorated with paintings of the artist.
The plant not only recycles waste into electricity but also serves a social function — it has a rehabilitation centre for the disabled.

Islands of waste Slag from the combustion of waste used in construction. It is compressed in a huge briquettes, which later build buildings and even entire Islands.
The most famous of them — the artificial island of Odaiba in Tokyo Bay, which is a luxury residential complex. Generally, such Islands post anything: housing, parks, factories, airports — in General, increase the size of the state at the expense of the former debris.
Not all the trash is burning — 17-18% of waste in Japan recycled. For example, of glass make the new bottle, and turn broken glass into building materials, in particular glass dust is used for walls.
Of recycled plastic in Japan made sports uniforms, work clothing, carpet.

The philosophy of "mottainai" Japan recycles 90% of waste, but still concerned about their number. According to statistics, the average Japanese person produces about a kilogram of garbage.
Realizing that all rework is impossible, the Japanese decided to follow the example of other countries and introduce a program of "zero waste". Its essence is to minimize not only waste, but in General the materials used.
Society embraced the idea of a "mottainai", which reads: "don't kill the not yet fully".
In the town of Kamikatsu the government implements the idea of a complete abandonment of disposable products. In 2003, the municipality began to actively carry out special structural reform aimed at reducing the amount of disposable goods. The ultimate goal — by 2020 to make the city became totally "waste-free".
Now 60% of the population, Kamikatsu made their choice in favor of multiple use products that significantly reduce the amount of waste. By the way, every dealer shall submit an annual report that he had personally done to it less was purchased, for example, plastic bags.

Green tokens as a sign of rejection of the package, Reducing consumption of plastic bags is one of the important directions of the movement "mottainai".
The fact that the Japanese are very fond of when each product, each product is Packed in an individual box or bag. Due to this feature, in Japan, annually use about 30 billion packages.
The government began to promote their economical use: now in stores do not give the default package, first ask whether he is the buyer. In some supermarkets the buyer to take special green token and put it in my shopping cart — so he will give the merchant to understand what's in the package is not needed.
The principle of "mottainai" applies not only to packaging but also all household goods. It also complies with the principles of Shintoism is the main religion of Japan. According to the concept of "mottainai", all the earthly blessings bestowed from above and to waste anything unnecessarily, to lose or throw away is a sin.
So those Japanese who don't want to ruin your karma, try careful with products and taught to this younger generation. published
Author: Asya Malyutina P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: recyclemag.ru/article/kak-sortiruyut-i-pererabatyivayut-musor-v-yaponii