944
65 years of nuclear tests
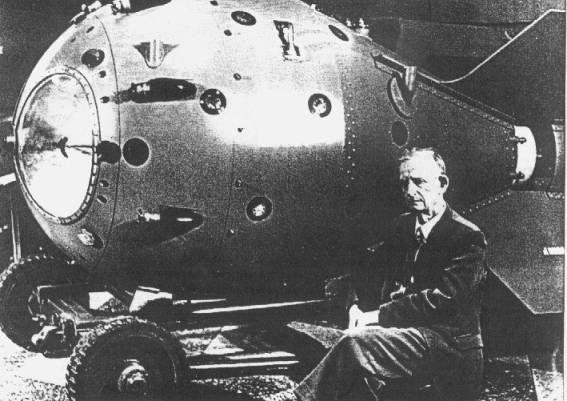
For the first time a nuclear weapon has been created in the US during the project "Manhattan" in 1945 by the NKVD Agency of the United States informed in detail about all of Stalin's work on the program. When the last Soviet leader was informed of the nuclear research by Harry Truman, the latter was surprised how easy Stalin reacted to this, and even thought that he did not understand. In fact, the project "Manhattan" was so secretive that Truman did not know about him before he became president.
In August 1945, Truman ordered the bombing of two Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Most likely, the act was motivated by a desire to show the world its power and ruthlessness as the first test has been carried out for three weeks before that.
The first Soviet nuclear test was conducted August 29, 1949.
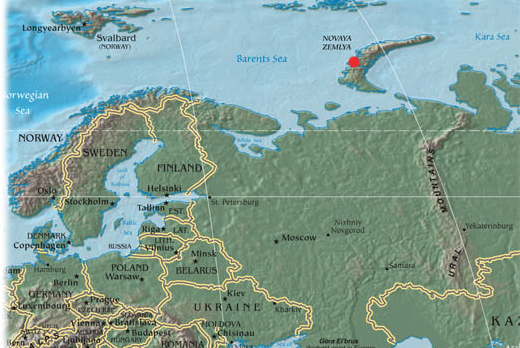
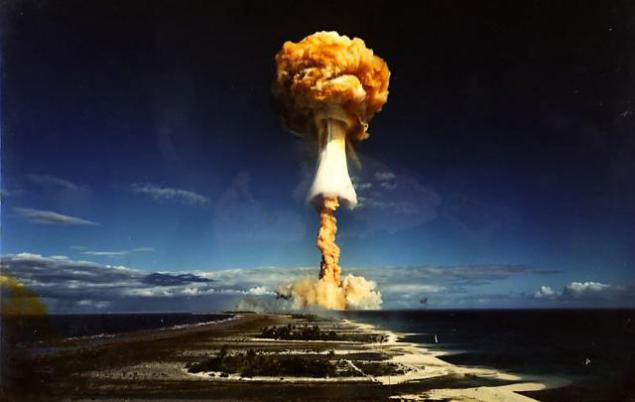
In the Soviet Union - August 12 1953 the largest thermonuclear charge for all the tests was the Soviet "Tsar-bomb" (100 megatonnes) tested at half its capacity - about 57 megatons exploded at the site of dry nose, at the site in the New Earth. < br />
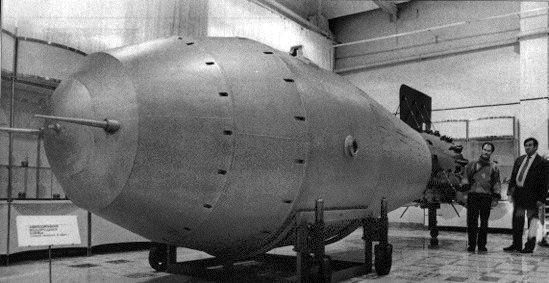
Tsar Bomb - AN602 (aka "Tsar-bomb", it "gruel", and also (erroneously) RDS-202 and RN202) - thermonuclear bombs, developed in the USSR in 1954-1961 gg. a group of nuclear physicists headed by Academician of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR Igor Kurchatov. The most powerful bomb in the history of mankind. According to various sources there has from 57 to 58, 6 megatons of TNT equivalent.
The development team consisted of Sakharov, VB Adamski, N. Babaev, A. Trutnev Yu, N. Smirnov and others.
Place explosion:
The carrier "Super bomb" has been created, but the real test was postponed for political reasons: Khrushchev was going to the United States and the Cold War was a pause. Tu-95B ferried to the airfield in Uzin, where it was used as a training aircraft, and is not listed as a fighting machine. However, in 1961, with the beginning of a new round of the Cold War, the test "the Super" again become relevant. On Tu-95B immediately replaced all the connectors on the system electrics reset and removed flaps bomb bay - a real bomb by weight (26, 5 tons [10], including the weight of the parachute system - 0, 8 tons [11]) and the size was slightly greater layout (in particular, it is now a vertical dimension greater than the size of the bomb bay in height). The plane was also covered with a special reflective white paint.


In 1963, all nuclear and many non-nuclear states signed a treaty on the limitation of nuclear tests, in which the duty to refrain from nuclear tests in the atmosphere, underwater and in outer space permitted underground tests. France continued ground testing until 1974, and China - until 1980. The last underground nuclear test was conducted in 1990 by the Soviet Union, Great Britain in 1991, the United States in 1992, France and China in 1996. After the adoption of a treaty on the complete prohibition of nuclear tests in 1996, all these countries have committed not to resume nuclear weapons tests. Do not signatories, India and Pakistan conducted nuclear tests last in 1998.
October 9, 2006 to conduct a nuclear test North Korea said. May 25, 2009 North Korea made a second nuclear test.
September 22, 1979 was carried out nuclear tests on the island of Bouvet Island (South Africa). None of the countries responsible for the bombing did not take.
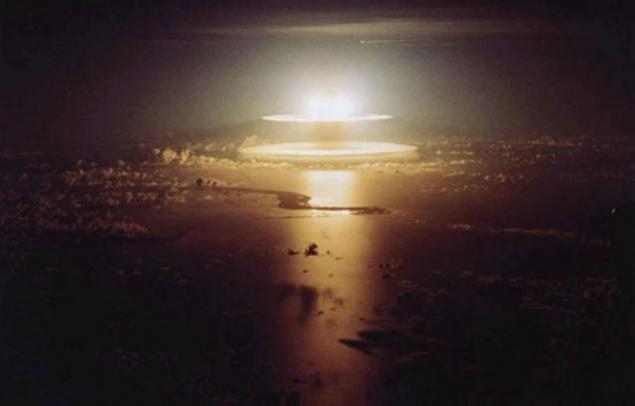


"Nuclear arms race" - the confrontation between the USSR and the United States for supremacy in the field of nuclear weapons during the Cold War. During the Cold War, and some other countries have been developing nuclear weapons, but no state to produce it on a scale in which this is done the two superpowers. Sometimes referred to as the nuclear arms race confrontation between India and Pakistan in the late 90s.
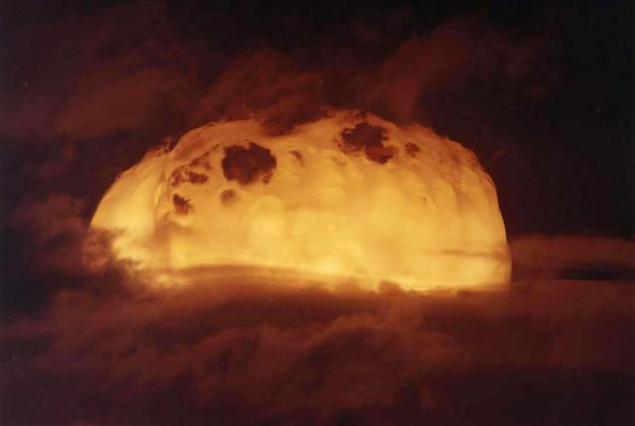
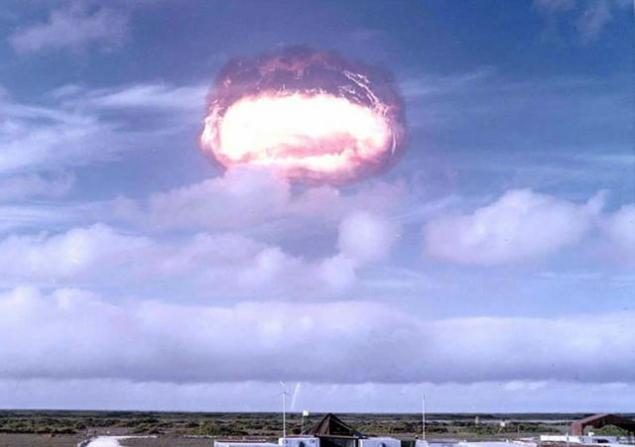


In the first years after the Second World War, the US was the only "nuclear state" in the world. US leaders knew that the Soviet Union is very far from creating its own bomb. Meanwhile, the US tried to make the most use out of their temporary superiority. In particular, there have been attempts by the pressure to negotiate with Stalin on issues such as Berlin and Czechoslovakia. In this situation, the Soviet leader decided that just because of this US Open will not risk a new war against the Soviet regime.
Meanwhile, in the Soviet Union were developing most actively to create its own nuclear bomb. During the war, the study was limited due to lack of uranium, but deliveries from eastern Europe are now solved this problem. For physicists have created all conditions to speed up the pace of work. The curator of works was Lavrenti Beria. The work of Soviet scientists checked using the information sent by agents from the United States.
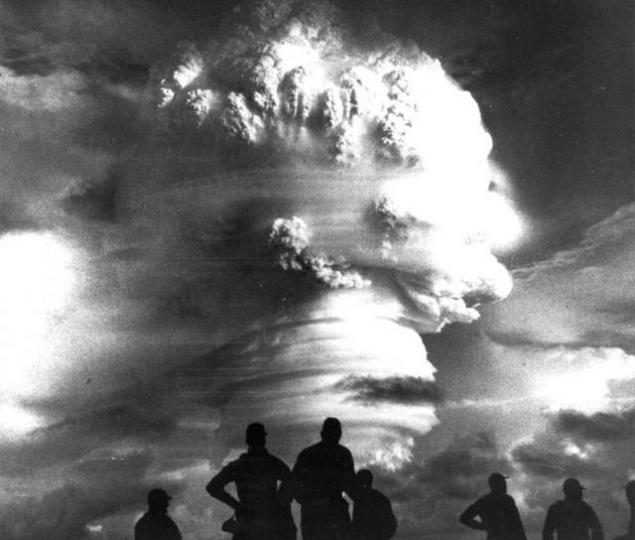
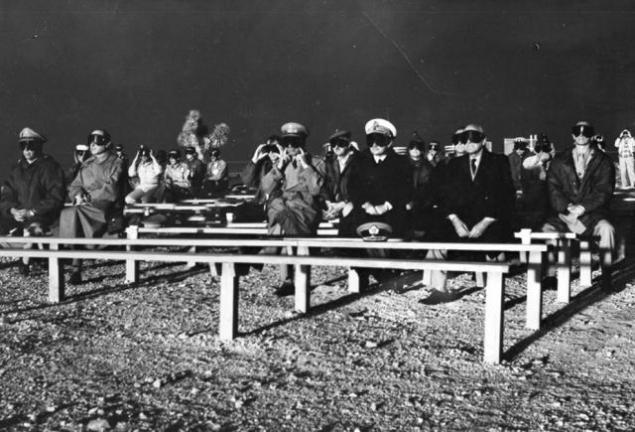


In the United States believed that the Soviet Union would not be nuclear weapons at least until the mid-50s, when the 29 August 1949 the work of Soviet nuclear physicists ended triumphant success that shook the entire world. The bomb RDS-1, exploded that day in the West called "Joe-1". Start a nuclear race.
Also atomic bomb test on Aug. 29, 1949, in the Soviet Union by the end of 1949 had made two bomb RDS-1, and in 1950 - nine. In January-February 1951 it was made four atomic bombs. Thus, the USSR to March 1, 1951 there were 15 nuclear bombs such as RDS-1. By the end of 1951 it was made even 29 atomic bomb RDS-1, including the first three series produced atomic bombs.
After a successful trial September 24, 1951 the Soviet nuclear charge "502-M" (RDS-2) by the end of 1951 it began to produce atomic bombs of the type RDS-2. On 1 January 1952 the USSR had 35 nuclear bombs.
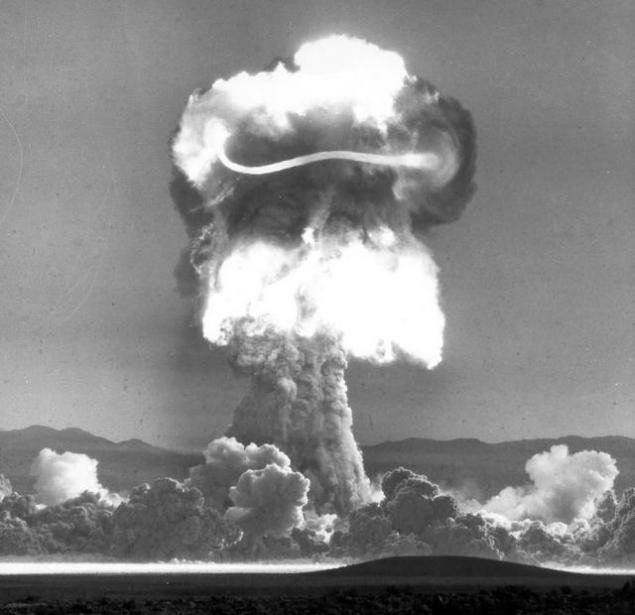
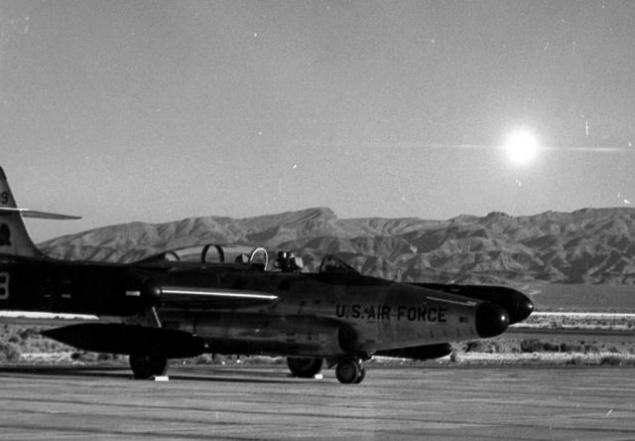
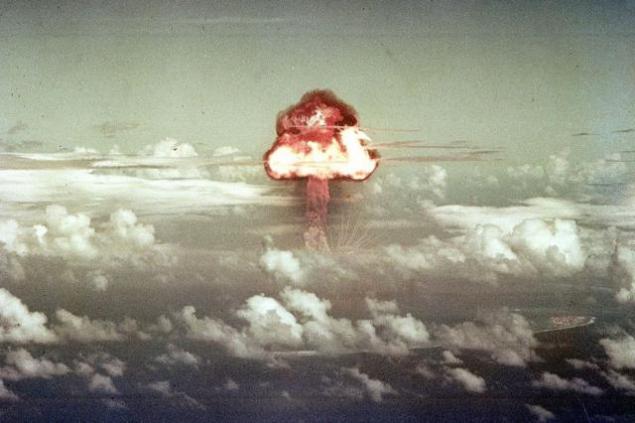




October 18, 1951, Soviet aviation atomic bomb (RDS-3 with nuclear warheads "M-501") was first tested by dropping it from an airplane (Tu-4). [1]
We invest huge amounts of money to improving the quality of weapons and increase its amount. Both nations quickly began to develop thermonuclear weapons. US detonated a device on November 1, 1952. The newly surprising of all, the Soviet Union made a thermonuclear explosion in just 8 months. Soviet hydrogen bomb RDS-6s was almost entirely the product of its own design as well as espionage in the United States has not brought results.
It was actively developing and their means of delivery of nuclear weapons in the first place they were bombers. In this area, the United States began working with obvious handicap, but the advent of jet interceptor has reduced the US advantage in the no. In the early 50s the US Air Force were presented to jet bombers B-47 and B-52's, able to penetrate Soviet airspace.


Discharging
The fear of mutual destruction, the economic problems associated with the arms race, made it possible to start the process of detente. USSR and the USA, taught by experience of the early '60s were able to agree on some of the provisions that limit the growth of nuclear arsenals. Treaties were signed SALT SALT-I and-II, of the Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, the ABM.
But even so, nuclear stocks continued to grow. Systems have been developed missiles with multiple warheads. Both countries were still able to destroy each other several times.
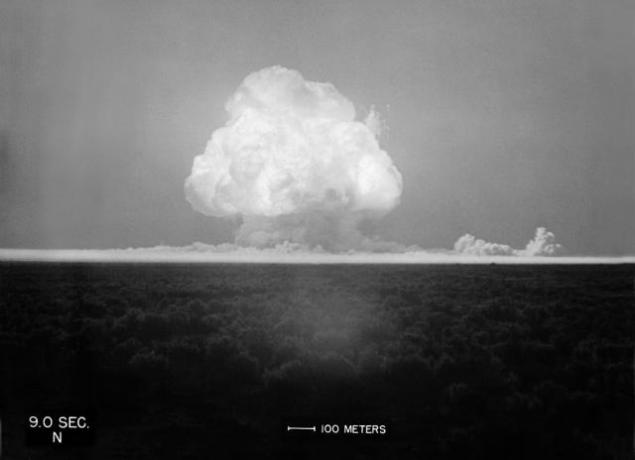
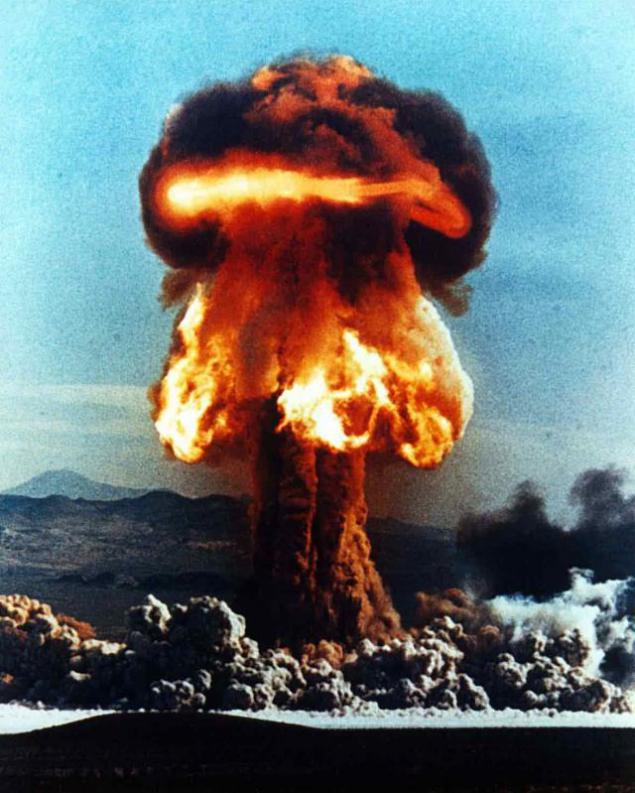


After the Cold War
With the end of the Cold War, spending on nuclear arsenal began to decline sharply, especially in Russia. The pace of development of new systems significantly decreased. However, in the US, and Russia's nuclear stockpiles are still measured in thousands of warheads. In the United States it launched a large-scale program for the disposal of nuclear weapons.
After the end of the Cold War, such as huge amounts of money are invested in the development of nuclear weapons, is now invested in the program for the restoration of environmental damage caused by the nuclear standoff. It is symbolic that the majority of plants for the production of nuclear weapons have been converted into factories for recycling the same weapon.
Russia is confronted with additional difficulties associated with the collapse of the Soviet Union. In addition to the Russian Federation, the Soviet nuclear weapons still housed in some republics (Belarus, Kazakhstan, Ukraine). Under international pressure (in fact, the United States and Russia), these states have agreed to export stored their nuclear warheads to Russia and under the guarantees of its security from the Western countries refused to claim for membership in the nuclear club.
Nuclear artillery
Deep-water nuclear explosion
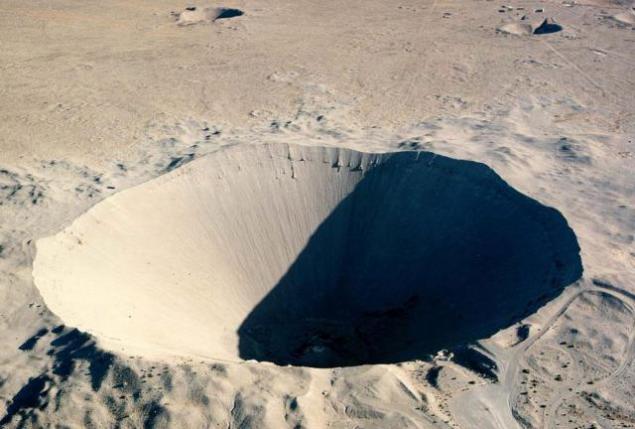
Underground nuclear explosion























