973
Animals in space
19 ph.
Animals in space - animals in scientific research purposes are sent to space on space ships. Before the release of the person in space (1961) Animal flights were intended to check whether the future astronauts to survive the flight, and if so, how the flight may affect their health. In the era of manned space flight animals sent into space for the study of various kinds of biological processes, the effects of microgravity and other purposes.

2. Dogs
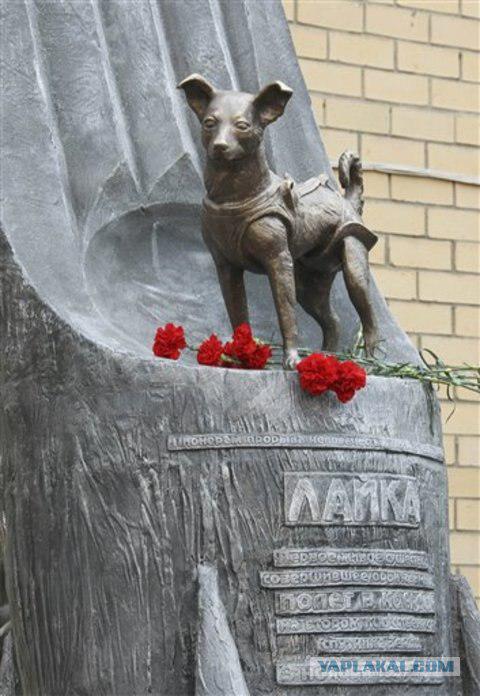
The animals for the needs of space exploration began to use very early. Already on the first Soviet satellite, launched on 3 November 1957, it was a living being - the dog Laika.

3. At the time, people still knew very little about the space, and the spacecraft is not yet able to return from orbit. Therefore Laika forever remain in outer space. Laika lived a few hours in weightlessness, and then, as the official reports, "astronaut" put to sleep.
Until a few months of the second Soviet satellite with dead Laika cheat coils and in April of 1958 he entered the Earth's atmosphere and burned.

4. When the British SPCA protested about the martyrdom of dogs, the Soviet industry to respond quickly released cigarettes "likes" with the image of the legendary dogs.

5. The first experiments with sending into space dogs began in 1951 suborbital flight made dog Gypsy, dezik, pliers, fashionista, gnats, unlucky, Siskin, Little Lady, Bold, Baby, Snowflake, Bear, Sandy, Zib, Fox, Rita, Bulba , Button, Minda, Albina, Red, join of Palma, The Brave One, motley, Pearl, fry, Fluff, Belyanka, Zhulba, Button. 1960 was an attempt to bring into space dogs Bars and chanterelles, but at 28, 5 seconds after the start of the rocket exploded.

6. The first successful orbital flight with the return to Earth carried dogs Belka and Strelka 19 August 1960.

7. In the USSR was produced before the last flight of Yuri Gagarin's test launch of a satellite with an asterisk and a dog dummy cosmonaut, the dog returned, the dummy ejected and returned to the parachute. "Dress rehearsal" was successful - after circumnavigation round expedition safely returned to Earth. Three days later, at a conference at the Academy of Sciences present all eyes were fixed on a star, and who was sitting in the front row Gagarin attention if no one paid.
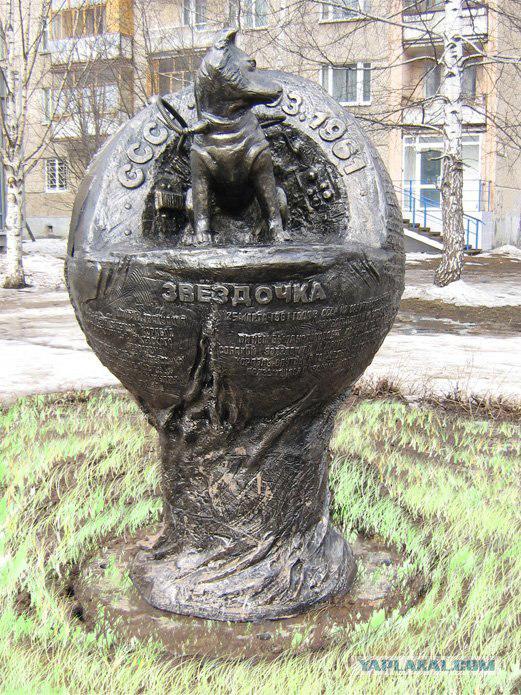

8. 5th Soviet spaceship-satellite with the dog "star" on the board. Launched March 25, 1961

9. Monkey
Soviet scientists have repeatedly launched monkeys (rhesus monkeys) into space.
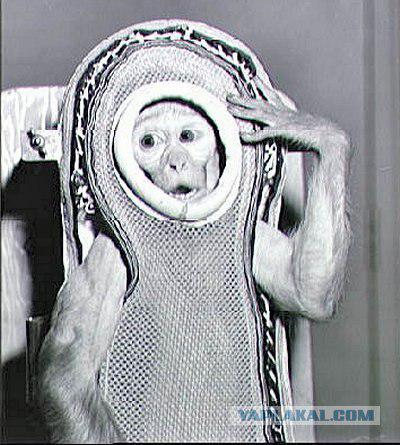

10. These animals implanted various sensors in the muscles and tendons, by which recorded EMG muscle activity and movement. They also implanted electrodes in the brain.

11. All pets monkeys were first epitope Research Institute, later SRI MP.
The Americans launched into space monkey named Bonnie in 1969. However, the animal itself felt bad and return to Earth perished.

12. Rats and mice
In the Soviet Union conducted experiments to launch into space of pregnant rats (they are fertilized before the start). It was found that one-third of the females occurs ectopic pregnancy, the embryo is not implanted in the uterus. Even if everything goes normally, the rat loses a quarter of the weight. And the fruit behind in development by 10 percent. However, after landing on a special diet rat goes on the amendment.
Unsweetened in space and male rats, but no worries of these animals are not burdened. The weight of the testes in males decreases the sperm concentration falls. The interest in the pleasures of even the most loving male disappears. Term of replanting male to female before insemination increases as compared with the earth 3 times. A week stay in weightlessness (this period of adaptation for humans) males being developed and how to break the chain.
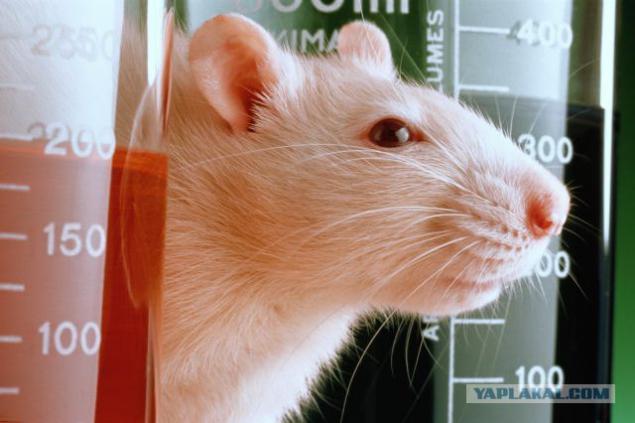

13. To sum up, the Russian researchers believe that the physiological capabilities of laboratory rats were sufficient to adapt to weightlessness and recover from it. It is essential that the main burden of adjustment falls on the beginning of the flight, and with increasing duration of the body gets used. We can therefore expect that the longer flights will not be fatal to mammals.

14. Orbital Experiment Moscow students "Space BUTTERFLY»
In 2005, the Center for Environmental Education MGDD (U) T students groups of additional education "EXCITING Entomology" developed a draft of the orbital experiment in gravitational biology "Cosmic Butterfly". As part of the Moscow public scientific and educational program "Experiment in Space" this collective project has been reviewed by experts. He successfully passed two rounds of competition of research projects students held during the implementation of this program. After that, the project was officially approved for implementation on biosatellite "Foton-M» №3, which was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on Sept. 14, 2007 and spent 12 days in orbit.

15. What is the essence of the experiment? It is well known that adult butterflies hatch from pupae, which previously occur very complex biological processes (metamorphosis). Thus from crawling wormlike larvae formed a charming flying insects. And how these processes affect the extreme gravitational effects of space flight (overload and weightlessness)? Students formulate the goal of his experiment as follows: to investigate the effects of weightlessness, overloads and other conditions of space flight on the development process in the butterfly pupa stage, and formed the vitality of adults (adult butterflies).

16. In the first half of the 1960's space experiments on living beings have ceased to be the prerogative of the Soviet Union and the United States: in 1963, the French sent into space Felisett cat with implanted electrodes in the brain, and in three years the Chinese have launched rockets with dogs on board
His "living area" is almost every space crew. On board the space stations and shuttles delivered amazing experiment: Can a spider weave a web of weightlessness, and the bees - to build a cell where the fish will float in space, where there is no difference between the top and bottom.
(Felix the Cat. The Islamic Republic of Comoros. 1992)

17. The first animal surviving in open space.
Tardigrades (Tardigrada), smuggled into orbit a group of scientists under the leadership of Ingemar Yёnssona (Ingemar Jönsson) from University College Kristianstad (Högskolan Kristianstad), were the first animals that were able to survive the harmful effects of radiation, extreme cold and vacuum of space ... and even give birth!
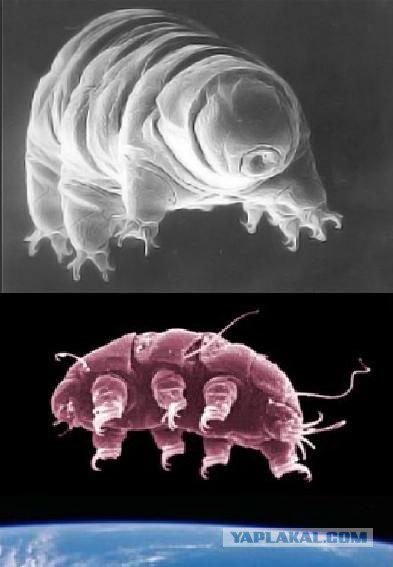
18. In recent years, since the beginning of the construction of heavy comic station "Mir" and ISS. Animals live in space with the astronauts aboard the space station. At the station "Mir" more than 10 years acted biological unit "Nature" specially designed for laboratory experiments with animals and plants.
Here the animals not only lived, but also successfully bred. In a special incubator was withdrawn several generations of birds. It is particularly interesting to study the plants grown in space. The conditions of weightlessness on fruit trees are obtained several times larger than Earth.

19. The results of experiments with animals and plants, the ongoing aboard the space station, will be useful to future interplanetary missions. In today's spaceship to Mars.

Source:
Animals in space - animals in scientific research purposes are sent to space on space ships. Before the release of the person in space (1961) Animal flights were intended to check whether the future astronauts to survive the flight, and if so, how the flight may affect their health. In the era of manned space flight animals sent into space for the study of various kinds of biological processes, the effects of microgravity and other purposes.

2. Dogs
The animals for the needs of space exploration began to use very early. Already on the first Soviet satellite, launched on 3 November 1957, it was a living being - the dog Laika.

3. At the time, people still knew very little about the space, and the spacecraft is not yet able to return from orbit. Therefore Laika forever remain in outer space. Laika lived a few hours in weightlessness, and then, as the official reports, "astronaut" put to sleep.
Until a few months of the second Soviet satellite with dead Laika cheat coils and in April of 1958 he entered the Earth's atmosphere and burned.

4. When the British SPCA protested about the martyrdom of dogs, the Soviet industry to respond quickly released cigarettes "likes" with the image of the legendary dogs.

5. The first experiments with sending into space dogs began in 1951 suborbital flight made dog Gypsy, dezik, pliers, fashionista, gnats, unlucky, Siskin, Little Lady, Bold, Baby, Snowflake, Bear, Sandy, Zib, Fox, Rita, Bulba , Button, Minda, Albina, Red, join of Palma, The Brave One, motley, Pearl, fry, Fluff, Belyanka, Zhulba, Button. 1960 was an attempt to bring into space dogs Bars and chanterelles, but at 28, 5 seconds after the start of the rocket exploded.

6. The first successful orbital flight with the return to Earth carried dogs Belka and Strelka 19 August 1960.

7. In the USSR was produced before the last flight of Yuri Gagarin's test launch of a satellite with an asterisk and a dog dummy cosmonaut, the dog returned, the dummy ejected and returned to the parachute. "Dress rehearsal" was successful - after circumnavigation round expedition safely returned to Earth. Three days later, at a conference at the Academy of Sciences present all eyes were fixed on a star, and who was sitting in the front row Gagarin attention if no one paid.

8. 5th Soviet spaceship-satellite with the dog "star" on the board. Launched March 25, 1961

9. Monkey
Soviet scientists have repeatedly launched monkeys (rhesus monkeys) into space.

10. These animals implanted various sensors in the muscles and tendons, by which recorded EMG muscle activity and movement. They also implanted electrodes in the brain.

11. All pets monkeys were first epitope Research Institute, later SRI MP.
The Americans launched into space monkey named Bonnie in 1969. However, the animal itself felt bad and return to Earth perished.

12. Rats and mice
In the Soviet Union conducted experiments to launch into space of pregnant rats (they are fertilized before the start). It was found that one-third of the females occurs ectopic pregnancy, the embryo is not implanted in the uterus. Even if everything goes normally, the rat loses a quarter of the weight. And the fruit behind in development by 10 percent. However, after landing on a special diet rat goes on the amendment.
Unsweetened in space and male rats, but no worries of these animals are not burdened. The weight of the testes in males decreases the sperm concentration falls. The interest in the pleasures of even the most loving male disappears. Term of replanting male to female before insemination increases as compared with the earth 3 times. A week stay in weightlessness (this period of adaptation for humans) males being developed and how to break the chain.

13. To sum up, the Russian researchers believe that the physiological capabilities of laboratory rats were sufficient to adapt to weightlessness and recover from it. It is essential that the main burden of adjustment falls on the beginning of the flight, and with increasing duration of the body gets used. We can therefore expect that the longer flights will not be fatal to mammals.

14. Orbital Experiment Moscow students "Space BUTTERFLY»
In 2005, the Center for Environmental Education MGDD (U) T students groups of additional education "EXCITING Entomology" developed a draft of the orbital experiment in gravitational biology "Cosmic Butterfly". As part of the Moscow public scientific and educational program "Experiment in Space" this collective project has been reviewed by experts. He successfully passed two rounds of competition of research projects students held during the implementation of this program. After that, the project was officially approved for implementation on biosatellite "Foton-M» №3, which was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on Sept. 14, 2007 and spent 12 days in orbit.

15. What is the essence of the experiment? It is well known that adult butterflies hatch from pupae, which previously occur very complex biological processes (metamorphosis). Thus from crawling wormlike larvae formed a charming flying insects. And how these processes affect the extreme gravitational effects of space flight (overload and weightlessness)? Students formulate the goal of his experiment as follows: to investigate the effects of weightlessness, overloads and other conditions of space flight on the development process in the butterfly pupa stage, and formed the vitality of adults (adult butterflies).

16. In the first half of the 1960's space experiments on living beings have ceased to be the prerogative of the Soviet Union and the United States: in 1963, the French sent into space Felisett cat with implanted electrodes in the brain, and in three years the Chinese have launched rockets with dogs on board
His "living area" is almost every space crew. On board the space stations and shuttles delivered amazing experiment: Can a spider weave a web of weightlessness, and the bees - to build a cell where the fish will float in space, where there is no difference between the top and bottom.
(Felix the Cat. The Islamic Republic of Comoros. 1992)

17. The first animal surviving in open space.
Tardigrades (Tardigrada), smuggled into orbit a group of scientists under the leadership of Ingemar Yёnssona (Ingemar Jönsson) from University College Kristianstad (Högskolan Kristianstad), were the first animals that were able to survive the harmful effects of radiation, extreme cold and vacuum of space ... and even give birth!

18. In recent years, since the beginning of the construction of heavy comic station "Mir" and ISS. Animals live in space with the astronauts aboard the space station. At the station "Mir" more than 10 years acted biological unit "Nature" specially designed for laboratory experiments with animals and plants.
Here the animals not only lived, but also successfully bred. In a special incubator was withdrawn several generations of birds. It is particularly interesting to study the plants grown in space. The conditions of weightlessness on fruit trees are obtained several times larger than Earth.

19. The results of experiments with animals and plants, the ongoing aboard the space station, will be useful to future interplanetary missions. In today's spaceship to Mars.

Source:























