758
Asymmetrical plane
Despite the fact that World War II ended, the results of creative engineers of III Reich is still there with a genuine interest from people interested in the history of technology.
It has a lot of explanation, and one of them is the fact that the level of tasks and the development of a flight of fancy (especially long-term) of the German engineers that time simply did not have analogues. The fact that in other countries was seen only as a curious project, the Germans managed to not use practice. This was highlighted in the aviation industry.
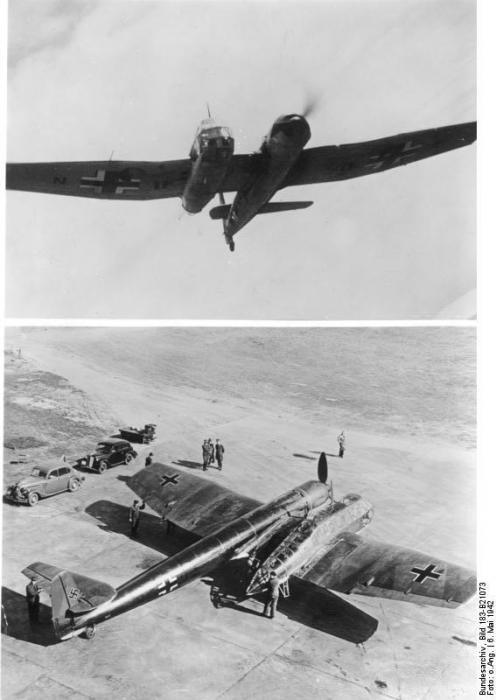

Among the most unusual configurations, ever to appear in the history of aviation, conscious, perhaps, one of the most original was neighbor reconnaissance / spotter asymmetrical design VV.141 Dr. Richard Vogt

B early 1937 RLM (Reichsluftfahrt Ministerium) issue the companies Arado and Focke-Wulf on the near scout / light bomber / spotter that can perform tasks easily and director dymzaves stormtrooper. The setting determines the crew of three, all-round visibility for the crew and engine power 850-900 hp on takeoff. From the outset, the Technical Department favored Arado, but the result was created Ar.198 bad. Hamburger flyugtsoygbau RLM was not included in the list of participants, but the engineer Richard Vogt, who had some ideas about this, proposed initiative project.

The technical department is not connected with the project, you must install the same engine, but for tactical reasons, it was clear that the army is unlikely the aircraft was designed with lots of engines. Vogt decided that the only way to ensure all-round visibility with a single-engine airplane - apply the asymmetrical arrangement in which the crew is placed in the glass gondola right. He also believed that the unbalanced circuit will get rid of torque screw - a perennial headache for the design of single-engine airplanes.
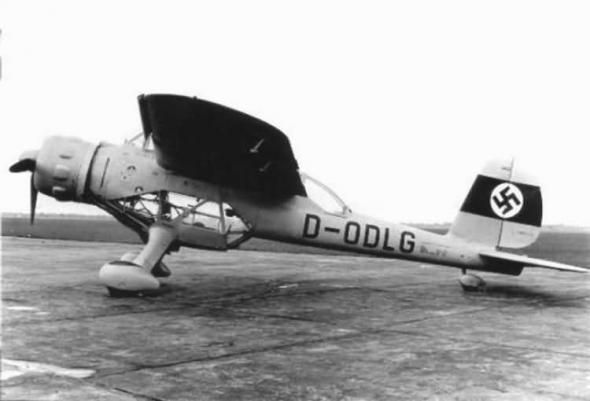

Thus Vogt proposed project asymmetrical RLM aircraft Arado but has already started to assemble Ar.198, and it is not surprising that unusual arrangement did not cause interest. However, Ernst Udet, the newly appointed chief of the design section of the Technical Department, Vogt has some support, and Hamburger Flyugtsoygverke started to self-finance the project. The first flight of this strange aircraft, the designation Ha.141 0 (D-ORJE), held February 25, 1938

Except for the excessive sensitivity control and a small landing Ha.141 Kozlenev V0 behaved remarkably well, followed by a formal contract for three prototypes, and existing in it was not included. After lengthy negotiations, agreed RLM still turn the plane of the three experimental machines. Thus D-ORJE received official designation VV.141 V2, when the company name was changed to Abteylung flyugtsoygbau der shifsverft Blohm und Voss. The second aircraft was the first official experienced under the designation VV.141 V1 (# 171).

The cockpit did not work for RLM, and VV.141 V1 gondola crew was redesigned and became more like a cabin Fw.189, created at the same time. Glazing consisting of a number of flat panels. It was the setting of two fixed 7.9 mm machine guns forward and two machine guns at the same mobile unit. The first really got weapons VV.141 V3. It was provided, and the suspension of four 50 kg bombs. Common sizes VV.141 V1 rose slightly: range from 15 to 15, 1 m, the area of the wing 40, 1 to 40, 5 m, length 11 1 to 11 4 m. VV.141 V1 (D- OTTO) had an empty weight of 3092 kg and 3832 kg takeoff. Flight tests began in September 1938. At the beginning of the test revealed a problem with the hydraulics, and 5 October 1938 was followed by a forced landing on its belly after the chassis to release only half.

Fortunately he was soon ready VV.141 V3 (D-OLGA), which is already considered a prototype for the series.

Performance characteristics BV.141A
Type - spotter reconnaissance, light bomber
The engine - a BMW 132N, 9-cylinder radial, rated at 865 hp and 960 hp of the earth at an altitude of 3000 m
Armament:
2 * 7.9 mm fixed MG-17 shooting forward
2 * 7, 9 mm MG-15 mobile units for self
4 * 50 kg bomb
Maximum speed:
338 km / h at ground
397 km / h at an altitude of 3800 m
Cruising speed:
309 km / h at ground
363 km / h at an altitude of 4500 m
Flight range - 1133 km
The ceiling - 9000 m
Weight:
Blank - 3170 kg
Takeoff - 3900 kg
Dimensions:
span - 15, 5 m
length - 12, 15 m
height - 4, 1 m
wing area - 41, 5 square meters

CPR generally disliked unusual appearance BV-141, but, as the required technical justification for departing aircraft, referred to the fact that VV.141A-0 allegedly had insufficient thrust-weight ratio. Vogt has suggested that it will take more powerful powerplant, and in early January 1939 was the version designed for more powerful VMW 801. The design of the aircraft has been completely redesigned, the layout of the new VV.141B been inspected Commission RLM February 14, 1940 Less than a year January 9, 1941 the first of the five pre-VV.141B 0 (V9) NC + OZ made its first flight. Although the Blohm und Voss received a contract for only five VV.141B-0, RLM planned to order five more pre-series and 10-series VV.141B 1.
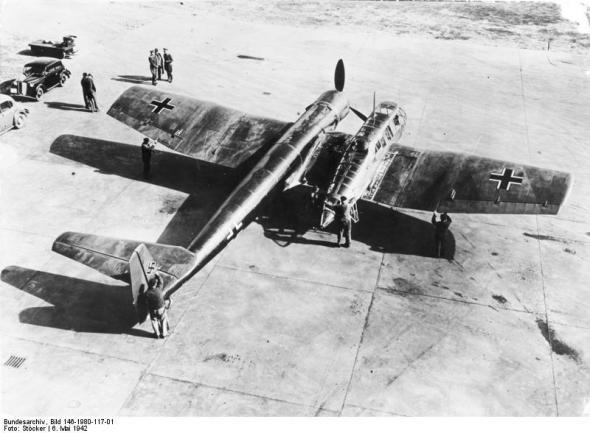

It soon became clear that the handling had VV.141B worse than its predecessor. Static tests in November 1940 highlighted the need to strengthen certain nodes. Taken remake tail, landing gear and control systems. Static tests have shown that hydraulic problems were, and revealed shortcomings in the landing gear mechanism. Then, when the engine runs, problems have arisen with the BMW 801. By the time the flight testing static is still ongoing, and, as a consequence, the maximum speed VV.141 V9 was limited to 450 km / h. Trimmer aileron was ineffective, and the ailerons themselves too sensitive. Continued troubles with hydraulics and virtually throughout the test program.
Completion of the remaining four VV.141B-0 delayed due to waiting for resolution of problems c VV.141 V9. Compared with VV.141A, in a series of different sizes increased, and changed the shape of the wing. Instead oval fuselage of steel round over the entire length, and the tail has been completely redesigned. On VV.141 V2 has been tested another innovation - an asymmetric stabilizer: the right side of the stabilizer was removed, and the left plane is increased. One reason was the desire to improve the field of fire an arrow, the other - especially when asymmetric circuit aerodynamics of the aircraft. Since the test showed no change with the handling of such plumage was used to VV.141B.
VV.141 V9 admitted to the test center at Rechlin in May 1941, June 1 was joined V10 (NC + RA), which is three months collecting dust in anticipation of the delivery screw. Official test program is always accompanied by a variety of minor troubles. When the fourth VV.141 V12 (NC + RF) arrived in Travemünde for testing weapons, it turned out that when shooting cabin was filled with powder gases. Meanwhile, the tests began V11 (NC + RC), but minor defects followed one after another, and it is not surprising that the fifth and final VV.141B V13 (NC + RH) was prepared only to the May 15, 1943
In the fall of 1941 V10 was put in teaching and reconnaissance units in Grossenhain (Saxony) for military trials. Shortly afterwards Milch ordered that on the basis of existing VV.141 formed at least one squadron for combat on the Eastern Front.
In the spring of 1942, release Bv.141V stopped, although remaining in the backlog and planes were collected. This decision was certainly influenced by the fact that the problems were solved successfully BV.141 FW.189, and numerous minor defects VV.141. In addition, after damage plants Focke-Wulf on the Blohm und Voss was transferred production Fw.200 Condor, which took 80% of the capacity.
In total, according to various sources, it was released 28 ... 38 aircraft
There is a statement that was included in the BV.141 albums with silhouettes of enemy aircraft for air defense and settlement of the Red Army pilots in 1941, 1942.
From outstanding aircraft squadron was formed, which had to be noted at Stalingrad as spotters, and by some accounts as towing gliders. Also in June 1942 planes asymmetric schemes were reported in the Kharkov region.
In the English-language sites have met the approval of these aircraft met even on the Eastern Front in 1944. Total fought aircraft is usually estimated at 5 ... 10 cars.
I did not hit the front of the machine used to train pilots.
At the moment not aware of any BV.141 preserved to this day. While there may be somewhere in the Russian forests and swamps still lie fragments of this interesting machine.
via dr-lecktor

Source:
It has a lot of explanation, and one of them is the fact that the level of tasks and the development of a flight of fancy (especially long-term) of the German engineers that time simply did not have analogues. The fact that in other countries was seen only as a curious project, the Germans managed to not use practice. This was highlighted in the aviation industry.

Among the most unusual configurations, ever to appear in the history of aviation, conscious, perhaps, one of the most original was neighbor reconnaissance / spotter asymmetrical design VV.141 Dr. Richard Vogt

B early 1937 RLM (Reichsluftfahrt Ministerium) issue the companies Arado and Focke-Wulf on the near scout / light bomber / spotter that can perform tasks easily and director dymzaves stormtrooper. The setting determines the crew of three, all-round visibility for the crew and engine power 850-900 hp on takeoff. From the outset, the Technical Department favored Arado, but the result was created Ar.198 bad. Hamburger flyugtsoygbau RLM was not included in the list of participants, but the engineer Richard Vogt, who had some ideas about this, proposed initiative project.

The technical department is not connected with the project, you must install the same engine, but for tactical reasons, it was clear that the army is unlikely the aircraft was designed with lots of engines. Vogt decided that the only way to ensure all-round visibility with a single-engine airplane - apply the asymmetrical arrangement in which the crew is placed in the glass gondola right. He also believed that the unbalanced circuit will get rid of torque screw - a perennial headache for the design of single-engine airplanes.

Thus Vogt proposed project asymmetrical RLM aircraft Arado but has already started to assemble Ar.198, and it is not surprising that unusual arrangement did not cause interest. However, Ernst Udet, the newly appointed chief of the design section of the Technical Department, Vogt has some support, and Hamburger Flyugtsoygverke started to self-finance the project. The first flight of this strange aircraft, the designation Ha.141 0 (D-ORJE), held February 25, 1938

Except for the excessive sensitivity control and a small landing Ha.141 Kozlenev V0 behaved remarkably well, followed by a formal contract for three prototypes, and existing in it was not included. After lengthy negotiations, agreed RLM still turn the plane of the three experimental machines. Thus D-ORJE received official designation VV.141 V2, when the company name was changed to Abteylung flyugtsoygbau der shifsverft Blohm und Voss. The second aircraft was the first official experienced under the designation VV.141 V1 (# 171).

The cockpit did not work for RLM, and VV.141 V1 gondola crew was redesigned and became more like a cabin Fw.189, created at the same time. Glazing consisting of a number of flat panels. It was the setting of two fixed 7.9 mm machine guns forward and two machine guns at the same mobile unit. The first really got weapons VV.141 V3. It was provided, and the suspension of four 50 kg bombs. Common sizes VV.141 V1 rose slightly: range from 15 to 15, 1 m, the area of the wing 40, 1 to 40, 5 m, length 11 1 to 11 4 m. VV.141 V1 (D- OTTO) had an empty weight of 3092 kg and 3832 kg takeoff. Flight tests began in September 1938. At the beginning of the test revealed a problem with the hydraulics, and 5 October 1938 was followed by a forced landing on its belly after the chassis to release only half.

Fortunately he was soon ready VV.141 V3 (D-OLGA), which is already considered a prototype for the series.

Performance characteristics BV.141A
Type - spotter reconnaissance, light bomber
The engine - a BMW 132N, 9-cylinder radial, rated at 865 hp and 960 hp of the earth at an altitude of 3000 m
Armament:
2 * 7.9 mm fixed MG-17 shooting forward
2 * 7, 9 mm MG-15 mobile units for self
4 * 50 kg bomb
Maximum speed:
338 km / h at ground
397 km / h at an altitude of 3800 m
Cruising speed:
309 km / h at ground
363 km / h at an altitude of 4500 m
Flight range - 1133 km
The ceiling - 9000 m
Weight:
Blank - 3170 kg
Takeoff - 3900 kg
Dimensions:
span - 15, 5 m
length - 12, 15 m
height - 4, 1 m
wing area - 41, 5 square meters

CPR generally disliked unusual appearance BV-141, but, as the required technical justification for departing aircraft, referred to the fact that VV.141A-0 allegedly had insufficient thrust-weight ratio. Vogt has suggested that it will take more powerful powerplant, and in early January 1939 was the version designed for more powerful VMW 801. The design of the aircraft has been completely redesigned, the layout of the new VV.141B been inspected Commission RLM February 14, 1940 Less than a year January 9, 1941 the first of the five pre-VV.141B 0 (V9) NC + OZ made its first flight. Although the Blohm und Voss received a contract for only five VV.141B-0, RLM planned to order five more pre-series and 10-series VV.141B 1.

It soon became clear that the handling had VV.141B worse than its predecessor. Static tests in November 1940 highlighted the need to strengthen certain nodes. Taken remake tail, landing gear and control systems. Static tests have shown that hydraulic problems were, and revealed shortcomings in the landing gear mechanism. Then, when the engine runs, problems have arisen with the BMW 801. By the time the flight testing static is still ongoing, and, as a consequence, the maximum speed VV.141 V9 was limited to 450 km / h. Trimmer aileron was ineffective, and the ailerons themselves too sensitive. Continued troubles with hydraulics and virtually throughout the test program.
Completion of the remaining four VV.141B-0 delayed due to waiting for resolution of problems c VV.141 V9. Compared with VV.141A, in a series of different sizes increased, and changed the shape of the wing. Instead oval fuselage of steel round over the entire length, and the tail has been completely redesigned. On VV.141 V2 has been tested another innovation - an asymmetric stabilizer: the right side of the stabilizer was removed, and the left plane is increased. One reason was the desire to improve the field of fire an arrow, the other - especially when asymmetric circuit aerodynamics of the aircraft. Since the test showed no change with the handling of such plumage was used to VV.141B.
VV.141 V9 admitted to the test center at Rechlin in May 1941, June 1 was joined V10 (NC + RA), which is three months collecting dust in anticipation of the delivery screw. Official test program is always accompanied by a variety of minor troubles. When the fourth VV.141 V12 (NC + RF) arrived in Travemünde for testing weapons, it turned out that when shooting cabin was filled with powder gases. Meanwhile, the tests began V11 (NC + RC), but minor defects followed one after another, and it is not surprising that the fifth and final VV.141B V13 (NC + RH) was prepared only to the May 15, 1943
In the fall of 1941 V10 was put in teaching and reconnaissance units in Grossenhain (Saxony) for military trials. Shortly afterwards Milch ordered that on the basis of existing VV.141 formed at least one squadron for combat on the Eastern Front.
In the spring of 1942, release Bv.141V stopped, although remaining in the backlog and planes were collected. This decision was certainly influenced by the fact that the problems were solved successfully BV.141 FW.189, and numerous minor defects VV.141. In addition, after damage plants Focke-Wulf on the Blohm und Voss was transferred production Fw.200 Condor, which took 80% of the capacity.
In total, according to various sources, it was released 28 ... 38 aircraft
There is a statement that was included in the BV.141 albums with silhouettes of enemy aircraft for air defense and settlement of the Red Army pilots in 1941, 1942.
From outstanding aircraft squadron was formed, which had to be noted at Stalingrad as spotters, and by some accounts as towing gliders. Also in June 1942 planes asymmetric schemes were reported in the Kharkov region.
In the English-language sites have met the approval of these aircraft met even on the Eastern Front in 1944. Total fought aircraft is usually estimated at 5 ... 10 cars.
I did not hit the front of the machine used to train pilots.
At the moment not aware of any BV.141 preserved to this day. While there may be somewhere in the Russian forests and swamps still lie fragments of this interesting machine.
via dr-lecktor

Source: