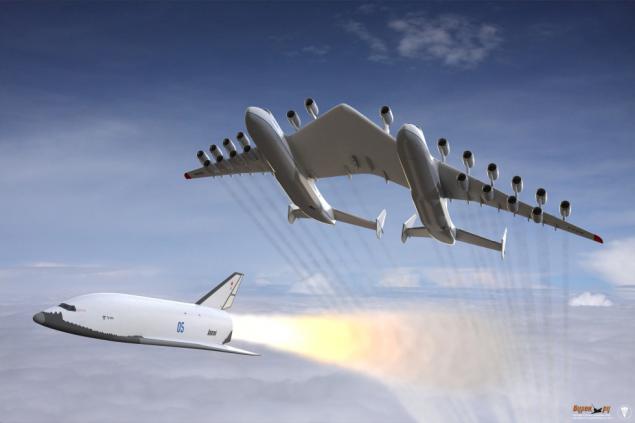

The idea of starting a spacecraft from the air carrier is regularly invited as a way to facilitate the access of radical humanity into space. However, only one booster utilizes this principle. About what is beneficial and what difficulties creates an air start this post.
A bit of history h4>
Rocket planes h5>
Air Launch very successfully used in the United States after the war for the study of flight at high speeds and altitudes. Bell X-1, which for the first time since the world was overcome by the speed of sound, was launched from the suspension on a bomber B-29:
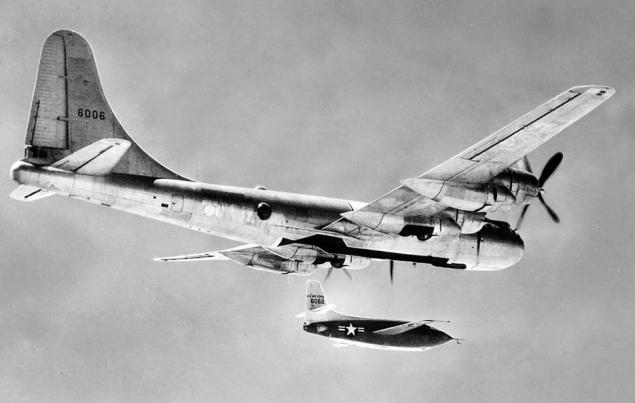

The decision was very logical - the use of rocket engines meant a small amount of fuel, which would not be enough for a good start from the ground. Model X-1 was developed - X-1A crossed the border into two Mach and studied the behavior of the aircraft at high altitudes (up to 27 km). Modifications X-1B, C, D, E were used for further studies.
The next big step was the rocket plane X-15. He also started with the air carrier - B-52 bomber:

The powerful engine developed a thrust of 250 kN (71% of the engine thrust rocket Redstone), could reach a speed of 7,000 km / h and a height of 80 km. It would seem that the US has two roads into space - fast and "dirty" on capsules «Mercury», missiles «Redstone» and «Atlas» and longer, but much more beautiful on the X-15, X-20 and subsequent projects. However, "aviation-'program has been in the shadow of space flight, and despite successfully achieved the goal, did not get such a brilliant development as a ruler« Mercury »-« Gemini »-« Apollo »

Neil Armstrong. Flew the X-15, but left the project on time. I>
Ballistic missiles h5>
An alternative approach was to develop a ballistic missile launch air. In the late fifties, when ballistic missiles require a few hours to prepare for the start, they lost strategic bombers in flexibility and reaction time on duty. Bombers could clock patrol the borders of the country of the enemy, and, after the team could strike for tens of minutes, or could also be quickly withdrawn. A ballistic missiles had a crucial advantage impossible to intercept. Had the idea of combining the advantages of the two systems - the development of a ballistic missile for strategic bomber. Thus was born the project GAM-87 Skybolt:
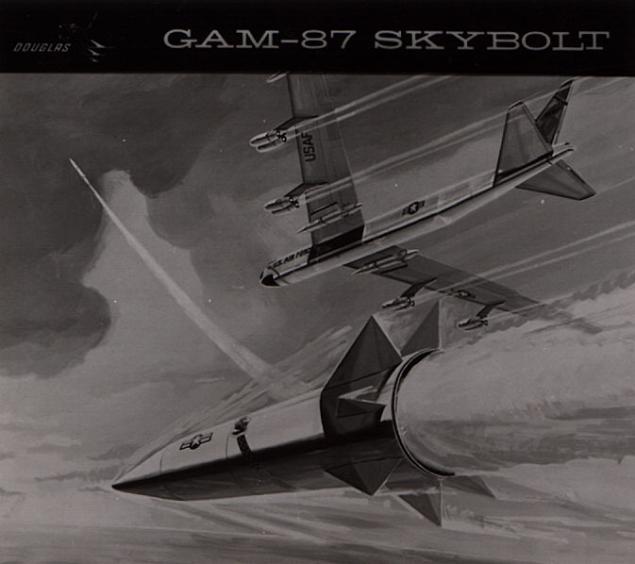

The first test launches began in 1961, the first fully successful launch took place on 19 December 1962. However, by this time the Navy received ballistic missiles for submarines Polaris, which could "patrol" under water for months. US Air Force developed solid-fuel missile Minuteman, figures which were comparable with Skybolt, but the missile was in the mine, ready for launch, which was much more convenient. The project was closed.
October 24 1974 Minuteman III missile was dropped as an experiment from the cargo compartment transporter C-5:
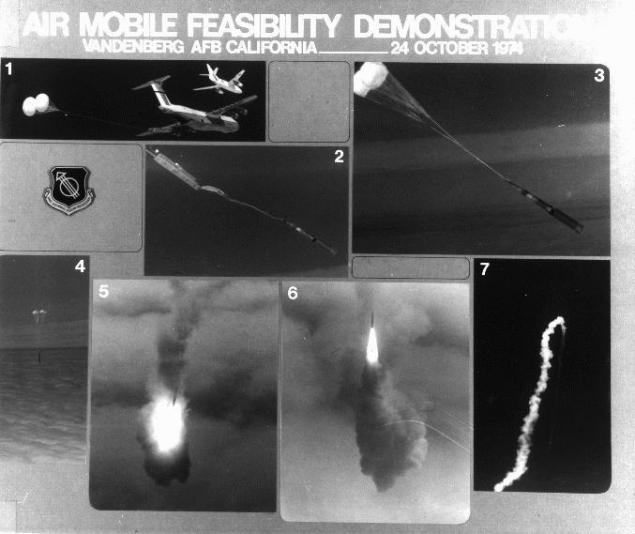

The test was successful, but the military did not see the need for such a system, and the project was canceled.
The Soviet "Spiral» h5>
In the USSR, the project was a significant one, but extremely interesting:

The system of hypersonic aircraft-razgonnika and orbital plane had to start from the runway, climb up to 30 km and speeds of up to 6M (6700 km / h). Then the orbital plane with a boost stage to fuel a pair of fluorine / hydrogen disconnected and dispersed on their own before going into orbit. The project was started in 1964 and officially closed in 1969 (although the orbital plane "underground" was tested as a test of future technologies "Buran"). It is sad (why - see below) that the plane-razgonnik not been built and tested.
Recommend read more online Buran.ru.
Present h4>
Currently, there is one air carrier rocket launch, the two realized the project suborbital air-launched aircraft and models for testing hypersonic engines. Let us examine them in more detail:
RN Pegasus h5>

The first launch - in 1990, a total of 42 start-up, 3 failures, 2 partial success (just below the desired orbit), 443 kg into low orbit. As the air carrier uses a modified passenger aircraft L-1011 . Separation from the carrier is made at the height of 12 kilometers and a speed of not more than 0, 95M (1,000 km / h).
SpaceShipOne h5>
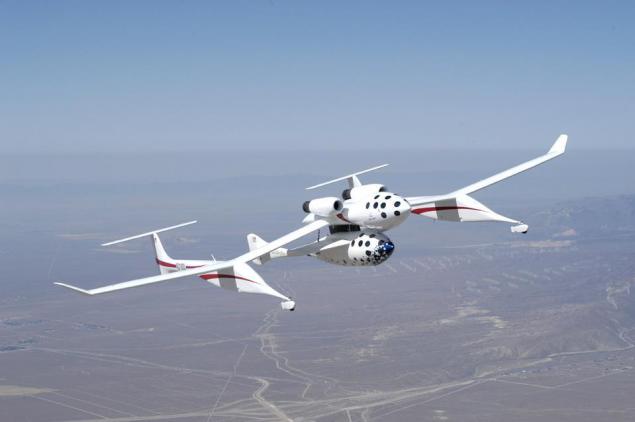

Suborbital air-launched aircraft. Designed for the competition Ansari X-Prize , made in 2003-2004, 17 flights, including the last three - suborbital space flights to an altitude of about 100 km. Despite optimistic обещания «in the next 5 years will be able to fly into space about 3 000» i> project was actually stopped after winning the X-Prize, and for the past ten years, no space tourists on suborbital trajectories do not fly.
SpaceShipTwo h5>
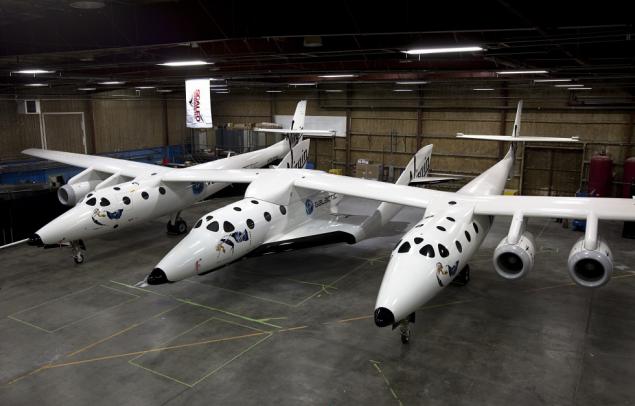

Suborbital air-launched aircraft. Developed for ten years instead of SpaceShipOne. Currently undergoing test flights, the maximum height reached on February 2014 - 23 km.
X-43, X-51 h5>
Unmanned vehicles to test hypersonic engines.
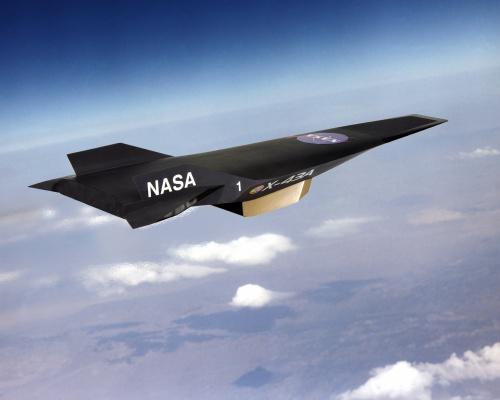

X-43 was designed as a large-scale model of the future space plane X-30 . Made three flight. First, in June 2001 ended in failure due to errors in the calculations that led to the loss of stabilization booster. Second, in March 2004, was a success, it has been 6 speed, 83m. The third flight took place in November 2004, was 12 seconds speed reached 9, 6M.

X-51 was designed for slower (~ 5M), but longer flights. Made four flight - a relatively successful first in May 2010 (200 of the planned 300 seconds 5M), two failed, and fully successful (210 seconds 5M as planned) in May 2013.
The calculations profitability of air-start h4>
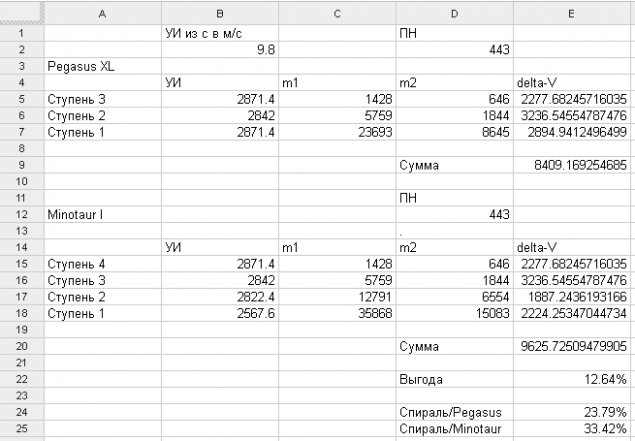
The Pegasus gives us a very convenient way to determine the degree of profitability of air-launched. The fact that the Minotaur I rocket has as the third and fourth stages of the second and third stage of "Pegasus", displays the same payload, but starts from the ground. Comparison of the mass seems to be markedly in favor of "Pegasus" - air-launched rocket weighs 23 tons, and land - 36 tons. However, to fully compare these launch vehicles, it is necessary to calculate the reserve characteristic velocity, which is given stage rockets. On a material Encyclopedia Astronautica ( data for Pegasus-XL , data for the Minotaur I ) were calculated reserves characteristic velocity levels for the same payload:
Документ settled in Google Docs
The result was a very curious - due to start saving air 12, 6 percent of the intrinsic rate. On the one hand, it is quite noticeable benefit. On the other hand, it is not so much to cause an explosive growth of air-start.
Pay attention to the hypothetical comparison with the "spiral". If the "Pegasus" was on the plane-razgonnike "Spiral", the separation would occur at a speed of ~ 1800 m / s and an altitude of 30 km, which would save at least 2000 m / s characteristic velocity. The same principle goes a comparison with the "Minotaur". Notice how increased profits. We conclude that the benefit of air-launched the greatest extent determined by the carrier - the higher the speed and height of the separation, the greater the benefit.
General discussion of the pros and cons of air-start h4>
Benefits h5>
The reduction of gravitational loss
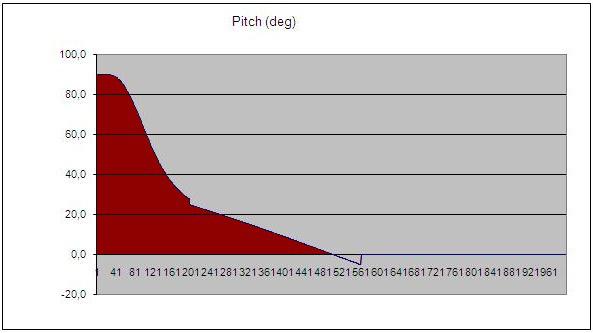
The model graph the pitch angle. The area of the curvilinear trapezoid (shaded red) - gravitational losses. I>
Reducing losses drag
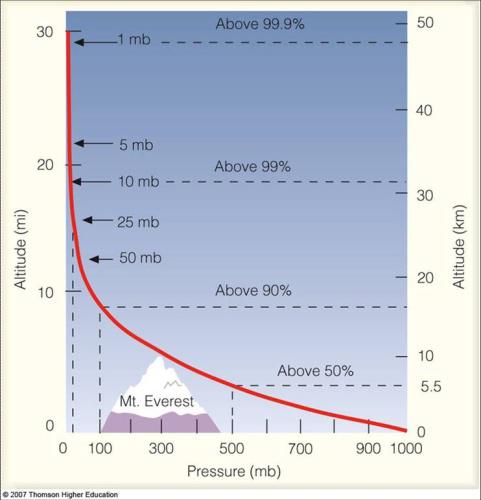
At an altitude of 12 km, which starts "Pegasus", the pressure is about 5 times less than at sea level (~ 200 mbar). At an altitude of 30 km - is a hundred times smaller (~ 10 mbar).
jet engine has a higher specific impulse
The ability to use existing infrastructure
The ability to start with the correct latitude
Disadvantages h5>
Very poor scalability
Liquid fuels require rework media
The problems of structural strength of the payload and the launcher
The need to develop powerful hypersonic engines
Conclusion h4>
Aerospace systems can be a very effective means of delivering cargo into orbit. But only if these loads will be small (probably no more than five tons, if predict based on the achievements of progress) and the carrier - hypersonic. Attempts to create a flying monsters type double AN-225 with twenty-four engines or even some super-heavy pattern winning art of common sense - is a dead end at the present level of our knowledge.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/214335/






































