2496
The cave Movil (21 photos)
One blogger described the amazing cave, which is located near the Romanian town of Mangalia and its unique ecosystem.
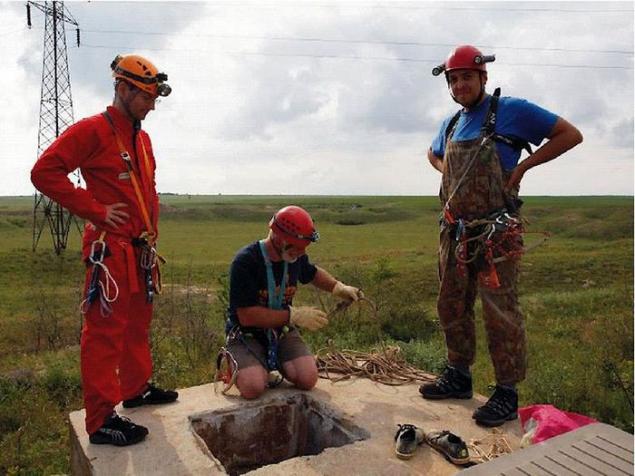

In 1986, during the geological studies before the construction of the power plant near the Romanian town of Mangalia at a depth of about 18 meters it was found closed cave system with specific conditions. Fueled groundwater with a high content of hydrogen sulfide (8-12 mg / l), a cave named Movil, had its own atmosphere, oxygen-poor (7-10%), rich in carbon dioxide (2-3.5%) and containing a significant amount of methane (1 -2%). Her research began in 1990.
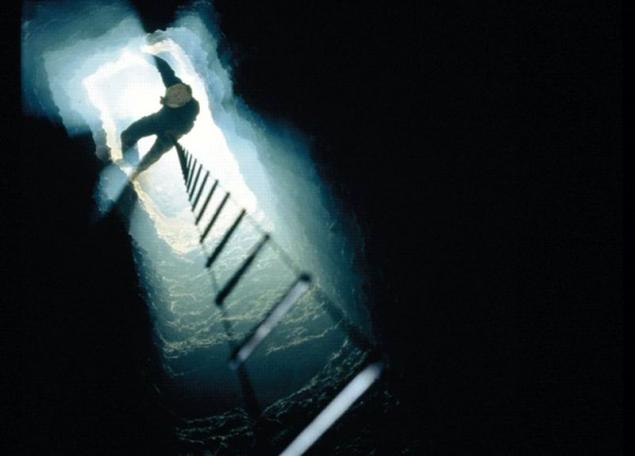

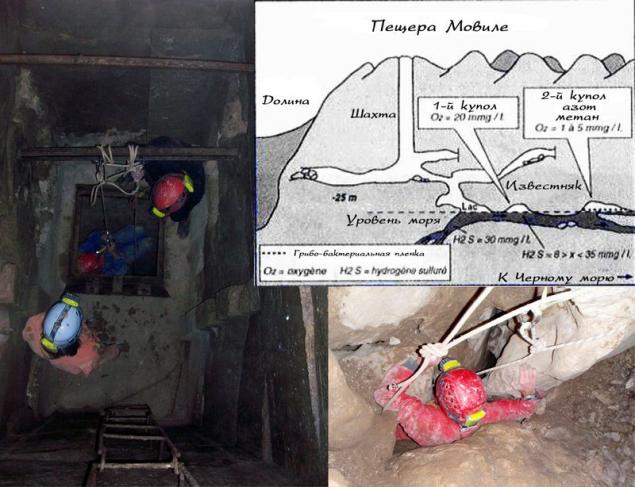
The beauty of this relatively small cave (length of the explored part of about 300 m) with narrow aisles, covered with mud, not amazing - standard limestone dirty hole with a lake, dividing the above-water part of the three isolated cavity. The chip in the other.


The point is that this cave contains a unique ecosystem, exist and develop the past 5 million years, presumably without regard to the earth's surface by chemosynthesis - and not from a single microorganism, as one might assume. In the closed stone cell area of about 1,200 m² was found 46 species of terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates, 33 of them - are endemic, previously unknown and can not be found anywhere else. Among these arthropods, leeches and molluscs, not to mention all sorts of rotifers and nematodes.


The ancestors of all of the company came under the ground, as I said, about five million years ago - when he was still alive yours, dear reader, a common ancestor with bonobos and Romanian climate was tropical - and successfully outlasted in warm caves subsequent glacial periods , more and more troglomorfiruya, that is adapting to the way of life underground and "heavenly" atmosphere.
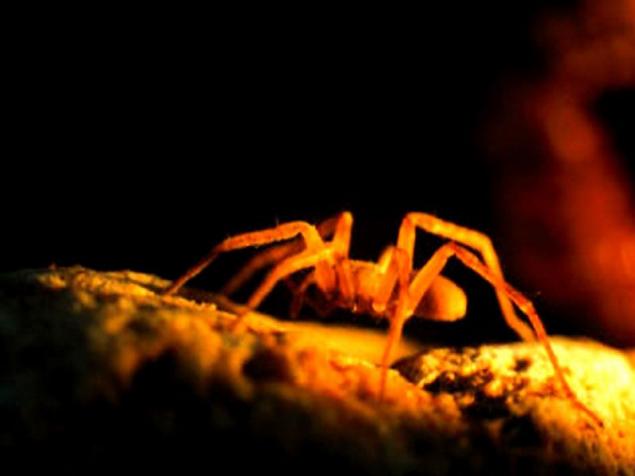

Clepoy spider Agraecina cristiani touch patrols freeboard of the grotto in search of springtails and woodlice. The inhabitants of the cave blind and guided by touch and smell (or more precisely, on the chemical sense - the sense of smell in invertebrates are often inseparable from taste), as well as capturing the slightest vibration stone, air or water.
At the very bottom of the food chain are movilskoy autotrophic bacteria - here they perform the same role that the plants on the surface - that is, converted into organic minerals, but not at the expense of sunlight and oxidizing hydrogen sulfide. As a result, the cycle of reactions of organic sulfur precipitates and micro-organisms obtain energy for organic synthesis from carbon dioxide and water.

These autotrophic bacteria are a source of food for other heterotrophic bacteria and fungi. Together, they form a bacterial mats and films covering the walls of caves and water surface, especially in the third, distant air bell, where the atmosphere is more "ethereal" and serve as food for the local "herbivorous" Fauna - isopods, springtails, woodlice, pseudoscorpions on hunted predators - 5-cm centipedes and spiders. And under the water, the underside of the bacterial film - its food pyramid: worms, crustaceans, snails and top predators - leeches with water scorpions.
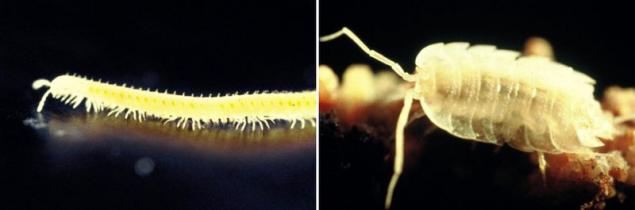
Left: centipede Arheboreoiulus sp. crawling in the dark in search of food. Right: land woodlouse Armadillidium tabacarui.
The largest predator movilskoy ecosystem - centipede Criptops.


The productivity of this ecosystem is quite large: per square meter, researchers counted fifteen hundred springtails. They were hunted blind spiders, whose closest relatives - sighted - now are found in the Canary Islands, which gives us an idea of the European climate in the Pliocene.

Spider crawling on the calcite crystals.
Aquatics Movil live mainly in the upper desyatisantimetrovyh layer under the surface, more or less saturated with oxygen coming from the air. Here there may be only anaerobes. Underwater species Movil changed compared with their counterparts from the larger world is smaller than the ground, and among them only 25% against 75% of endemic species of terrestrial movilskih troglodytes. This suggests that the message of the cave with sea or river water was interrupted later than the message from the surface of the land.
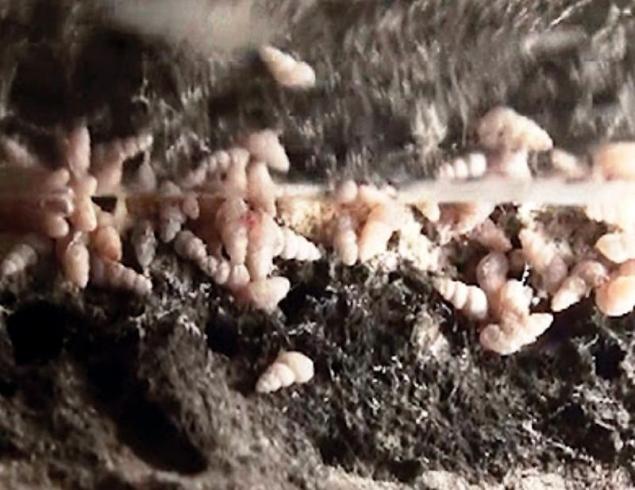
Snails are extremely resistant to hydrogen sulfide, eat a bacterial film on the water surface. These unique shellfish are the main by consumers in the ecosystem of the cave Movil.

Water scorpion Nepa anophthalma (right - in the nymph stage) - another endemic Movil. He hunts for crustaceans and insects, and lives mostly in water.
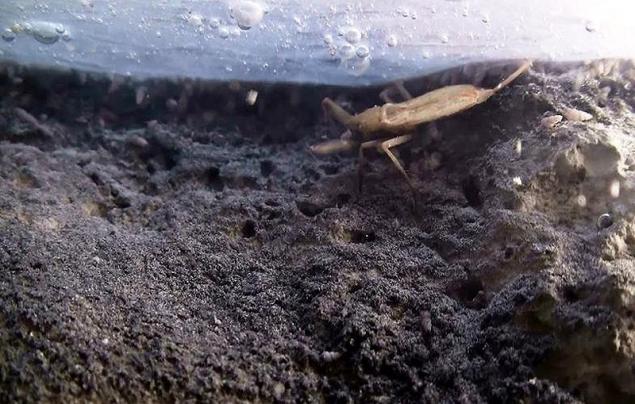

Water scorpion in his element. On top of the bottom surface is visible bacterial mat - they look like wet wipes and supported floating bubbles.

Predatory leeches, one of the most spectacular creatures of the cave Movil, eat snails, worms and other invertebrates.
Filmed by laser confocal microscopy, a small crustacean ostracod representative plankton underground lake Movil.
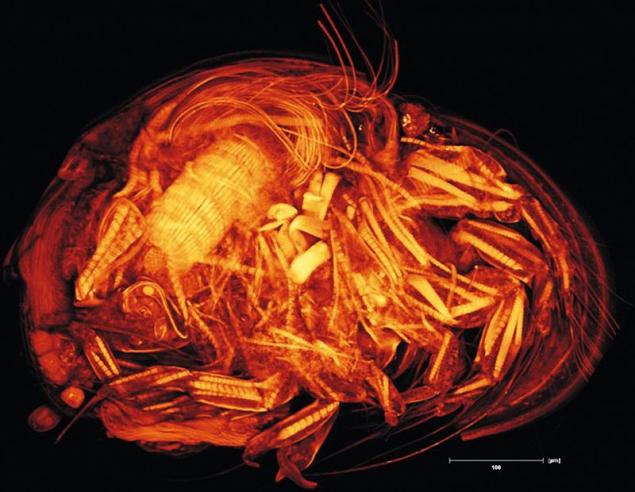

In itself, the human presence in this place is seriously life threatening ecosystems: only one process of breathing caver can cause an imbalance of the gas composition of the atmosphere grottoes. Therefore, access to the cave is allowed only for research purposes with the permission of the custodians. Visits are limited to two hours twice a month, groups of no more than three people in a clean overalls and shoes ... and even better without it:
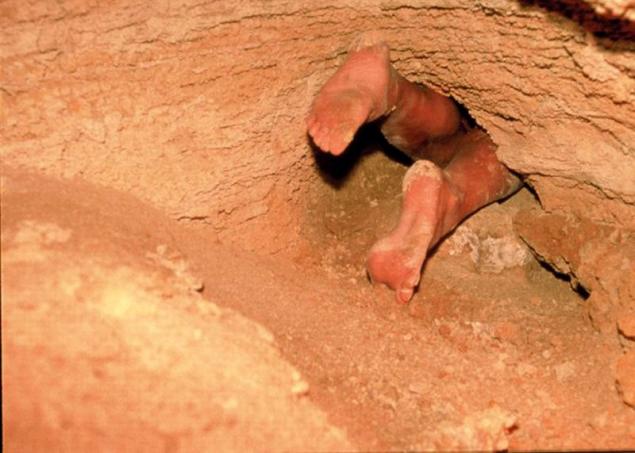

From unauthorized access and influence of the environment cave is protected by two hatches and a tight cover.
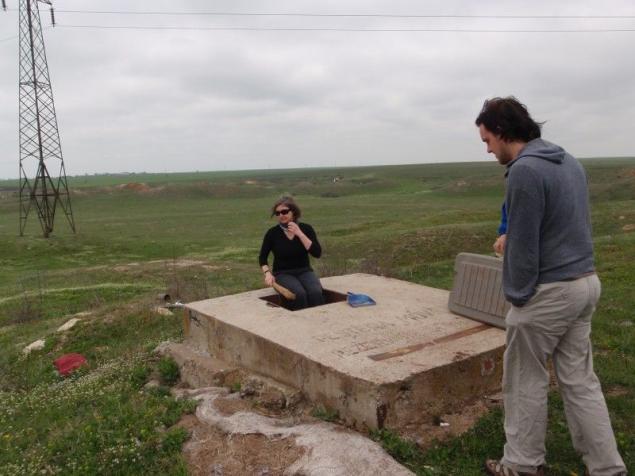

Themselves chemotrophic ecosystems are not so rare in the world, unique Movil is that for a very long time it has existed and developed without regard to the surface. The isotopic composition of the water showed that precipitation does not penetrate into the cave, the water comes only from the depths. Is there life on Mars? Is not there life on Mars? Science still does not know things ... Suppose you today will dream blind spiders, picking their way to the touch in the eternal darkness and silence of the stone labyrinth.

Source: haritonoff.livejournal.com

In 1986, during the geological studies before the construction of the power plant near the Romanian town of Mangalia at a depth of about 18 meters it was found closed cave system with specific conditions. Fueled groundwater with a high content of hydrogen sulfide (8-12 mg / l), a cave named Movil, had its own atmosphere, oxygen-poor (7-10%), rich in carbon dioxide (2-3.5%) and containing a significant amount of methane (1 -2%). Her research began in 1990.


The beauty of this relatively small cave (length of the explored part of about 300 m) with narrow aisles, covered with mud, not amazing - standard limestone dirty hole with a lake, dividing the above-water part of the three isolated cavity. The chip in the other.


The point is that this cave contains a unique ecosystem, exist and develop the past 5 million years, presumably without regard to the earth's surface by chemosynthesis - and not from a single microorganism, as one might assume. In the closed stone cell area of about 1,200 m² was found 46 species of terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates, 33 of them - are endemic, previously unknown and can not be found anywhere else. Among these arthropods, leeches and molluscs, not to mention all sorts of rotifers and nematodes.


The ancestors of all of the company came under the ground, as I said, about five million years ago - when he was still alive yours, dear reader, a common ancestor with bonobos and Romanian climate was tropical - and successfully outlasted in warm caves subsequent glacial periods , more and more troglomorfiruya, that is adapting to the way of life underground and "heavenly" atmosphere.

Clepoy spider Agraecina cristiani touch patrols freeboard of the grotto in search of springtails and woodlice. The inhabitants of the cave blind and guided by touch and smell (or more precisely, on the chemical sense - the sense of smell in invertebrates are often inseparable from taste), as well as capturing the slightest vibration stone, air or water.
At the very bottom of the food chain are movilskoy autotrophic bacteria - here they perform the same role that the plants on the surface - that is, converted into organic minerals, but not at the expense of sunlight and oxidizing hydrogen sulfide. As a result, the cycle of reactions of organic sulfur precipitates and micro-organisms obtain energy for organic synthesis from carbon dioxide and water.

These autotrophic bacteria are a source of food for other heterotrophic bacteria and fungi. Together, they form a bacterial mats and films covering the walls of caves and water surface, especially in the third, distant air bell, where the atmosphere is more "ethereal" and serve as food for the local "herbivorous" Fauna - isopods, springtails, woodlice, pseudoscorpions on hunted predators - 5-cm centipedes and spiders. And under the water, the underside of the bacterial film - its food pyramid: worms, crustaceans, snails and top predators - leeches with water scorpions.

Left: centipede Arheboreoiulus sp. crawling in the dark in search of food. Right: land woodlouse Armadillidium tabacarui.
The largest predator movilskoy ecosystem - centipede Criptops.


The productivity of this ecosystem is quite large: per square meter, researchers counted fifteen hundred springtails. They were hunted blind spiders, whose closest relatives - sighted - now are found in the Canary Islands, which gives us an idea of the European climate in the Pliocene.

Spider crawling on the calcite crystals.
Aquatics Movil live mainly in the upper desyatisantimetrovyh layer under the surface, more or less saturated with oxygen coming from the air. Here there may be only anaerobes. Underwater species Movil changed compared with their counterparts from the larger world is smaller than the ground, and among them only 25% against 75% of endemic species of terrestrial movilskih troglodytes. This suggests that the message of the cave with sea or river water was interrupted later than the message from the surface of the land.

Snails are extremely resistant to hydrogen sulfide, eat a bacterial film on the water surface. These unique shellfish are the main by consumers in the ecosystem of the cave Movil.

Water scorpion Nepa anophthalma (right - in the nymph stage) - another endemic Movil. He hunts for crustaceans and insects, and lives mostly in water.

Water scorpion in his element. On top of the bottom surface is visible bacterial mat - they look like wet wipes and supported floating bubbles.

Predatory leeches, one of the most spectacular creatures of the cave Movil, eat snails, worms and other invertebrates.
Filmed by laser confocal microscopy, a small crustacean ostracod representative plankton underground lake Movil.

In itself, the human presence in this place is seriously life threatening ecosystems: only one process of breathing caver can cause an imbalance of the gas composition of the atmosphere grottoes. Therefore, access to the cave is allowed only for research purposes with the permission of the custodians. Visits are limited to two hours twice a month, groups of no more than three people in a clean overalls and shoes ... and even better without it:

From unauthorized access and influence of the environment cave is protected by two hatches and a tight cover.

Themselves chemotrophic ecosystems are not so rare in the world, unique Movil is that for a very long time it has existed and developed without regard to the surface. The isotopic composition of the water showed that precipitation does not penetrate into the cave, the water comes only from the depths. Is there life on Mars? Is not there life on Mars? Science still does not know things ... Suppose you today will dream blind spiders, picking their way to the touch in the eternal darkness and silence of the stone labyrinth.

Source: haritonoff.livejournal.com
Mysterious corners of our planet (11 photos)
Advertising campaign for the Museum. AV Shchusev (12 photos)























