1887
Low tide gold bars (11 photos)
In Vienna, the Austrian factory has Ögussa GmbH, which produces billets for jewelry factories and workshops.
It is also engaged in manufacturing of laboratory equipment, non-ferrous and precious metals, pours dimensional gold and silver bullion.
The raw materials used for the bullion jewelry scrap, defective and fashion jewelry.

Applicants for melting scrap gold is loaded into special furnaces under the influence of a high temperature liquid is brought to a homogeneous mass, which molds to produce ingots.
Material entering the melt, called the feedstock, or blend. The charge may be a pure metal, ingots and defective products, scrap and waste of jewelry production. Feedstock material required to be subjected to various processing.

Waste and scrap of precious metals are a cleansing process, and only then enter the melt.

The melting of precious metals produced in induction furnaces with a graphite crucible. The charge material is charged into the crucible - melting furnace refractory vessel in which molten metal.
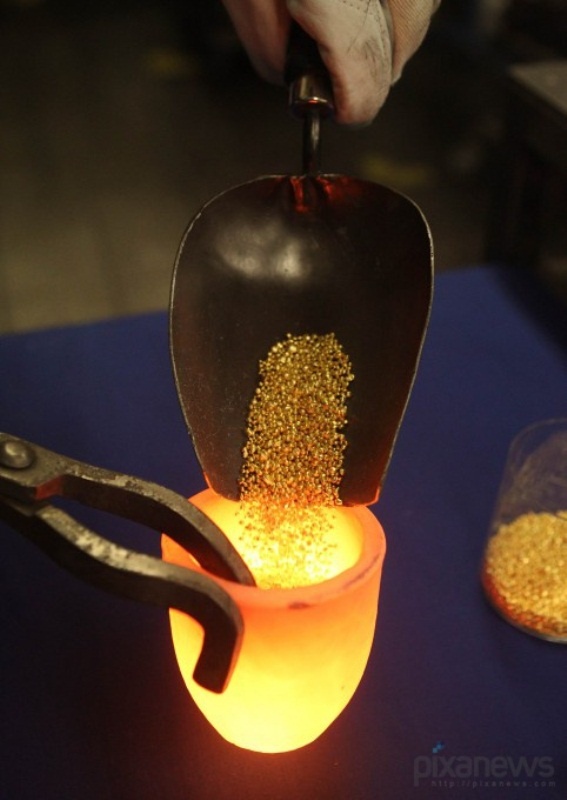

The crucible before loading it into a heated metal on the bottom of the heated crucible is filled flux. Then, the crucible is charged with the charge and set the desired temperature. After melting of the charge melt covered with a small amount of fresh flux and mixed. Without lowering the heating temperature, the melt is allowed to settle to the flux otshlakoval unwanted oxides and impurities introduced deoxidizer.
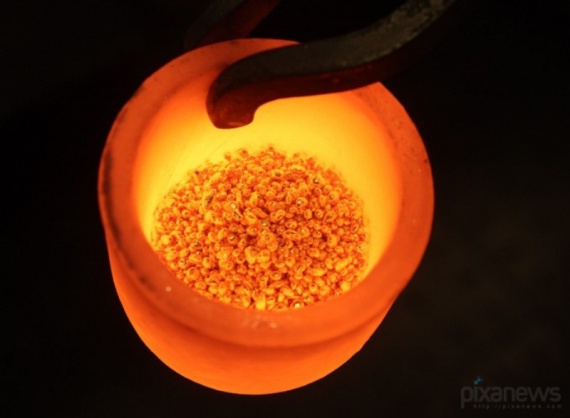

When melting of the gold melt was heated up to 1200 ... 1250 ° C
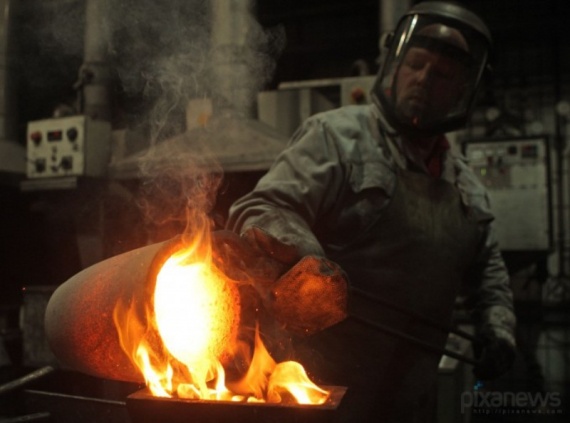

For the casting of ingots of precious metals used iron and steel molds.

Mould or Ingus is a metal bar with a milled groove shape future ingot. Molds calcined to a temperature of 500 ... 550 ° C with the technological lubricants. Grease provides good quality cast ingots, t. E. A good melt flow in the cell. The whole process resembles, as a hostess in the kitchen preparing shortcake in tins - the form must be heated, then lubricate the special graphite coating, to gold is not burnt.

When the melt is prepared, the metal is cast. The melt is cast through the spout of the crucible into molds, and after complete crystallization and aging ingot recovered.
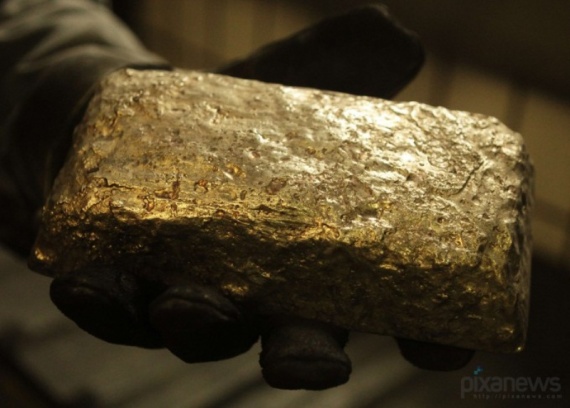

The molten gold and viscous fluid resembles jelly. It hardens pretty quickly - even in the gas plume and hot form, it crystallizes in a few seconds. After that, workers removed the ingot and drop it in cold water.

Before the ingot is stamped on the information about it in the chemical laboratory of the plant is given a small probe melting. If gold is not enough clean it again remelting.
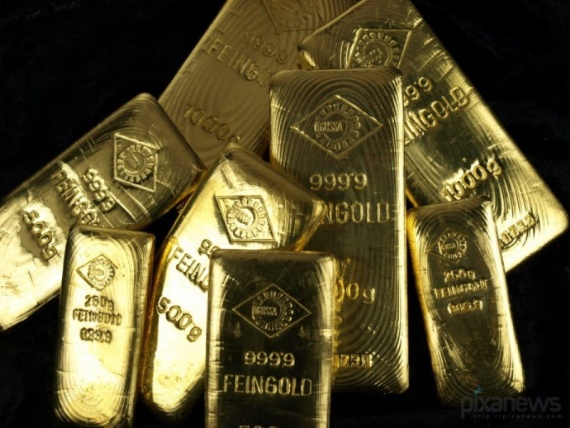

Each bar gets its own number, in addition to this it stands out stigma and zolotoizgotovitelya sample.
Source: pixanews.com
It is also engaged in manufacturing of laboratory equipment, non-ferrous and precious metals, pours dimensional gold and silver bullion.
The raw materials used for the bullion jewelry scrap, defective and fashion jewelry.

Applicants for melting scrap gold is loaded into special furnaces under the influence of a high temperature liquid is brought to a homogeneous mass, which molds to produce ingots.
Material entering the melt, called the feedstock, or blend. The charge may be a pure metal, ingots and defective products, scrap and waste of jewelry production. Feedstock material required to be subjected to various processing.

Waste and scrap of precious metals are a cleansing process, and only then enter the melt.

The melting of precious metals produced in induction furnaces with a graphite crucible. The charge material is charged into the crucible - melting furnace refractory vessel in which molten metal.

The crucible before loading it into a heated metal on the bottom of the heated crucible is filled flux. Then, the crucible is charged with the charge and set the desired temperature. After melting of the charge melt covered with a small amount of fresh flux and mixed. Without lowering the heating temperature, the melt is allowed to settle to the flux otshlakoval unwanted oxides and impurities introduced deoxidizer.

When melting of the gold melt was heated up to 1200 ... 1250 ° C

For the casting of ingots of precious metals used iron and steel molds.

Mould or Ingus is a metal bar with a milled groove shape future ingot. Molds calcined to a temperature of 500 ... 550 ° C with the technological lubricants. Grease provides good quality cast ingots, t. E. A good melt flow in the cell. The whole process resembles, as a hostess in the kitchen preparing shortcake in tins - the form must be heated, then lubricate the special graphite coating, to gold is not burnt.

When the melt is prepared, the metal is cast. The melt is cast through the spout of the crucible into molds, and after complete crystallization and aging ingot recovered.

The molten gold and viscous fluid resembles jelly. It hardens pretty quickly - even in the gas plume and hot form, it crystallizes in a few seconds. After that, workers removed the ingot and drop it in cold water.

Before the ingot is stamped on the information about it in the chemical laboratory of the plant is given a small probe melting. If gold is not enough clean it again remelting.

Each bar gets its own number, in addition to this it stands out stigma and zolotoizgotovitelya sample.
Source: pixanews.com