165
Lectins: The Invisible Enemy That Ruins Health

Lectins are a group of proteins naturally present in various plants. They serve to protect plants from pests such as insects and fungi. However, despite their natural role, lectins can have negative effects on human health if their intake is not controlled. In this article, we will look at what lectins are, how they affect the body, and what measures can be taken to minimize their harmful effects.
What are lectins?
Lectins are a type of protein that binds to carbohydrates and play an important role in plants, protecting them from pests and diseases. They are found in seeds, legumes, cereals, nuts and some vegetables. The most well-known sources of lectins include beans, lentils, soybeans, tomatoes and potatoes.
“Lectins are natural biologically active substances that perform a protective function in plants, but can have a detrimental effect on humans if incorrectly consumed.” – Dr. Anna Kovaleva, biochemist
How do lectins affect the human body?
Although lectins are a natural component of plant foods, their excessive consumption can lead to a variety of health problems:
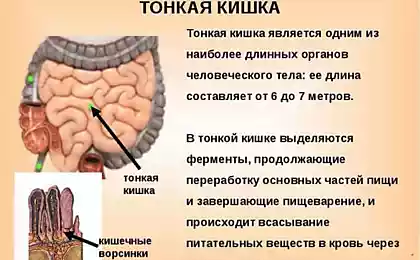
- Digestive disorder: Lectins can bind to the surface of intestinal cells, disrupting nutrient absorption and causing inflammation.
- Intestinal wall damage: In some cases, lectins can contribute to the development of “leakage” of the intestine, which allows toxins to enter the bloodstream.
- Immune reactions: Lectins can stimulate the immune system, causing chronic inflammation and increasing the risk of autoimmune diseases.
- Reduced absorption of minerals: Lectins bind to minerals such as calcium, iron and zinc, reducing their bioavailability.
Popular Sources of Lectins
Lectins are present in a wide range of plant foods. Some of the most significant sources include:
- Legume: Beans, lentils, peas and soybeans contain high levels of lectins.
- Evil: Wheat, oats, barley and corn are also rich in lectins.
- Some Vegetables: Tomatoes, potatoes and eggplant contain moderate amounts of lectins.
- Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, peanuts and flax seeds contain lectins in smaller amounts.
Measures to reduce the level of lectins in nutrition
Although lectins can be harmful, there are effective ways to reduce them in food:
- Soaking: Soaking legumes and cereals overnight helps break down some of the lectins.
- Sprouting: Sprouting seeds and grains reduces lectins and increases the bioavailability of nutrients.
- Heat treatment: Cooking, frying and fermentation significantly reduce the level of lectins in foods.
- Removal of the Peel: In some cases, removing the skin of vegetables and fruits can reduce the amount of lectins.
Potential Benefits of Lectins
Despite their negative aspects, lectins also have a number of beneficial properties:
- Antibacterial properties: Lectins can help protect the body from pathogenic bacteria.
- Antivirus Properties: Some lectins are able to inhibit viral infections.
- Antioxidant properties: Lectins have antioxidant properties that help fight oxidative stress.
- Support for the immune system: In moderation, lectins can stimulate the immune system.
Expert opinion
Experts emphasize that lectins are not an absolute enemy, but their excessive consumption can harm health. It is important to balance the diet, use methods to reduce lectins and take into account the individual characteristics of the body.
“Lectins are just one of many components of our diet. Their impact on health depends on general lifestyle, cooking methods and individual sensitivity. — Dr. Sergey Ivanov, gastroenterologist.
Stories From Life
Many people have faced problems with lectin intake and have found ways to minimize their negative effects:
- Anna, 34: After diagnosing lectin sensitivity, I changed my diet to eliminate beans and cereals. This helped me get rid of chronic fatigue and improve digestion. ?
- Igor, 45 years old: “Using soaking and sprouting techniques, I was able to lower lectins in my diet, which had a positive effect on my health and overall well-being.” ?
- Maria, 28 years old: “I started fermenting my vegetables and noticed a significant improvement in skin condition and reduced inflammation in the body.”
Conclusion
Lectins are complex proteins that can have both negative and positive effects on human health. It is important to understand that they are not uniquely harmful, but their excessive consumption can lead to various problems. Using lectin-lowering techniques such as soaking, sprouting and heat treatment allows you to enjoy plant foods while minimizing health risks.
“Balance and a conscious approach to nutrition will help to get the maximum benefit from plant products without exposing the body to excessive exposure to lectins.” – Dr. Marina Kovaleva, Nutritiologist.
Watch your diet, consult with medical professionals and make a choice in favor of a healthy and balanced diet. Your health depends on how you take care of your body every day.
More than half of Zumers consider criticism in their address at work a sign of personal dislike
11 Rituals of Happiness