189
At what age can a child start using gadgets?
In the age of computer technology, the problem of children's dependence on gadgets is becoming more acute than ever. Many, probably, more than once have seen the picture when parents hand the child a smartphone to get rid of it. “Here you are, wise man, cartoons, and leave your parents alone!” is so familiar, isn’t it?

DepositPhotos
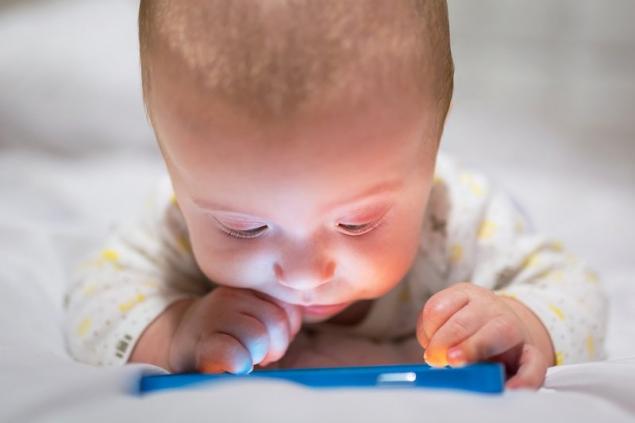
Kids get used to it quickly. While the gadget is in hand, do not make a sound, but it is worth taking it away - immediately into a scream. And then parents wonder why it is impossible to find a common language with children and why they do not develop relationships in real life.
Communication skills are laid in us since childhood. According to pediatricians, the age from 0 to 3 years is very important for the development of vision, the formation of the speech apparatus and the enrichment of the vocabulary of babies. It is especially important for children under 3 years of age to talk as much as possible with parents and peers, rather than with their mother’s smartphone.

DepositPhotos
The American Academy of Pediatrics states that children aged 0-2 years should not be exposed to electronic devices at all. And at the age of 3 to 5 years should use gadgets no more than one, from 6 to 18 years – two hours a day.
At the same time, statistics say that modern children spend an average of several times more time in front of the screen, 6-7 (!) hours a day. Most American children use mobile devices every day from the age of two, and from the age of 7-8 they already have constant access to the Internet.
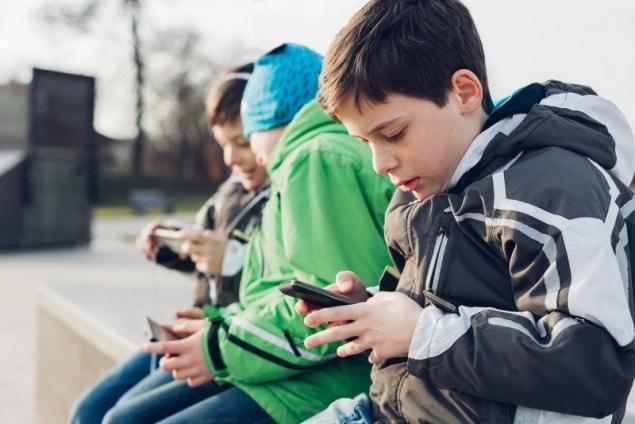

Mobile devices have significantly increased the availability of modern technologies for young children. So pediatrician Chris Rowan is pushing to ban the use of mobile electronic devices by children under the age of 12. Here are 10 main reasons for this decision.
Editorial Board So what should parents do? Maybe just take away all the gadgets, TV and forbid to go online? It's only worse. The child will be angry with the parents, and they will become enemies in his eyes.

DepositPhotos Gadgets are a necessary part of modern life. Let your child learn to use a smartphone, but not too soon. Do not push the phone into the hands of a one-year-old child just to distract his attention. In a year, a child can show so much interesting things in the familiar world around us, it does not need smartphones.
It is not necessary to pick up the smartphone, but it is still necessary to limit the time that the child spends at the screen. Pediatricians advise to develop clear rules for the use of gadgets for the whole family.
For example, identify spaces free of gadgets – kitchen, living room or car. It is advisable to agree that phones do not belong at the dinner table.
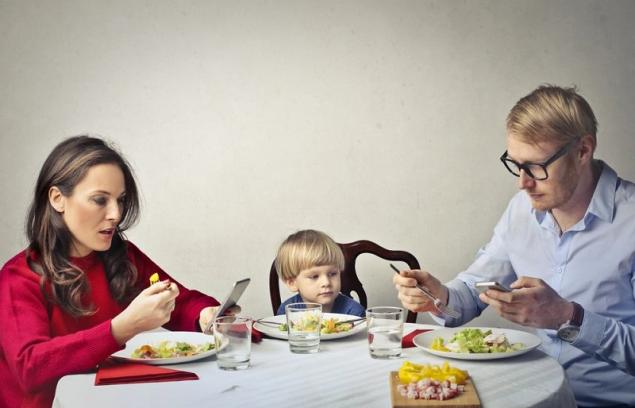

DepositPhotos
It would be good to insist that the hour before bed children do not watch anything. To achieve greater effect, you can show solidarity and introduce restrictions for yourself (maybe it will be useful for parents?).
The current time of technology and the Internet takes a child a lot of time for things that do not develop him: social networks, endless cartoons and games. Editorial "Site" I have prepared for you 20 ideas for an entertaining pastime with a child that he will definitely like.
In the parent chats of the Viber messenger, real madness is often created. Parents read 100,500 text messages a day, most of which are off-topic. The mother-of-four talks about how to deal with all this information and what to do with excessive parental activity.

DepositPhotos
Kids get used to it quickly. While the gadget is in hand, do not make a sound, but it is worth taking it away - immediately into a scream. And then parents wonder why it is impossible to find a common language with children and why they do not develop relationships in real life.
Communication skills are laid in us since childhood. According to pediatricians, the age from 0 to 3 years is very important for the development of vision, the formation of the speech apparatus and the enrichment of the vocabulary of babies. It is especially important for children under 3 years of age to talk as much as possible with parents and peers, rather than with their mother’s smartphone.

DepositPhotos
The American Academy of Pediatrics states that children aged 0-2 years should not be exposed to electronic devices at all. And at the age of 3 to 5 years should use gadgets no more than one, from 6 to 18 years – two hours a day.
At the same time, statistics say that modern children spend an average of several times more time in front of the screen, 6-7 (!) hours a day. Most American children use mobile devices every day from the age of two, and from the age of 7-8 they already have constant access to the Internet.

Mobile devices have significantly increased the availability of modern technologies for young children. So pediatrician Chris Rowan is pushing to ban the use of mobile electronic devices by children under the age of 12. Here are 10 main reasons for this decision.
- Dependence on gadgets
The more parents check email, scroll through the news feed, shoot monsters, and watch TV shows, the more distant they become from their children. The lack of adult attention is often compensated by the same gadgets and digital technologies. In some cases, the baby himself becomes dependent on portable devices, the Internet and television. Right now. child dependence on gadgets It became an epidemic. One in eleven children aged 8-18 years is a digital addict.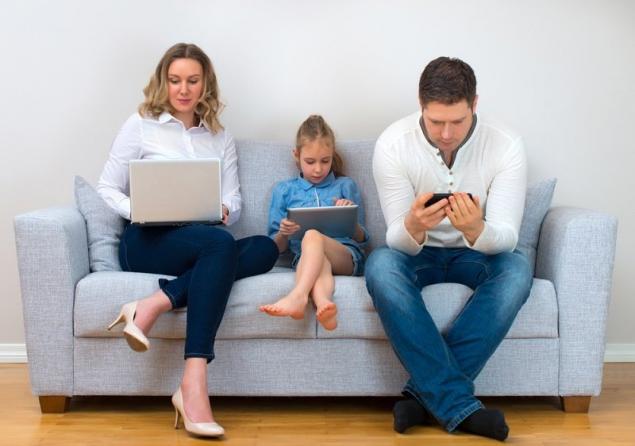
DepositPhotos - Harmful radiation
In 2011, the World Health Organization and the International Agency for Research on Cancer classified radio emission from cell phones and other wireless devices as a potential carcinogen, identifying group 2B ("possibly carcinogenic to humans" factors). However, it should be borne in mind that children are more sensitive to various negative influences, since their brains and immune systems are still developing.
DepositPhotos - Influence on brain development
A baby’s brain triples in size from birth to age two and continues to grow until age 21. Early brain development is determined by environmental stimuli or their absence. Stimulating the brain with excessive exposure to gadgets, as studies show, is fraught with cognitive delays, increased impulsivity, reduced ability to self-regulate and self-discipline.
DepositPhotos - Development gap
Sitting behind a tablet or phone, which means a lack of movement can lead to a delay in physical and mental development. This problem has become apparent in the US, where one in three children enters school with a developmental delay, which clearly affects their academic performance. Physical activity, in turn, improves attention and ability to learn and assimilate new things. Scientists say that the use of electronic technology harms the development of children and negatively affects their learning ability.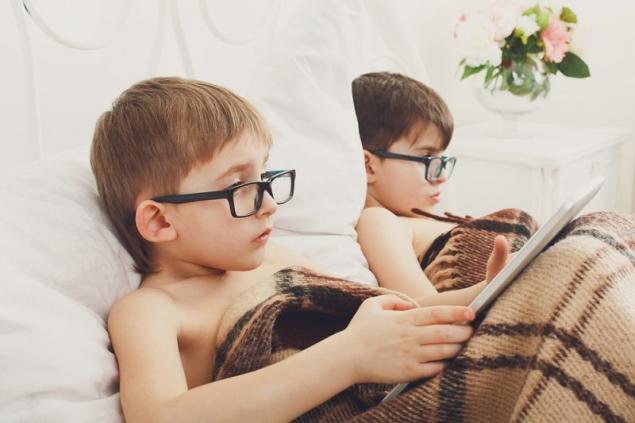
DepositPhotos - Obesity
TV watching and computer games are examples of non-food habits that are directly related to the epidemic of excess weight. Among children who are uncontrolled and constantly use portable electronic devices, obesity is 30% more common. One in four young Canadians and one in three American teenagers are overweight, and 30% of them will be diagnosed with diabetes.
In addition, adolescents who are obese are at higher risk of early stroke and heart attack, which seriously shorten their life expectancy. Scientists ring the bells, urging all parents to monitor the weight of children, because the first generation of the XXI century has a great chance to die before their parents.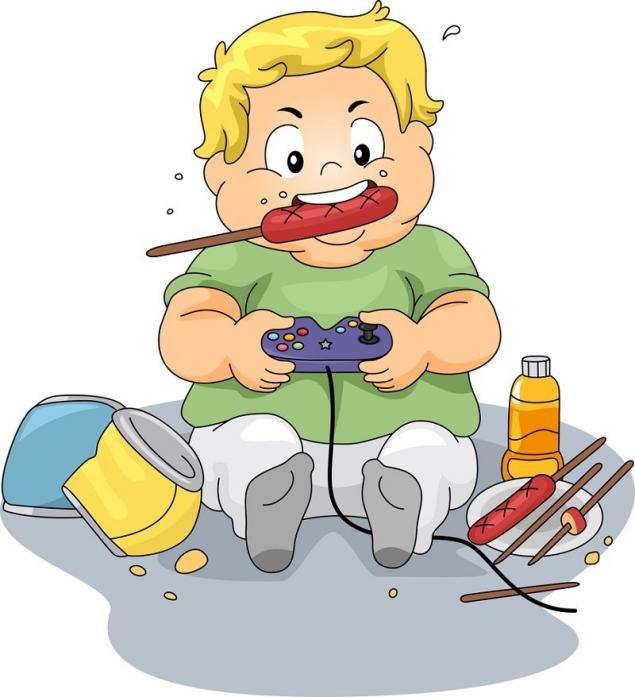
DepositPhotos - Sleep problems
Statistics show that 60% of parents do not control how closely their children are friends with all kinds of gadgets, and in three out of four families children are allowed to take electronic devices even with themselves to bed. The blue glow of the screens of phones, tablets and laptops prevents normal sleep, which leads to a reduction in rest time and lack of sleep. Scientists on the harm to the body compare lack of sleep with malnutrition: both deplete the body, and accordingly, negatively affects the success of school.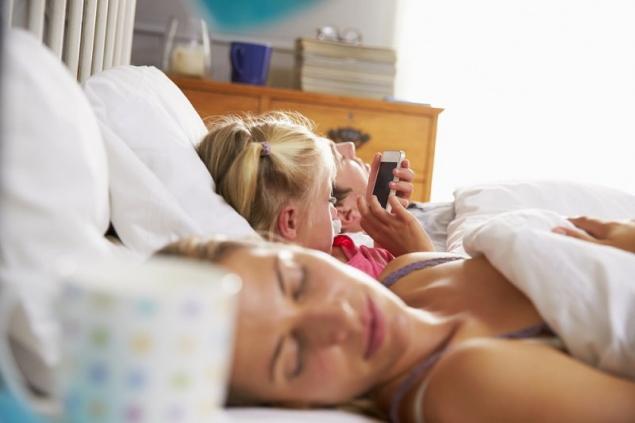
DepositPhotos - Psychological disorders
Internet hanging often leads to isolation and the development of phobias. This list can be safely supplemented by bipolar disorder, psychosis, behavioral disorders, autism and attachment disorder (that is, a violation of close emotional contact with parents). One in six Canadian children has some kind of mental illness, which is often treated only with strong psychotropic drugs.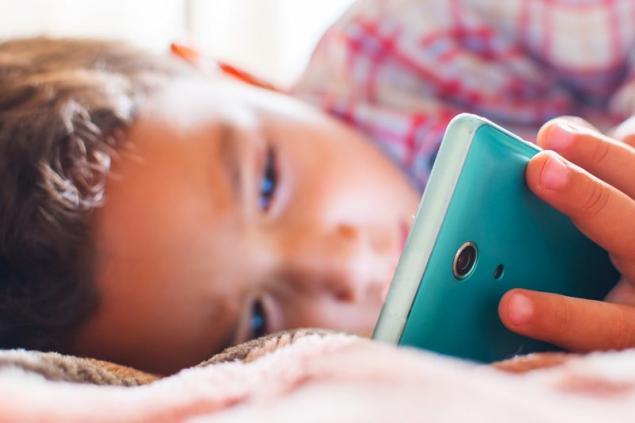
DepositPhotos - Aggressiveness
Cruelty on television and in computer games is reflected in real life. The child receives a ready-made scheme of behavior, which he can implement in the surrounding reality. And many researchers have come to the same conclusion: Screen violence has both short-term and long-term effects — aggression may not occur immediately.
618389
DepositPhotos - Digital dementia
Scientific observations prove that influence of gadgets on children At the age of 1-3 years leads to problems with concentration by the seventh year of life. Children who cannot concentrate simply lose the opportunity to learn and remember. - Distance from reality
Children’s excessive use of electronic technologies not only affects their psyche and ability to empathize, but also makes them more vulnerable in real life conditions that they, by and large, do not know. That is, time spent in the virtual world often does not teach them anything useful, and knowledge of electronic devices does not ensure success in the future, because technology is constantly improving, and it will become increasingly difficult to keep up with them.
343194
DepositPhotos
Editorial Board So what should parents do? Maybe just take away all the gadgets, TV and forbid to go online? It's only worse. The child will be angry with the parents, and they will become enemies in his eyes.

DepositPhotos Gadgets are a necessary part of modern life. Let your child learn to use a smartphone, but not too soon. Do not push the phone into the hands of a one-year-old child just to distract his attention. In a year, a child can show so much interesting things in the familiar world around us, it does not need smartphones.
It is not necessary to pick up the smartphone, but it is still necessary to limit the time that the child spends at the screen. Pediatricians advise to develop clear rules for the use of gadgets for the whole family.
For example, identify spaces free of gadgets – kitchen, living room or car. It is advisable to agree that phones do not belong at the dinner table.

DepositPhotos
It would be good to insist that the hour before bed children do not watch anything. To achieve greater effect, you can show solidarity and introduce restrictions for yourself (maybe it will be useful for parents?).
The current time of technology and the Internet takes a child a lot of time for things that do not develop him: social networks, endless cartoons and games. Editorial "Site" I have prepared for you 20 ideas for an entertaining pastime with a child that he will definitely like.
In the parent chats of the Viber messenger, real madness is often created. Parents read 100,500 text messages a day, most of which are off-topic. The mother-of-four talks about how to deal with all this information and what to do with excessive parental activity.