485
Lithium-ion batteries have got a built-in fire extinguisher
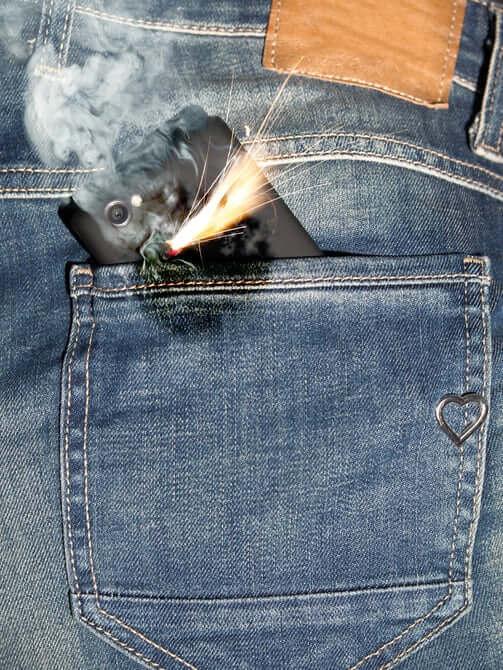
Li-ion rechargeable battery, which is the "driving force" of almost all mobile phones, tablet computers and electric cars have their weaknesses. Their main disadvantage is the high probability of fire in case of self-heating of the battery to high temperatures.
Good examples of this are the recent high-profile cases of fire Samsung Galaxy Note 7, the Chinese electric hoverboards and even robots. Replacement liquid flammable solid non-flammable electrolytes and the use of specialized chip controllers are partial measures to solve the problem.
But researchers from Stanford University have found another elegant solution — the introduction of a battery of my own "fire extinguisher", a special flame retardant that is triggered when the temperature rises above the critical point.

The introduction of deterrent fire technology in batteries is considered by scientists for a long time. Was developed a number of solutions, ranging from simple polymeric membranes installed between the cathode and the anode, to the more complex, consisting in the use of composite or ceramic materials. However, most of these solutions decreased the electrical characteristics of the battery and is not guaranteed to completely get rid of the risk of spontaneous combustion.
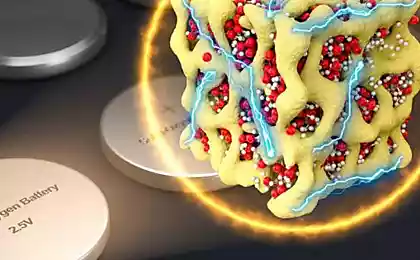
The solution found Stenfordsky scientists, by introducing into the battery part of the TPP (triphenyl phosphate, triphenyl phosphate), which is enclosed in a sheath of polymeric microfibers. If the battery works in normal mode, the polymeric shell prevents penetration of the composition of TPP into the electrolyte. But if the temperature rises above 160 degrees Celsius, the polymer sheath melts and releases to the electrolyte TPP, which is a chemical retarder that prevented the process of combustion. From the first glance it may seem that 160 degrees is a high enough temperature. However, at this temperature, conventional lithium electrolyte is only beginning to approach the point of "no return", after which irreversible processes and starts a fire.

This method was tested on the small batteries of different types with rigid housings. The researchers found that the material of the TPP is highly effective in preventing fire, or quickly extinguishes the flame if ignition occurs.
Further research in this direction will allow to equip their own "fire extinguisher" and larger batteries, including batteries with a soft polymer coating, only scientists have yet to figure out how it all will affect the mechanical impact, for example, is applied to the battery from outside pressure, which can destroy the shell of polymeric microfibers. published
Source: ecotechnology
Good examples of this are the recent high-profile cases of fire Samsung Galaxy Note 7, the Chinese electric hoverboards and even robots. Replacement liquid flammable solid non-flammable electrolytes and the use of specialized chip controllers are partial measures to solve the problem.
But researchers from Stanford University have found another elegant solution — the introduction of a battery of my own "fire extinguisher", a special flame retardant that is triggered when the temperature rises above the critical point.

The introduction of deterrent fire technology in batteries is considered by scientists for a long time. Was developed a number of solutions, ranging from simple polymeric membranes installed between the cathode and the anode, to the more complex, consisting in the use of composite or ceramic materials. However, most of these solutions decreased the electrical characteristics of the battery and is not guaranteed to completely get rid of the risk of spontaneous combustion.
The solution found Stenfordsky scientists, by introducing into the battery part of the TPP (triphenyl phosphate, triphenyl phosphate), which is enclosed in a sheath of polymeric microfibers. If the battery works in normal mode, the polymeric shell prevents penetration of the composition of TPP into the electrolyte. But if the temperature rises above 160 degrees Celsius, the polymer sheath melts and releases to the electrolyte TPP, which is a chemical retarder that prevented the process of combustion. From the first glance it may seem that 160 degrees is a high enough temperature. However, at this temperature, conventional lithium electrolyte is only beginning to approach the point of "no return", after which irreversible processes and starts a fire.

This method was tested on the small batteries of different types with rigid housings. The researchers found that the material of the TPP is highly effective in preventing fire, or quickly extinguishes the flame if ignition occurs.
Further research in this direction will allow to equip their own "fire extinguisher" and larger batteries, including batteries with a soft polymer coating, only scientists have yet to figure out how it all will affect the mechanical impact, for example, is applied to the battery from outside pressure, which can destroy the shell of polymeric microfibers. published
Source: ecotechnology
The whole truth about the Foundation — what you need to know to home to stand for long
“Drifting Island” for cleaning water bodies from heavy metals