423
Ejector for pumping station: principle of operation and installation rules
Deep aquifers are a common problem familiar to many land owners. Conventional surface pumping equipment can either not provide the house with water at all, or feeds it into the system too slowly and with weak pressure. An excellent way out of this situation can be an ejector for a water pumping station.
How it works.The deeper the water is, the harder it is to raise it to the surface. In practice, if the depth of the well is more than seven meters, the surface pump copes with its tasks with difficulty. Of course, for very deep wells it is more appropriate to purchase a high-performance submersible pump. But with the help of an ejector, you can improve the characteristics of the surface pump to an acceptable level and at a much lower cost.
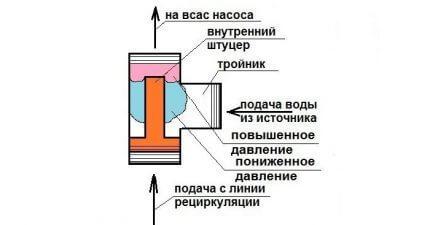
This scheme allows you to get an idea of the device and principle of operation of the ejector for the pump station. Accelerated backflow creates a low pressure area and transfers kinetic energy to the main stream of water. This unit has a relatively simple design, it can even be made independently from improvised materials. The principle of operation is based on giving the flow of water an additional acceleration, which will increase the amount of water coming from the source per unit time.
This solution is especially convenient for those who are going to install or have already installed a pump station with a surface pump. The ejector will increase the depth of water intake to 20-40 meters. It should also be noted that the acquisition of more powerful pumping equipment will lead to a noticeable increase in electricity consumption. In this sense, the ejector will bring significant benefits.
The ejector for the surface pump consists of the following elements:
A slight narrowing gives the flow of water a noticeable acceleration. Water enters the chamber of the mixer, creating an area with low pressure inside it. Under the influence of this process, a flow of water under higher pressure enters the mixer through the suction chamber.
The water in the ejector does not come from the well, but from the pump. That is, the ejector must be installed so that part of the water raised by the pump is returned to the ejector through the nozzle. The kinetic energy of this accelerated flow will be continuously transferred to the mass of water that is absorbed from the source.
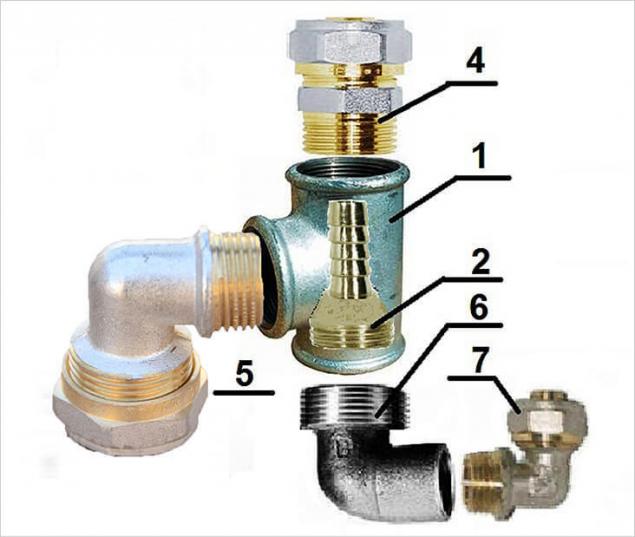
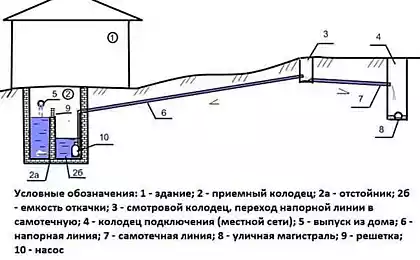
The diagram shows the device of the external ejector: 1 - tee; 2 - connector; 3 - adapter for the water pipe; 4, 5, 6 - corners Thus, a constant acceleration of the flow will be provided. Pumping equipment will need less energy to transport water to the surface. As a result, its efficiency will increase, as will the depth from which water can be drawn.
Some of the water produced in this way is sent through the recycling pipe again to the ejector, and the rest enters the water supply system at home. The presence of an ejector has another “plus”. It sucks water on its own, which additionally insures the pump from idle work, i.e. from a situation of “dry running” that is dangerous for all surface pumps.
To regulate the operation of the ejector, use a conventional crane. It is installed on a recycling pipe, through which water from the pump is sent to the nozzle of the ejector. With the help of a tap, the amount of water entering the ejector can be reduced or increased, thereby reducing or increasing the rate of return flow.
Choice: built-in or external? Depending on the place of installation, remote and built-in ejectors are distinguished. There is no big difference in the design features of these devices, but the location of the ejector still affects in some way both the installation of the pumping station and its operation. So, built-in ejectors are usually placed inside the pump housing or in close proximity to it.
As a result, the ejector takes up a minimum of space, and it does not have to be installed separately, it is enough to perform the usual installation of the pump station or the pump itself. In addition, the ejector located in the case is reliably protected from contamination. Dilution and reverse intake of water is made directly in the body of the pump. There is no need to install additional filters to protect the ejector from clogging with silt particles or sand.

Remote ejector for the pumping station is more difficult to install than the internal model, but this option creates a much smaller noise effect However, it should be remembered that the maximum efficiency of this model demonstrates at shallow depths, up to 10 meters. Pumps with built-in ejector are designed for such relatively shallow sources, their advantage is that they provide excellent pressure incoming water.
As a result, these characteristics are enough to use water not only for household needs, but also for irrigation or other economic operations. Another problem is the increased noise level, since the sound effect of water passing through the ejector is added to the vibration of the working pump.
If you decide to install a pump with a built-in ejector, you will have to take care of noise insulation especially carefully. Pumps or pump stations with a built-in ejector are recommended to be installed outside the home, for example, in a separate building or in a well caisson. The electric motor for the pump with an ejector should be more powerful than for a similar non-ejector model.
A remote or external ejector is installed at some distance from the pump, and this distance can be quite significant: 20-40 meters, some experts even consider 50 meters acceptable. Thus, the ejector can be placed directly in the water source, for example, in a well.
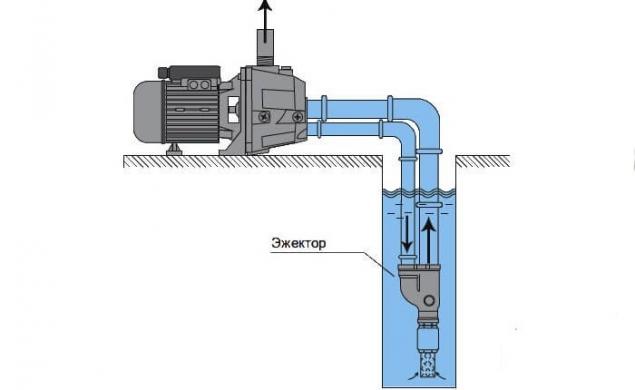
The external ejector does not so much increase the productivity of the pump, as it is designed to increase the depth of water intake from the source, which can reach 20-45 m. However, this type of device should be connected to the system using a recycling pipe, through which water will return to the ejector. The greater the depth of the device installation, the longer the pipe will have to be lowered into the well or well.
The presence of another pipe in the well is better to provide at the design stage of the device. Connecting the remote ejector also provides for the installation of a separate storage tank from which water will be taken for recycling.
This tank allows you to reduce the load on the surface pump, saving some energy. It is worth noting that the efficiency of the external ejector is somewhat lower than that of the models built into the pump, but the ability to significantly increase the depth of the fence makes you come to terms with this drawback.
When using an external ejector, there is no need to place a pumping station directly near the water source. It can be installed in the basement of a residential building. The distance to the source can vary within 20-40 meters, this will not affect the performance of the pumping equipment.
Ejector installation procedure As already mentioned, the installation of an ejector built into the pump does not cause any special problems, since the device is already in the device body. The surface pump is simply connected to the water supply hose on one side, as well as to the water supply system on the other side.
If it is used as part of the pumping station, the pump is connected to the accumulator by means of a special connection for five outlets. In addition, the pump will need to be connected to the contacts of the pressure relay to ensure that it is automatically turned on and off.
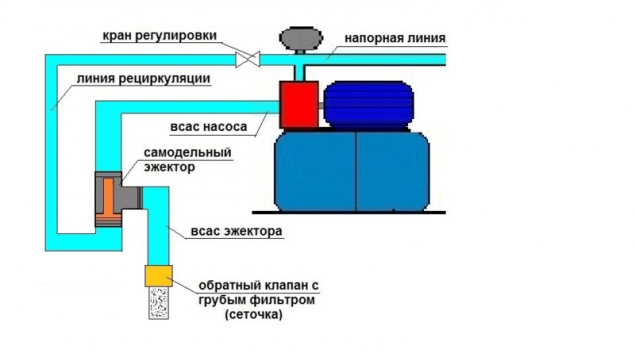
This diagram clearly shows the order of connecting the remote ejector to the pump station with indication of the places of installation of all the necessary nodes Before turning on the surface pump, it must be filled with water through the filling hole provided for this. You can not turn on such equipment without water, it can burn. If the pump installation is done correctly, the ejector will work without interruption.
But the installation of the remote ejector is made according to a more complex scheme. To begin with, you will need to install a pipe that will provide a return flow of water from the storage device to the ejector. A reverse valve is installed on the suction section of the ejector. It should be followed by a mesh filter that will protect the device from clogging.
On top of the recycling pipe, you need to install a control valve to regulate the amount of water that goes to the ejector. This node is not mandatory, but can significantly improve the situation with water pressure in the house. The less water will return to the ejector, the more it will remain for the water supply system at home.
Thus, it is possible to influence the water pressure in the water supply. With its lack, you should slightly twist the adjustment crane on the reverse highway. If the pressure is too large and creates an unnecessary load on the water supply system, it makes sense to direct more water to the ejector to improve the efficiency of the pumping equipment.
Some industrial models of ejectors are already equipped with a system of such adjustment. The instructions that are attached to the device usually describe in detail the order of setting the ejector.
Connecting a homemade ejector The built-in ejector is usually purchased simultaneously with the pump, but the external model is very often made with their own hands. It will be useful to consider the process of creating and connecting such a device. In order to make an ejector, you will need such details as a tee with internal threaded connections, fittings, taps, couplings, etc. The device is assembled as follows:
Connect the lower part of the tee with the connector so that the exit tube is at the top, and the connection with a smaller diameter was inside the ejector. Then you need to refine the design, cutting off the narrow part of the fitting, if it protrudes from the tee. If the fitting is too short, it is expanded using a polymer tube. On the upper side of the tee screw adapter with external thread. To the other end of the adapter, a PVC water pipe is attached using a fitting. Now to the bottom side of the tee, in which a narrow fitting is already inserted, the branch should be attached in the form of a corner. To this diversion, a pipe is attached, through which the return flow of water to the ejector will flow. To the side pipe of the tee is attached another corner. To this corner with the help of a tsang clamp, a pipe is attached, water from a well, well, etc. will be absorbed through it. The distance between the edge of the tee and the connection should be approximately 2-3 mm. This will ensure the creation of a dilution area with the necessary characteristics. A crimping nut is used to fix the recycling pipe.
It turns out that two elements are attached to the inner thread of the bottom pipe of the tee simultaneously. One of them is inside the tee and the other is outside. To both of them fit on the same threaded connection, you should cut off part of the thread of the fitter.
Of course, all threaded connections must be sealed and sealed. FUM tape is most often used for this. Sometimes not metal-plastic pipes are used to connect the ejector to the pumping station, but polyethylene structures. For their installation, special crimping elements should be used, and tsang clamps, which are good for metal plastic, will not work in this situation.

All threaded ejector connections should be carefully sealed and sealed, for example, with the help of FUM tape or other suitable material, you should think in advance about what kind of pipes will be connected to the remote ejector. Polyethylene structures bend well when heated, which allows you to do without corners when connecting the ejector. The pipe is simply bent in the right place and at the right angle, and then attached to the ejector.
So, the device has three outputs, each of which should be connected to the appropriate pipe. First, a pipe is usually installed through which water will be taken from the source. It joins the side exit from the ejector.
At the end of this pipe, a return valve and a mesh filter are necessarily installed. This pipe must be long enough to sink deep into the water. But do not take water at the bottom of the source, as this can lead to clogging of the ejector, even despite the presence of a filter.
Then you can connect the pipe to the lower end of the ejector, in which a narrowed connection is installed. This is the highway through which water is recycled. The second end of this pipe should be connected to a container from which water will be drawn to create a reverse flow.
The third pipe is an ordinary water main. At one end, it is mounted on the upper tube of the ejector, and the second is attached to the surface pump. It should be remembered that the diameter of the pipe through which water is taken from the source should exceed the size of the pipe through which water is supplied to the ejector.
If an inch pipe is used on the feed, then it is recommended to take the pipe a quarter of an inch more for suction. After all the connections are made, the ejector is lowered into water. Before the first start of the system, it must be filled with water. The pump is filled through a special hole. Pipes leading to the ejector must also be filled with water.
The initial start of the pumping station is recommended according to the following scheme:
Pour water into the pump through a special hole. Close the faucet through which water flows from the pumping station to the water supply system. Turn on the pump for about 10-20 seconds and turn off immediately. Open the faucet and blow some air out of the system. Repeat the cycle of short-term pump switches/offs in combination with air venting until the pipes are filled with water. Turn the pump on again. Wait for the pump to be filled and the pump to automatically shut down. Open any water tap. Wait until the water flows out of the accumulator, and the pump will turn on automatically. If the start of the system with the ejector water did not go, perhaps air leaks into the pipes somehow, or the initial pouring of water was not performed correctly. It makes sense to check the presence and condition of the return valve. If it is not there, the water will simply pour into the well, and the pipes will remain empty.
These points should be taken into account when using a pump station with an ejector, which starts after prolonged storage. The return valve, pipe integrity and tightness of the connections are best checked immediately.
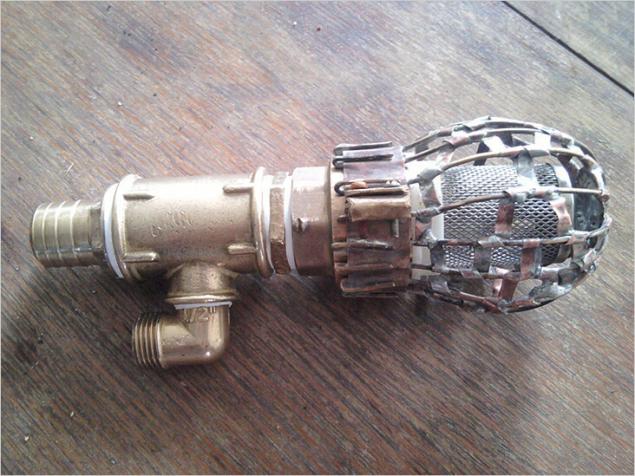

The lower tube of the ejector, through which the water is taken, should be protected from contamination with a mesh filter rough cleaning If everything is in order, and the water does not come, you need to check the voltage coming to the pumping station. If it is too low, the pump simply cannot operate at full capacity. It is necessary to establish a normal power supply of equipment, and the problem will disappear.
If the ejector is needed to improve the water pressure in the system, and not to increase the depth of water intake, you can use the above model of a homemade ejector. But it does not need to be immersed in water, it can be placed in a convenient place near the surface pump. In this case, the ejector will work in much the same way as the built-in industrial production model.
Useful video on ejectors In this video, the question of the depth of suction of the surface pump and options for solving the problem with an ejector are discussed in detail:
Here the principle of ejector operation is clearly demonstrated:
The ejector is a simple, but very useful device. This is a convenient and useful way to improve the performance of pumping equipment in a private home. But the installation of the ejector, especially the remote model, must be performed correctly, only in this way you can ensure a noticeable increase in water pressure. published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Source: sovet-ingenera.com/vodosnab/nasosy/ezhektor-dlya-nasosnoj-stancii-princip-raboty-i-pravila-ustanovki.html
How it works.The deeper the water is, the harder it is to raise it to the surface. In practice, if the depth of the well is more than seven meters, the surface pump copes with its tasks with difficulty. Of course, for very deep wells it is more appropriate to purchase a high-performance submersible pump. But with the help of an ejector, you can improve the characteristics of the surface pump to an acceptable level and at a much lower cost.

This scheme allows you to get an idea of the device and principle of operation of the ejector for the pump station. Accelerated backflow creates a low pressure area and transfers kinetic energy to the main stream of water. This unit has a relatively simple design, it can even be made independently from improvised materials. The principle of operation is based on giving the flow of water an additional acceleration, which will increase the amount of water coming from the source per unit time.
This solution is especially convenient for those who are going to install or have already installed a pump station with a surface pump. The ejector will increase the depth of water intake to 20-40 meters. It should also be noted that the acquisition of more powerful pumping equipment will lead to a noticeable increase in electricity consumption. In this sense, the ejector will bring significant benefits.
The ejector for the surface pump consists of the following elements:
- suction chamber;
- mixing assembly;
- diffuser;
- narrowed nozzle.
A slight narrowing gives the flow of water a noticeable acceleration. Water enters the chamber of the mixer, creating an area with low pressure inside it. Under the influence of this process, a flow of water under higher pressure enters the mixer through the suction chamber.
The water in the ejector does not come from the well, but from the pump. That is, the ejector must be installed so that part of the water raised by the pump is returned to the ejector through the nozzle. The kinetic energy of this accelerated flow will be continuously transferred to the mass of water that is absorbed from the source.

The diagram shows the device of the external ejector: 1 - tee; 2 - connector; 3 - adapter for the water pipe; 4, 5, 6 - corners Thus, a constant acceleration of the flow will be provided. Pumping equipment will need less energy to transport water to the surface. As a result, its efficiency will increase, as will the depth from which water can be drawn.
Some of the water produced in this way is sent through the recycling pipe again to the ejector, and the rest enters the water supply system at home. The presence of an ejector has another “plus”. It sucks water on its own, which additionally insures the pump from idle work, i.e. from a situation of “dry running” that is dangerous for all surface pumps.
To regulate the operation of the ejector, use a conventional crane. It is installed on a recycling pipe, through which water from the pump is sent to the nozzle of the ejector. With the help of a tap, the amount of water entering the ejector can be reduced or increased, thereby reducing or increasing the rate of return flow.
Choice: built-in or external? Depending on the place of installation, remote and built-in ejectors are distinguished. There is no big difference in the design features of these devices, but the location of the ejector still affects in some way both the installation of the pumping station and its operation. So, built-in ejectors are usually placed inside the pump housing or in close proximity to it.
As a result, the ejector takes up a minimum of space, and it does not have to be installed separately, it is enough to perform the usual installation of the pump station or the pump itself. In addition, the ejector located in the case is reliably protected from contamination. Dilution and reverse intake of water is made directly in the body of the pump. There is no need to install additional filters to protect the ejector from clogging with silt particles or sand.

Remote ejector for the pumping station is more difficult to install than the internal model, but this option creates a much smaller noise effect However, it should be remembered that the maximum efficiency of this model demonstrates at shallow depths, up to 10 meters. Pumps with built-in ejector are designed for such relatively shallow sources, their advantage is that they provide excellent pressure incoming water.
As a result, these characteristics are enough to use water not only for household needs, but also for irrigation or other economic operations. Another problem is the increased noise level, since the sound effect of water passing through the ejector is added to the vibration of the working pump.
If you decide to install a pump with a built-in ejector, you will have to take care of noise insulation especially carefully. Pumps or pump stations with a built-in ejector are recommended to be installed outside the home, for example, in a separate building or in a well caisson. The electric motor for the pump with an ejector should be more powerful than for a similar non-ejector model.
A remote or external ejector is installed at some distance from the pump, and this distance can be quite significant: 20-40 meters, some experts even consider 50 meters acceptable. Thus, the ejector can be placed directly in the water source, for example, in a well.

The external ejector does not so much increase the productivity of the pump, as it is designed to increase the depth of water intake from the source, which can reach 20-45 m. However, this type of device should be connected to the system using a recycling pipe, through which water will return to the ejector. The greater the depth of the device installation, the longer the pipe will have to be lowered into the well or well.
The presence of another pipe in the well is better to provide at the design stage of the device. Connecting the remote ejector also provides for the installation of a separate storage tank from which water will be taken for recycling.
This tank allows you to reduce the load on the surface pump, saving some energy. It is worth noting that the efficiency of the external ejector is somewhat lower than that of the models built into the pump, but the ability to significantly increase the depth of the fence makes you come to terms with this drawback.
When using an external ejector, there is no need to place a pumping station directly near the water source. It can be installed in the basement of a residential building. The distance to the source can vary within 20-40 meters, this will not affect the performance of the pumping equipment.
Ejector installation procedure As already mentioned, the installation of an ejector built into the pump does not cause any special problems, since the device is already in the device body. The surface pump is simply connected to the water supply hose on one side, as well as to the water supply system on the other side.
If it is used as part of the pumping station, the pump is connected to the accumulator by means of a special connection for five outlets. In addition, the pump will need to be connected to the contacts of the pressure relay to ensure that it is automatically turned on and off.

This diagram clearly shows the order of connecting the remote ejector to the pump station with indication of the places of installation of all the necessary nodes Before turning on the surface pump, it must be filled with water through the filling hole provided for this. You can not turn on such equipment without water, it can burn. If the pump installation is done correctly, the ejector will work without interruption.
But the installation of the remote ejector is made according to a more complex scheme. To begin with, you will need to install a pipe that will provide a return flow of water from the storage device to the ejector. A reverse valve is installed on the suction section of the ejector. It should be followed by a mesh filter that will protect the device from clogging.
On top of the recycling pipe, you need to install a control valve to regulate the amount of water that goes to the ejector. This node is not mandatory, but can significantly improve the situation with water pressure in the house. The less water will return to the ejector, the more it will remain for the water supply system at home.
Thus, it is possible to influence the water pressure in the water supply. With its lack, you should slightly twist the adjustment crane on the reverse highway. If the pressure is too large and creates an unnecessary load on the water supply system, it makes sense to direct more water to the ejector to improve the efficiency of the pumping equipment.
Some industrial models of ejectors are already equipped with a system of such adjustment. The instructions that are attached to the device usually describe in detail the order of setting the ejector.
Connecting a homemade ejector The built-in ejector is usually purchased simultaneously with the pump, but the external model is very often made with their own hands. It will be useful to consider the process of creating and connecting such a device. In order to make an ejector, you will need such details as a tee with internal threaded connections, fittings, taps, couplings, etc. The device is assembled as follows:
Connect the lower part of the tee with the connector so that the exit tube is at the top, and the connection with a smaller diameter was inside the ejector. Then you need to refine the design, cutting off the narrow part of the fitting, if it protrudes from the tee. If the fitting is too short, it is expanded using a polymer tube. On the upper side of the tee screw adapter with external thread. To the other end of the adapter, a PVC water pipe is attached using a fitting. Now to the bottom side of the tee, in which a narrow fitting is already inserted, the branch should be attached in the form of a corner. To this diversion, a pipe is attached, through which the return flow of water to the ejector will flow. To the side pipe of the tee is attached another corner. To this corner with the help of a tsang clamp, a pipe is attached, water from a well, well, etc. will be absorbed through it. The distance between the edge of the tee and the connection should be approximately 2-3 mm. This will ensure the creation of a dilution area with the necessary characteristics. A crimping nut is used to fix the recycling pipe.
It turns out that two elements are attached to the inner thread of the bottom pipe of the tee simultaneously. One of them is inside the tee and the other is outside. To both of them fit on the same threaded connection, you should cut off part of the thread of the fitter.
Of course, all threaded connections must be sealed and sealed. FUM tape is most often used for this. Sometimes not metal-plastic pipes are used to connect the ejector to the pumping station, but polyethylene structures. For their installation, special crimping elements should be used, and tsang clamps, which are good for metal plastic, will not work in this situation.

All threaded ejector connections should be carefully sealed and sealed, for example, with the help of FUM tape or other suitable material, you should think in advance about what kind of pipes will be connected to the remote ejector. Polyethylene structures bend well when heated, which allows you to do without corners when connecting the ejector. The pipe is simply bent in the right place and at the right angle, and then attached to the ejector.
So, the device has three outputs, each of which should be connected to the appropriate pipe. First, a pipe is usually installed through which water will be taken from the source. It joins the side exit from the ejector.
At the end of this pipe, a return valve and a mesh filter are necessarily installed. This pipe must be long enough to sink deep into the water. But do not take water at the bottom of the source, as this can lead to clogging of the ejector, even despite the presence of a filter.
Then you can connect the pipe to the lower end of the ejector, in which a narrowed connection is installed. This is the highway through which water is recycled. The second end of this pipe should be connected to a container from which water will be drawn to create a reverse flow.
The third pipe is an ordinary water main. At one end, it is mounted on the upper tube of the ejector, and the second is attached to the surface pump. It should be remembered that the diameter of the pipe through which water is taken from the source should exceed the size of the pipe through which water is supplied to the ejector.
If an inch pipe is used on the feed, then it is recommended to take the pipe a quarter of an inch more for suction. After all the connections are made, the ejector is lowered into water. Before the first start of the system, it must be filled with water. The pump is filled through a special hole. Pipes leading to the ejector must also be filled with water.
The initial start of the pumping station is recommended according to the following scheme:
Pour water into the pump through a special hole. Close the faucet through which water flows from the pumping station to the water supply system. Turn on the pump for about 10-20 seconds and turn off immediately. Open the faucet and blow some air out of the system. Repeat the cycle of short-term pump switches/offs in combination with air venting until the pipes are filled with water. Turn the pump on again. Wait for the pump to be filled and the pump to automatically shut down. Open any water tap. Wait until the water flows out of the accumulator, and the pump will turn on automatically. If the start of the system with the ejector water did not go, perhaps air leaks into the pipes somehow, or the initial pouring of water was not performed correctly. It makes sense to check the presence and condition of the return valve. If it is not there, the water will simply pour into the well, and the pipes will remain empty.
These points should be taken into account when using a pump station with an ejector, which starts after prolonged storage. The return valve, pipe integrity and tightness of the connections are best checked immediately.

The lower tube of the ejector, through which the water is taken, should be protected from contamination with a mesh filter rough cleaning If everything is in order, and the water does not come, you need to check the voltage coming to the pumping station. If it is too low, the pump simply cannot operate at full capacity. It is necessary to establish a normal power supply of equipment, and the problem will disappear.
If the ejector is needed to improve the water pressure in the system, and not to increase the depth of water intake, you can use the above model of a homemade ejector. But it does not need to be immersed in water, it can be placed in a convenient place near the surface pump. In this case, the ejector will work in much the same way as the built-in industrial production model.
Useful video on ejectors In this video, the question of the depth of suction of the surface pump and options for solving the problem with an ejector are discussed in detail:
Here the principle of ejector operation is clearly demonstrated:
The ejector is a simple, but very useful device. This is a convenient and useful way to improve the performance of pumping equipment in a private home. But the installation of the ejector, especially the remote model, must be performed correctly, only in this way you can ensure a noticeable increase in water pressure. published
P.S. And remember, just changing our consumption – together we change the world!
Source: sovet-ingenera.com/vodosnab/nasosy/ezhektor-dlya-nasosnoj-stancii-princip-raboty-i-pravila-ustanovki.html
Electric cars will not become mainstream before 2025
China approves standards for self-propelled vehicles in 2018