928
Theory of emotions Kellerman-Plutchik
The theory was developed in a monograph in 1962. She has received international recognition and was used to solve the structure of group processes helped to formulate the idea of intrapersonal processes and mechanisms of psychological protection.
Currently, the basic postulates of the theory are included in known directions psychotherapeutic and psychodiagnostic system.

FUNDAMENTALS OF THE THEORY OF EMOTIONS OUTLINED SIX TENETS
1. Emotions are the mechanisms of communication and survival, based on evolutionary adaptation. They are stored in functionally equivalent forms across all phylogenetic levels. Communication is due to the eight basic adaptive responses, which are the prototypes of the eight basic emotions:
2. Emotions have a genetic basis.
3. Emotion is a hypothetical construction based on the obvious phenomena of different classes. Hypothetical models are shown in table 1:
The stimulus event
Implicit cognition
Experience
Behavior
Effect
The threat
"Danger"
Fear, terror
Flight
Self-preservation
Obstacle
The "enemy"
Anger, rage
The attack, biting
Destruction
Potential partner
"To have"
Joy, ecstasy
Courtship mating
Reproduction
The loss of a significant individual
"Abandonment"
Sadness, grief
The call for assistance and reunification
Reintegration
Member of the group
"Friend"
Acceptance, trust
Courting, assistance
Affiliate, accession
Disgusting object
"Poison"
Disgust, hatred
The eruption, the repulsion
Rejection
New territory
"What is it?"
Waiting
Survey organization
The study
Unexpected new
"What is it?"
Surprise
Stop anxiety
Orientation
Table 1. The incentive effect
4. Emotions are chains of events with stabilizing feedback loops that support behavioral homeostasis. Developments in the environment the events are subjected to cognitive evaluation, the evaluation having feelings (emotions), accompanied by physiological changes. In response, the body performs the behavior, designed to give effect to the stimulus (table 1).
5. Relations among emotions can be represented in three-dimensional (spatial) structural model. The vertical vector represents the force of emotions, from left to right — vector similarities of the emotions, and the axis from front to back characterizes the polarity opposite emotions. This postulate includes a provision stating that some emotions are primary and others are derivatives or mixed (see scheme 1).
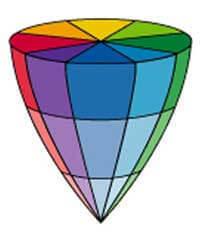
Scheme 1. A three-dimensional model of emotions PLUTCHIK
6. Emotions associated with specific traits or typologies. Diagnostic terms such as "depression", "manic", "paranoia" is considered as an extreme expression of such emotions as sadness, joy, and rejection (table 2).
EMOTION CLASSIFICATION
Biological regulatory processes
The behavior expression
Adaptive function
Subjectivisation
Traits
Diagnoses
Avoidance
Flight
Self-preservation
Fear
Timid
Passivity, anxiety
The approach
Attack
Destruction
Anger
Scandalous, quarrelsome
Aggressiveness
Association
Pairing
Reproduction
Joy
Friendly, sociable
Manic
Division
The signal of distress
Reunion
Sadness
Sad
Depressive
Swallowing
Food
Incorporation
The adoption
Gullible
Hysteria
Release
The eruption
Rejection
Disgust
Hostile
Paranoia
The beginning of action
Intelligence
The study
Waiting
Curious
Obsession
Stop
Fading
Orientation
Surprise
Impulsive
Instability
Table 2. Emotions and their derivatives
A structural model of emotions is the basis of constructing a theoretical model of psychological protection.
Model of mechanisms of psychological protection was designed by Robert Plutchik in collaboration with G. Kellermann and H. Conte in 1979.
STRUCTURAL THEORY OF PERSONALITY HENRY KELLERMAN
THE SECURITY MODEL INCLUDES FIVE PRINCIPLES
1. Specific protection are formed for coping with specific emotions.
2. There are eight basic mechanisms of protection, which are developed for coping with eight basic emotions.
3. Eight basic protective mechanisms have properties of both similarities and polarities.
4. Certain types of personality diagnoses are based on typical protective styles.
5. The individual may use any combination of protection mechanisms.
On the way to unwanted consciousness to the psyche distorted information. The distortion of reality through protection can occur in the following way:
1. protection lack of recycling as follows: denial, displacement, suppression.
2. protection with the transformation or distortion of the content of thoughts, feelings, behavior: rationalization, projection, alienation, substitution, reaction formation, compensation.
3. protection from discharge negative emotional stress: implement in action, the somatization of anxiety, sublimation.
4. protection of the manipulative type: regression, imagination, disease care or education of symptoms.
The result psychoevolutionary theory of emotions Robert Plutchik and structural theories of personality Henry Kellerman was the "Diagnostic system Kellerman-Plutchik", which formed the basis of psycho-diagnostic methodology "Index lifestyle" (Life Style Index).
The system is based on the theory that in every person there is a disposition (genetic predisposition) to a specific mental disorder. Psychological defense mechanism plays a regulatory role of intrapersonal balance due to the damping of the dominant emotion (scheme 2).
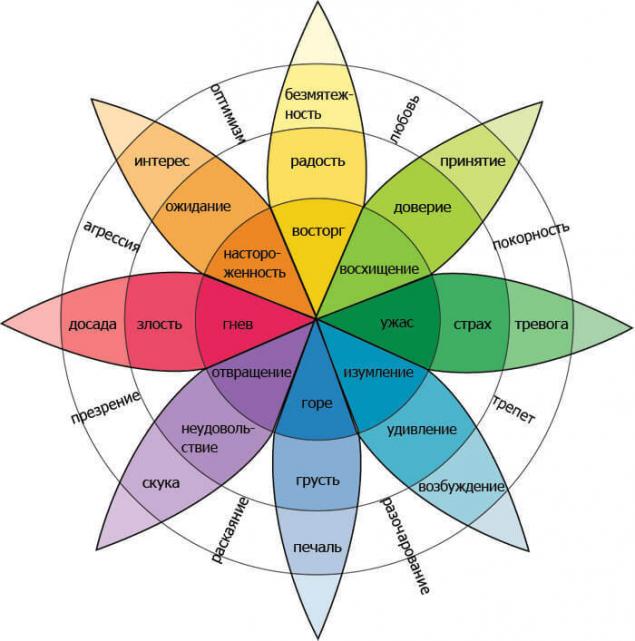
Scheme 2. The system of dispositions by Kellerman and Plutchik
According to the diagnostic system, analysis of the leading dispositions characterizes personal features of the subject.
When interacting with a stimulus occur are specific to the disposition of the experiences in the form of emotions. Leading emotion creates a need which is not always embedded in the frame acceptable performance. To maintain adaptation, it has a safety mechanism designed to suppress unacceptable emotions and individual experiences of the unconscious impulse that causes to overestimate the stimulus. Personal balance is achieved through the formation of protective behavior.
CHARACTERISTIC DISPOSITIONS
Disposition of of mania.
Leading emotion - the joy, the need to excess are pleasant incentives — hedonism. Protection - jet formation due to the suppression of the attractiveness of a pleasant stimulus with the " Super — Ego ". The development mechanism is associated with the final assimilation by the individual of "higher social value".Impulse – pay is the opposite. Revaluation of incentive: "Everything about this is disgusting".
Protective behavior is normal: strong feelings regarding violations of "personal space", underlined the desire to meet accepted standards of conduct, relevance, concern for the "decent" appearance, courtesy, helpfulness, selflessness, sociability. The rejection of everything associated with the functioning of the body and gender relations.
Disposition of hysteria.
Leading emotion – acceptance. Protection – denial. Evolves to contain the emotions of adopting others, if they demonstrate emotional indifference or rejection. Excessive adoption kompensiruet denial of those moments that "don't like" consciousness. The flow of positive qualities of the perceived object causes the hysteria to idealize it (for example, tantrums are often falling). Momentum - don't overlook it. Reassessment of stimulus does not occur, the stimulus is not seen.
Protective behavior is normal: sociability, desire to be the center of attention, thirst for recognition, arrogance, optimism, ease, boasting, self-pity, courtesy, affective demeanor, Paphos, easy portability of criticism and lack of self-criticism.
Aggressive disposition.
The leading emotion is anger. Protection substitution. Developed to deter the emotion of anger by a stronger, older or an important stakeholder as frustrator. Substitution may be sent as outward, forming destructive behavior, and inwards in the form of autoaggression. Impulse - attacking something that replaces it. Revaluation of the stimulus: "That's who to blame".
Protective behavior is normal: impulsivity, irritability, irascibility, demanding of others, the reactions of protest in response to criticism, the lack of a sense of guilt.
Disposition of psychopathy.
Leading emotion – surprise. Protection – regression. Develops in early childhood to curb the feelings of insecurity and fear of failure associated with the initiative. As a rule, encouraged adults with installation on an emotional symbiosis and infantilization of the child.Impulse – cry about it. Revaluation of incentive: "You have to help me".
Protective behavior is normal: impulsiveness, weakness of character, lack of deep interests, yielding to the influence of others, suggestibility, inability to finish the begun business, easy change of mood, the ability to easily establish contact surface. The tendency toward mysticism and superstition, intolerance loneliness, the need for stimulation, monitoring, reassurance, comfort, new experiences. In exquisite situation — increased drowsiness and excessive appetite, manipulation of small objects, involuntary actions (rubbing his hands, twist buttons, etc.), specific "children's" facial expressions and speech.
Depressive disposition.
Leading emotion – sadness. Protection – compensation compensates for the missing self-esteem that allows the person to cope with the condition of depression. Momentum – try to acquire it.Revaluation of the stimulus: "But I... I still... When I...".
Protective behavior is normal: constant suffering because of the loss of an imaginary object and loss of self-esteem. The behavior that caused the installation to the serious and methodical work on yourself, finding and fixing its shortcomings, the achievement of high results in activity; serious sports, collecting, the desire for originality.
Paranoid disposition.
Leading emotion – disgust (aversion). Protection – projection. Develops as a result of emotional rejection in early childhood from significant persons. Projection allows you to transfer your own inferiority onto others. Impulse is condemning it. Revaluation of the stimulus: "All people are evil".
Protective behavior in the norm: control, absence of suggestibility, increased criticalness, pride, vanity, selfishness, resentment, a keen sense of justice, arrogance, suspicion, jealousy, hostility, stubbornness, intransigence, intolerance to opposition, isolation, pessimism, hypersensitivity to criticism and comments, exactingness to himself and to others, the desire to achieve high performance in any activity.
Passive disposition.
Leading emotion – fear. Defense suppression (displacement). Developed to deter emotions of fear, manifestations of which are unacceptable to a positive self-image and threaten to hit in direct dependence on the aggressor. Momentum – I do not remember about it. Revaluation of the stimulus: "don't I know it".
Protective behavior is normal: the inertia and passivity, withdrawal, lack of initiative, tendency to be dependent on anyone, a careful avoidance of situations that may become problematic and cause fear, submissiveness, timidity, forgetfulness, fear of meeting new people.
Obsessive disposition.
Leading emotion – waiting. Protection – rationalization (intellectualization and sublimation). Develops in early adolescence to contain the emotions of expectation or anticipation of fear to get over the disappointment of failure and uncertainty in competition with their peers. Impulse – preobreli, reconsider it. Revaluation of incentive: "Everything is explainable".
Protective behavior is normal: increased control in order to know the emotions of others, the tendency to analysis and introspection, responsibility, honesty, thoroughness, love of order, eharacteristic bad habits, prudence, discipline, individualism, the desire to stick around the middle.published
Author: Maxim Velichko
Source: psy-diagnoz.com/theories/103-teoriya-emotsij.html
Currently, the basic postulates of the theory are included in known directions psychotherapeutic and psychodiagnostic system.

FUNDAMENTALS OF THE THEORY OF EMOTIONS OUTLINED SIX TENETS
1. Emotions are the mechanisms of communication and survival, based on evolutionary adaptation. They are stored in functionally equivalent forms across all phylogenetic levels. Communication is due to the eight basic adaptive responses, which are the prototypes of the eight basic emotions:
- Incorporation of eating food or the adoption of favorable stimuli inside the body. This psychological mechanism is known as intreccia.
- Rejection - ridding the body of anything the what was perceived earlier.
- Patronage behavior is designed to ensure the avoidance of danger or harm. This includes flight and any other action that increases the distance between the body and source of danger.
- Destruction - behavior designed to destroy the barrier that hinders satisfaction of important needs.
- Reproduction , reproductive behavior, which can be defined in terms of approximation, the tendency to preserve the contact and mixing of genetic materials.
- Reintegration is the behavioral reaction to the loss of something important, something possessed or enjoyed. Its function is to regain custody.
- Orientation is a behavioural response to the contact with unknown, new, or undefined object.
- The study of behavior, providing the individual's schematic representation of this environment.
2. Emotions have a genetic basis.
3. Emotion is a hypothetical construction based on the obvious phenomena of different classes. Hypothetical models are shown in table 1:
The stimulus event
Implicit cognition
Experience
Behavior
Effect
The threat
"Danger"
Fear, terror
Flight
Self-preservation
Obstacle
The "enemy"
Anger, rage
The attack, biting
Destruction
Potential partner
"To have"
Joy, ecstasy
Courtship mating
Reproduction
The loss of a significant individual
"Abandonment"
Sadness, grief
The call for assistance and reunification
Reintegration
Member of the group
"Friend"
Acceptance, trust
Courting, assistance
Affiliate, accession
Disgusting object
"Poison"
Disgust, hatred
The eruption, the repulsion
Rejection
New territory
"What is it?"
Waiting
Survey organization
The study
Unexpected new
"What is it?"
Surprise
Stop anxiety
Orientation
Table 1. The incentive effect
4. Emotions are chains of events with stabilizing feedback loops that support behavioral homeostasis. Developments in the environment the events are subjected to cognitive evaluation, the evaluation having feelings (emotions), accompanied by physiological changes. In response, the body performs the behavior, designed to give effect to the stimulus (table 1).
5. Relations among emotions can be represented in three-dimensional (spatial) structural model. The vertical vector represents the force of emotions, from left to right — vector similarities of the emotions, and the axis from front to back characterizes the polarity opposite emotions. This postulate includes a provision stating that some emotions are primary and others are derivatives or mixed (see scheme 1).

Scheme 1. A three-dimensional model of emotions PLUTCHIK
6. Emotions associated with specific traits or typologies. Diagnostic terms such as "depression", "manic", "paranoia" is considered as an extreme expression of such emotions as sadness, joy, and rejection (table 2).
EMOTION CLASSIFICATION
Biological regulatory processes
The behavior expression
Adaptive function
Subjectivisation
Traits
Diagnoses
Avoidance
Flight
Self-preservation
Fear
Timid
Passivity, anxiety
The approach
Attack
Destruction
Anger
Scandalous, quarrelsome
Aggressiveness
Association
Pairing
Reproduction
Joy
Friendly, sociable
Manic
Division
The signal of distress
Reunion
Sadness
Sad
Depressive
Swallowing
Food
Incorporation
The adoption
Gullible
Hysteria
Release
The eruption
Rejection
Disgust
Hostile
Paranoia
The beginning of action
Intelligence
The study
Waiting
Curious
Obsession
Stop
Fading
Orientation
Surprise
Impulsive
Instability
Table 2. Emotions and their derivatives
A structural model of emotions is the basis of constructing a theoretical model of psychological protection.
Model of mechanisms of psychological protection was designed by Robert Plutchik in collaboration with G. Kellermann and H. Conte in 1979.
STRUCTURAL THEORY OF PERSONALITY HENRY KELLERMAN
THE SECURITY MODEL INCLUDES FIVE PRINCIPLES
1. Specific protection are formed for coping with specific emotions.
2. There are eight basic mechanisms of protection, which are developed for coping with eight basic emotions.
3. Eight basic protective mechanisms have properties of both similarities and polarities.
4. Certain types of personality diagnoses are based on typical protective styles.
5. The individual may use any combination of protection mechanisms.
On the way to unwanted consciousness to the psyche distorted information. The distortion of reality through protection can occur in the following way:
- ignored or not perceived;
- being perceived to be forgotten;
- in the event of admission to consciousness and of remembering interpreted convenient for the individual.
- First there are mechanisms, which are based on perceptual processes (sensation, perception and attention). That perception is responsible for the protection associated with ignorance, lack of understanding of the information. These include denial and regression, which are the most primitive and characterize the "abusers" of their personality as emotionally immature.
- Further there protection associated with memory, namely, forgetting information is repression and suppression.
- With the development of processes of thinking and imagination formed the most complex and Mature types of protection associated with processing and reassessment information is rationalization.
1. protection lack of recycling as follows: denial, displacement, suppression.
2. protection with the transformation or distortion of the content of thoughts, feelings, behavior: rationalization, projection, alienation, substitution, reaction formation, compensation.
3. protection from discharge negative emotional stress: implement in action, the somatization of anxiety, sublimation.
4. protection of the manipulative type: regression, imagination, disease care or education of symptoms.
The result psychoevolutionary theory of emotions Robert Plutchik and structural theories of personality Henry Kellerman was the "Diagnostic system Kellerman-Plutchik", which formed the basis of psycho-diagnostic methodology "Index lifestyle" (Life Style Index).
The system is based on the theory that in every person there is a disposition (genetic predisposition) to a specific mental disorder. Psychological defense mechanism plays a regulatory role of intrapersonal balance due to the damping of the dominant emotion (scheme 2).

Scheme 2. The system of dispositions by Kellerman and Plutchik
According to the diagnostic system, analysis of the leading dispositions characterizes personal features of the subject.
When interacting with a stimulus occur are specific to the disposition of the experiences in the form of emotions. Leading emotion creates a need which is not always embedded in the frame acceptable performance. To maintain adaptation, it has a safety mechanism designed to suppress unacceptable emotions and individual experiences of the unconscious impulse that causes to overestimate the stimulus. Personal balance is achieved through the formation of protective behavior.
CHARACTERISTIC DISPOSITIONS
Disposition of of mania.
Leading emotion - the joy, the need to excess are pleasant incentives — hedonism. Protection - jet formation due to the suppression of the attractiveness of a pleasant stimulus with the " Super — Ego ". The development mechanism is associated with the final assimilation by the individual of "higher social value".Impulse – pay is the opposite. Revaluation of incentive: "Everything about this is disgusting".
Protective behavior is normal: strong feelings regarding violations of "personal space", underlined the desire to meet accepted standards of conduct, relevance, concern for the "decent" appearance, courtesy, helpfulness, selflessness, sociability. The rejection of everything associated with the functioning of the body and gender relations.
Disposition of hysteria.
Leading emotion – acceptance. Protection – denial. Evolves to contain the emotions of adopting others, if they demonstrate emotional indifference or rejection. Excessive adoption kompensiruet denial of those moments that "don't like" consciousness. The flow of positive qualities of the perceived object causes the hysteria to idealize it (for example, tantrums are often falling). Momentum - don't overlook it. Reassessment of stimulus does not occur, the stimulus is not seen.
Protective behavior is normal: sociability, desire to be the center of attention, thirst for recognition, arrogance, optimism, ease, boasting, self-pity, courtesy, affective demeanor, Paphos, easy portability of criticism and lack of self-criticism.
Aggressive disposition.
The leading emotion is anger. Protection substitution. Developed to deter the emotion of anger by a stronger, older or an important stakeholder as frustrator. Substitution may be sent as outward, forming destructive behavior, and inwards in the form of autoaggression. Impulse - attacking something that replaces it. Revaluation of the stimulus: "That's who to blame".
Protective behavior is normal: impulsivity, irritability, irascibility, demanding of others, the reactions of protest in response to criticism, the lack of a sense of guilt.
Disposition of psychopathy.
Leading emotion – surprise. Protection – regression. Develops in early childhood to curb the feelings of insecurity and fear of failure associated with the initiative. As a rule, encouraged adults with installation on an emotional symbiosis and infantilization of the child.Impulse – cry about it. Revaluation of incentive: "You have to help me".
Protective behavior is normal: impulsiveness, weakness of character, lack of deep interests, yielding to the influence of others, suggestibility, inability to finish the begun business, easy change of mood, the ability to easily establish contact surface. The tendency toward mysticism and superstition, intolerance loneliness, the need for stimulation, monitoring, reassurance, comfort, new experiences. In exquisite situation — increased drowsiness and excessive appetite, manipulation of small objects, involuntary actions (rubbing his hands, twist buttons, etc.), specific "children's" facial expressions and speech.
Depressive disposition.
Leading emotion – sadness. Protection – compensation compensates for the missing self-esteem that allows the person to cope with the condition of depression. Momentum – try to acquire it.Revaluation of the stimulus: "But I... I still... When I...".
Protective behavior is normal: constant suffering because of the loss of an imaginary object and loss of self-esteem. The behavior that caused the installation to the serious and methodical work on yourself, finding and fixing its shortcomings, the achievement of high results in activity; serious sports, collecting, the desire for originality.
Paranoid disposition.
Leading emotion – disgust (aversion). Protection – projection. Develops as a result of emotional rejection in early childhood from significant persons. Projection allows you to transfer your own inferiority onto others. Impulse is condemning it. Revaluation of the stimulus: "All people are evil".
Protective behavior in the norm: control, absence of suggestibility, increased criticalness, pride, vanity, selfishness, resentment, a keen sense of justice, arrogance, suspicion, jealousy, hostility, stubbornness, intransigence, intolerance to opposition, isolation, pessimism, hypersensitivity to criticism and comments, exactingness to himself and to others, the desire to achieve high performance in any activity.
Passive disposition.
Leading emotion – fear. Defense suppression (displacement). Developed to deter emotions of fear, manifestations of which are unacceptable to a positive self-image and threaten to hit in direct dependence on the aggressor. Momentum – I do not remember about it. Revaluation of the stimulus: "don't I know it".
Protective behavior is normal: the inertia and passivity, withdrawal, lack of initiative, tendency to be dependent on anyone, a careful avoidance of situations that may become problematic and cause fear, submissiveness, timidity, forgetfulness, fear of meeting new people.
Obsessive disposition.
Leading emotion – waiting. Protection – rationalization (intellectualization and sublimation). Develops in early adolescence to contain the emotions of expectation or anticipation of fear to get over the disappointment of failure and uncertainty in competition with their peers. Impulse – preobreli, reconsider it. Revaluation of incentive: "Everything is explainable".
Protective behavior is normal: increased control in order to know the emotions of others, the tendency to analysis and introspection, responsibility, honesty, thoroughness, love of order, eharacteristic bad habits, prudence, discipline, individualism, the desire to stick around the middle.published
Author: Maxim Velichko
Source: psy-diagnoz.com/theories/103-teoriya-emotsij.html