525
The garden on straw units—a perfect solution
Growing vegetables on straw blocks — a new trend in organic farming. However, it is becoming popular with gardeners in the West. These garden beds do not require a lot of costs can be made anywhere in the garden, regardless of the soil and give good yields. It is an excellent option for running and developing areas.

Joel Karsten wrote a book "Garden on straw units" (Straw Bale Gardens), which brought an interesting table of comparison of traditional method and know-how on the straw:
An indicator Patch on a straw blocks Traditional vegetable garden Raised beds, container gardening labor Costs 75% less 100% less, especially in the first year of Raised beds, the ease of planting Yes No weed Yes weed a little, especially in the first year of Little monetary investment Yes Yes? Good survival rate of plants right? Yes, the Impossibility to fill (flood) plants Yes — - Well it keeps the humidity Yes Able to apply drip irrigation Yes Yes Yes Not needed rotation Yes - Mobility Yes inpatient beds depending on the size of the container, usually a stationary Need the tools to care no Yes Yes the Possibility of planting perennials no Yes Yes Pests and disease, possible Yes, possible Resistance of plants to frost higher less higher Compactness Yes — possible due to the compacted and joint planting, and placing of containers in various parts of the site And although many of these points are very controversial, especially from the point of view of organic farming, however, straw may indeed may be a good help, especially in undeveloped areas while you prepare the beds, plant cover crops and make compost — it is possible to get a decent harvest in the first year of virtually all cultures.
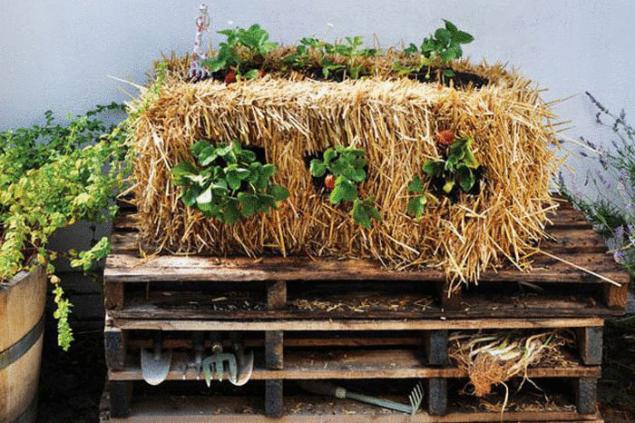

Straw block — excellent battery water. A few days after starting irrigation, straw block begins to heat up — it multiply and recycle organic matter, the microorganisms, consequently a large amount of carbon dioxide that also need plants. The porous structure of the straw allows it to breathe, that is, to draw oxygen inside and provide them with the bacteria.
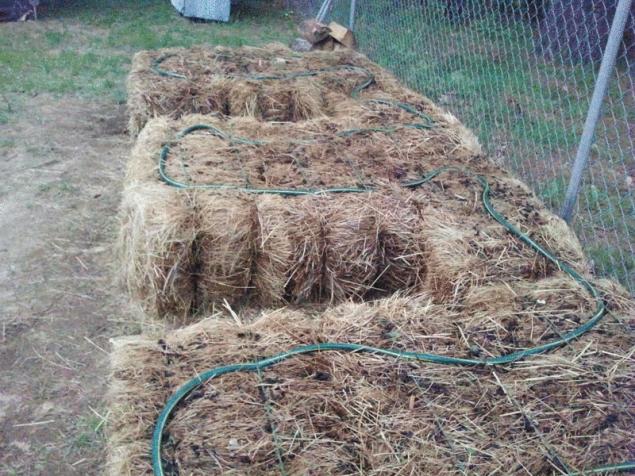

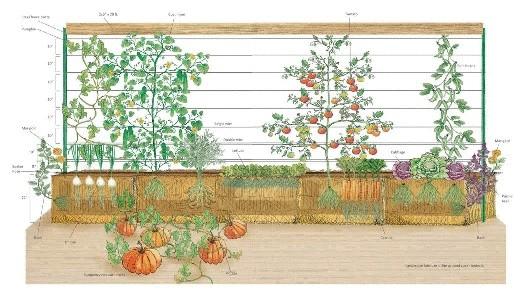
The garden on straw blocks to make not difficult, but it requires some preparations. First, you need to buy bales of straw, and make sure they are not moldy or caked.
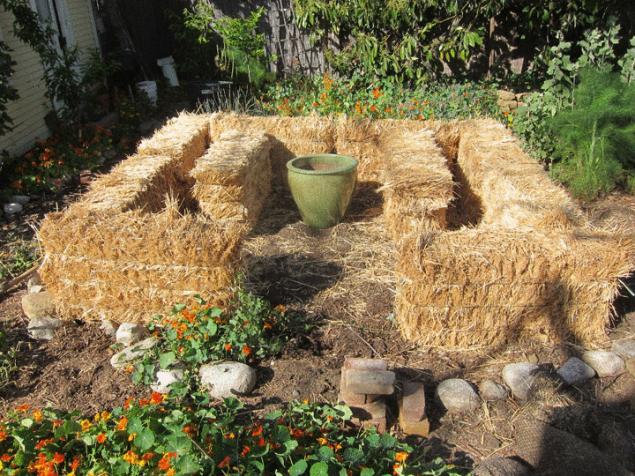

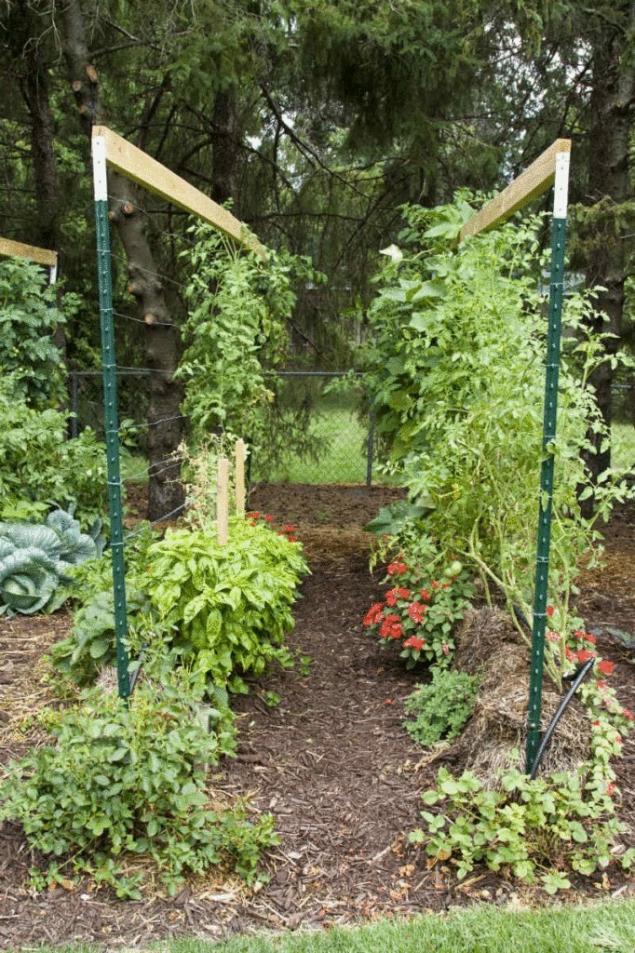
Then place them on the site. There is a lot of space for creativity: as in parcel geometry and in the vertical direction. There are some feature of the location of such beds on the slopes, because straw blocks can tip over by the wind.

The next stage is creating a breeding ground for plants. Initially for 3 days straw blocks abundantly shed water. Then comes the turn of nitrogen fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulphate) for another 5-7 days. For organic farming can be replaced by compost tea and other natural sources of nitrogen. While inside the bale begins to occur an active microbiological processes, and they are heated from the inside. You can "help" by adding the drug is effective microorganisms. 2-3 days of active irrigation and can be planted seedlings.
The seedling is planted with a lump of earth into the hole, done garden shovel or your hands. If you plant seeds, you need to put a bit of earth, or mixture with compost on the surface of the bales. There are almost no restrictions — virtually any annual crops will grow well in straw.
Remember to make drip irrigation!
For places with possible night frosts will provide the opportunity to shelter plants. For taller plants — make a trellis. The same beds can be arranged in the greenhouse.
Further care — as in the normal version, except for weeding, cultivation and mulching, which clearly reduces the time and labor costs.
Very difficult time pests. The straw is easy to penetrate or to postpone there eggs/larvae, so you need to carefully monitor the condition of the plants.
The spent bed can be transferred to compost, use as mulch or use it to make stationary. In any case, they are waste-free and even after harvest, can benefit your garden.
Another plus is that under a thatched bale will perepel all weeds, will divorce in a large number of worms and decomposed straw will significantly add to the fertility of the soil. Therefore, if after a year of straw blocks from this place clean, that will be clean, fertile soil, which is quite a bit paraglide with plane and also to plant anything.
I recommend also to watch diary of the experiment enthusiast from Ukraine (tag experiment):
Source: brukva.net

Joel Karsten wrote a book "Garden on straw units" (Straw Bale Gardens), which brought an interesting table of comparison of traditional method and know-how on the straw:
An indicator Patch on a straw blocks Traditional vegetable garden Raised beds, container gardening labor Costs 75% less 100% less, especially in the first year of Raised beds, the ease of planting Yes No weed Yes weed a little, especially in the first year of Little monetary investment Yes Yes? Good survival rate of plants right? Yes, the Impossibility to fill (flood) plants Yes — - Well it keeps the humidity Yes Able to apply drip irrigation Yes Yes Yes Not needed rotation Yes - Mobility Yes inpatient beds depending on the size of the container, usually a stationary Need the tools to care no Yes Yes the Possibility of planting perennials no Yes Yes Pests and disease, possible Yes, possible Resistance of plants to frost higher less higher Compactness Yes — possible due to the compacted and joint planting, and placing of containers in various parts of the site And although many of these points are very controversial, especially from the point of view of organic farming, however, straw may indeed may be a good help, especially in undeveloped areas while you prepare the beds, plant cover crops and make compost — it is possible to get a decent harvest in the first year of virtually all cultures.

Straw block — excellent battery water. A few days after starting irrigation, straw block begins to heat up — it multiply and recycle organic matter, the microorganisms, consequently a large amount of carbon dioxide that also need plants. The porous structure of the straw allows it to breathe, that is, to draw oxygen inside and provide them with the bacteria.

The garden on straw blocks to make not difficult, but it requires some preparations. First, you need to buy bales of straw, and make sure they are not moldy or caked.

Then place them on the site. There is a lot of space for creativity: as in parcel geometry and in the vertical direction. There are some feature of the location of such beds on the slopes, because straw blocks can tip over by the wind.

The next stage is creating a breeding ground for plants. Initially for 3 days straw blocks abundantly shed water. Then comes the turn of nitrogen fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulphate) for another 5-7 days. For organic farming can be replaced by compost tea and other natural sources of nitrogen. While inside the bale begins to occur an active microbiological processes, and they are heated from the inside. You can "help" by adding the drug is effective microorganisms. 2-3 days of active irrigation and can be planted seedlings.
The seedling is planted with a lump of earth into the hole, done garden shovel or your hands. If you plant seeds, you need to put a bit of earth, or mixture with compost on the surface of the bales. There are almost no restrictions — virtually any annual crops will grow well in straw.

Remember to make drip irrigation!
For places with possible night frosts will provide the opportunity to shelter plants. For taller plants — make a trellis. The same beds can be arranged in the greenhouse.
Further care — as in the normal version, except for weeding, cultivation and mulching, which clearly reduces the time and labor costs.
Very difficult time pests. The straw is easy to penetrate or to postpone there eggs/larvae, so you need to carefully monitor the condition of the plants.
The spent bed can be transferred to compost, use as mulch or use it to make stationary. In any case, they are waste-free and even after harvest, can benefit your garden.
Another plus is that under a thatched bale will perepel all weeds, will divorce in a large number of worms and decomposed straw will significantly add to the fertility of the soil. Therefore, if after a year of straw blocks from this place clean, that will be clean, fertile soil, which is quite a bit paraglide with plane and also to plant anything.
I recommend also to watch diary of the experiment enthusiast from Ukraine (tag experiment):
- The beginning - preparation units: they spilled water, and fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, then "Baikal EM")
- Planting seedlings into straw blocks
- Intermediate result
- Harvest
- Pests attacked the potatoes
- The soil of the straw unit at the end of the season
- The end of the season
- modernfarmer.com/2013/07/straw-bale-gardening/
- www.growandmake.com/straw_bale_garden
- www.rootsimple.com/2013/04/our-new-straw-bale-garden-part-1/
- Joel Karsten Straw Bale Gardens: The Breakthrough Method for Growing Vegetables Anywhere, Earlier and with No Weeding, Cool Springs Press; First edition, 2013.
Source: brukva.net
High blood pressure, minimizes the symptoms of dementia
Amazing pictures in the fantasy style Margarita Kireeva






















