395
The proposed method of extraction of water on the moon
The planetary community from the USA and Russia suggested future colonists of the moon to get water on the Earth's satellite by distillation (evaporation and subsequent cooling and condensation of its vapors). The results of their research, the authors published in the journal Icarus, and briefly they can be found on the New Scientist website.
Scientists have proposed to distill water, which, presumably, begins to evaporate from the lunar soil during sunrise. To such conclusions the authors came analyzing the observed data and assuming the existence of periodic phase changes of water on the moon.
According to researchers, despite the extremely sparse atmosphere of the satellite of the Earth and a small acceleration of free fall, with the onset of night on the moon the water begins to cool, and dawn — evaporate.
To save water, the scientists propose to place a special plastic dome, which in daylight might condense water. According to the calculations of planetary scientists, with each cubic meter of the lunar regolith can collect up to 190 milliliters of water.
As scholars have noted, despite the fact that at the poles of the moon water is much more (it's already installed), its production in other parts of the Earth satellite has a chance to become no less effective: the solar day (lasting on the moon around the earth month) you can get enough volume of water.
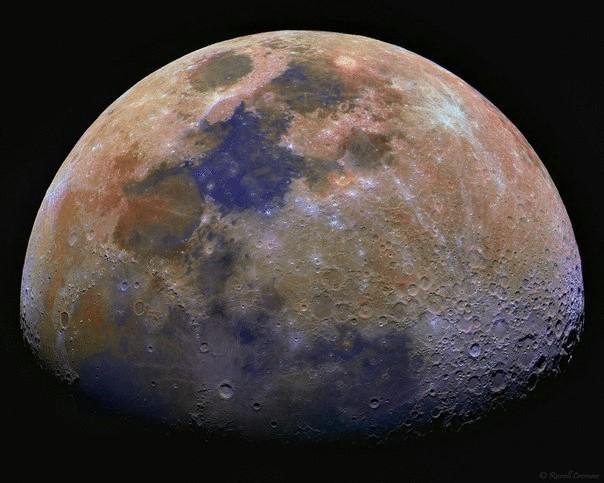

Experts have admitted the existence of water molecules on the moon, after analyzing the data obtained by the instrument Lunar Exploration Neutron Detector (LEND) Lunar Orbiter Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) between 2009 and 2011.
Tool found diurnal variations of neutron flux near the equator of the moon, the reduction of which is consistent with the presence of volatile hydrogen-containing compounds. The peak hydrogen content in the atmosphere of the moon was observed at dawn and low at dusk. Scientists thought that the most likely volatile compound is probably water.
LEND detector developed at the Institute of space research of the Russian Academy of Sciences dedicated to the study of hydrogen content on the moon. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: vk.com/wiki_science?z=photo-49512136_371730639%2Falbum-49512136_00%2Frev
Scientists have proposed to distill water, which, presumably, begins to evaporate from the lunar soil during sunrise. To such conclusions the authors came analyzing the observed data and assuming the existence of periodic phase changes of water on the moon.
According to researchers, despite the extremely sparse atmosphere of the satellite of the Earth and a small acceleration of free fall, with the onset of night on the moon the water begins to cool, and dawn — evaporate.
To save water, the scientists propose to place a special plastic dome, which in daylight might condense water. According to the calculations of planetary scientists, with each cubic meter of the lunar regolith can collect up to 190 milliliters of water.
As scholars have noted, despite the fact that at the poles of the moon water is much more (it's already installed), its production in other parts of the Earth satellite has a chance to become no less effective: the solar day (lasting on the moon around the earth month) you can get enough volume of water.

Experts have admitted the existence of water molecules on the moon, after analyzing the data obtained by the instrument Lunar Exploration Neutron Detector (LEND) Lunar Orbiter Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) between 2009 and 2011.
Tool found diurnal variations of neutron flux near the equator of the moon, the reduction of which is consistent with the presence of volatile hydrogen-containing compounds. The peak hydrogen content in the atmosphere of the moon was observed at dawn and low at dusk. Scientists thought that the most likely volatile compound is probably water.
LEND detector developed at the Institute of space research of the Russian Academy of Sciences dedicated to the study of hydrogen content on the moon. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: vk.com/wiki_science?z=photo-49512136_371730639%2Falbum-49512136_00%2Frev
The creators hoverboard plans to teach a house fly during earthquakes
Australia launches its first floating PV power plant