512
When stuffy: a stuffy room and hypercapnia
Though people often hear that they lack oxygen, in fact the problem in a stuffy room often is with a different gas — carbon dioxide.
Today we talk about the excess carbon dioxide in the body (hypercapnia), which traps us in many a stuffy room (and not only) is the cause of many troubles.

Carbon dioxide CO2 enters the earth's atmosphere. Its average concentration in the air is approximately of 0.035% or 350 ppm — ppm (parts per million). Geochemical studies have shown that about the same level within a few hundredths of a percent — has remained unchanged for hundreds of thousands of years.
But the atmosphere of places of human habitation — cities, especially metropolises, really is generated when our direct participation. In the second half of the last century the concentration of CO2 in the countryside was the same "renesemee" 350 ppm in small towns to 500 ppm, in the large industrial centers of 600-700 ppm. And this, however, did not limit.
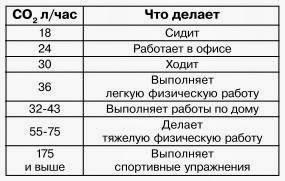
You know that we inhale oxygen (O2) and exhale carbon dioxide (CO2) and breath depends on the activity (table). Carbon dioxide in the premises is formed only as a product of human activity, which exhales 100 times more CO2 than inhales. Consuming about 30 liters of oxygen per hour, each of us allocates 20-25 liters of carbon dioxide. People in the room produces approximately 35.2 grams of CO2 per hour, respectively, if the room is 20 m2 with a height of 2.5 meters, without ventilation every hour, the concentration of carbon dioxide will rise 584ppm every hour.
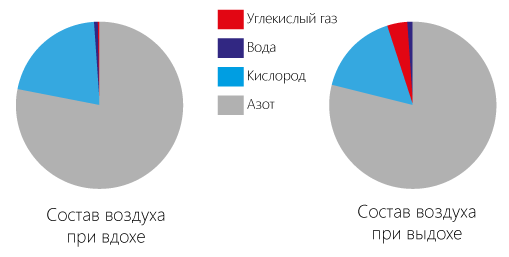
A slight increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in humans causes a feeling of "spartali" air of stuffiness. We clearly feel it when you come into the room. But our respiratory center plastic and after 10 minutes we stop to notice it. A more significant increase of concentration, the symptoms become worse: "heavy" head, dizziness, headaches, and up to irreversible changes in the human body. At the same time most of us know the feeling of stuffiness in the room and the symptoms associated with this including fatigue, drowsiness, irritability. Such a state many associate with lack of oxygen. Actually, these are symptoms caused by the excess level of carbon dioxide in the air. Still enough oxygen and carbon dioxide already in excess.
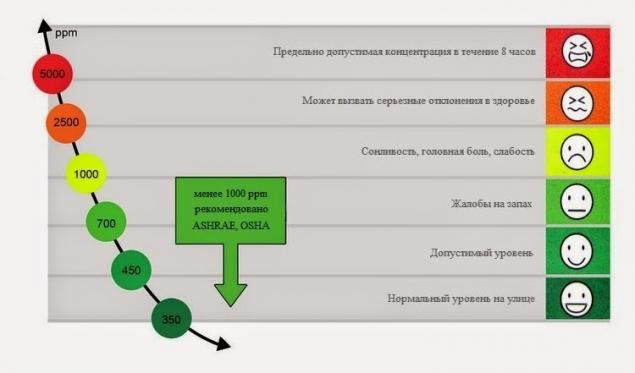
Symptoms in healthy adults , the Concentration of carbon dioxide

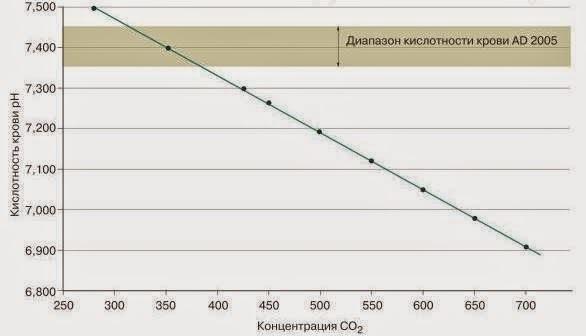
The main mechanisms of action of carbon dioxide (chronic excess): 1. The expansion of the blood vessels of the brain: headache. People stradajosie migraines and predisposed to headaches, celebrate their appearance at the level of 1000 ppm. 2. Negative impact on the respiratory system. In the first place for asthmatics, people with bronchite etc. speeds up attacks. 3. Impact on performance: attention, switching, stress, etc. 4. The change in acid-base status of blood. Long-term effects have not been studied, causes mild acidosis.
5. Worsens sleep (increased snoring), possibly marked deterioration in the quality of sleep.published Author: Andrey Blueskin P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/04/kogda-dushno-dushnoe-pomeshhenie-i-giperkapniya.html
Today we talk about the excess carbon dioxide in the body (hypercapnia), which traps us in many a stuffy room (and not only) is the cause of many troubles.

Carbon dioxide CO2 enters the earth's atmosphere. Its average concentration in the air is approximately of 0.035% or 350 ppm — ppm (parts per million). Geochemical studies have shown that about the same level within a few hundredths of a percent — has remained unchanged for hundreds of thousands of years.
But the atmosphere of places of human habitation — cities, especially metropolises, really is generated when our direct participation. In the second half of the last century the concentration of CO2 in the countryside was the same "renesemee" 350 ppm in small towns to 500 ppm, in the large industrial centers of 600-700 ppm. And this, however, did not limit.

You know that we inhale oxygen (O2) and exhale carbon dioxide (CO2) and breath depends on the activity (table). Carbon dioxide in the premises is formed only as a product of human activity, which exhales 100 times more CO2 than inhales. Consuming about 30 liters of oxygen per hour, each of us allocates 20-25 liters of carbon dioxide. People in the room produces approximately 35.2 grams of CO2 per hour, respectively, if the room is 20 m2 with a height of 2.5 meters, without ventilation every hour, the concentration of carbon dioxide will rise 584ppm every hour.

A slight increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in humans causes a feeling of "spartali" air of stuffiness. We clearly feel it when you come into the room. But our respiratory center plastic and after 10 minutes we stop to notice it. A more significant increase of concentration, the symptoms become worse: "heavy" head, dizziness, headaches, and up to irreversible changes in the human body. At the same time most of us know the feeling of stuffiness in the room and the symptoms associated with this including fatigue, drowsiness, irritability. Such a state many associate with lack of oxygen. Actually, these are symptoms caused by the excess level of carbon dioxide in the air. Still enough oxygen and carbon dioxide already in excess.

Symptoms in healthy adults , the Concentration of carbon dioxide
- Normal levels of outdoor 350 — 450 ppm
- Acceptable levels < 600 ppm
- Complaints of stale air 600 — 1000 ppm
- The maximum level of ASHRAE standards and OSHA 1000 ppm
- A General sluggishness of 1000 — 2500 ppm
- Possible adverse effects on health 2500 — 5000 ppm
- The maximum allowable concentration for 8 hour working day
- 5000 ppm

The main mechanisms of action of carbon dioxide (chronic excess): 1. The expansion of the blood vessels of the brain: headache. People stradajosie migraines and predisposed to headaches, celebrate their appearance at the level of 1000 ppm. 2. Negative impact on the respiratory system. In the first place for asthmatics, people with bronchite etc. speeds up attacks. 3. Impact on performance: attention, switching, stress, etc. 4. The change in acid-base status of blood. Long-term effects have not been studied, causes mild acidosis.

5. Worsens sleep (increased snoring), possibly marked deterioration in the quality of sleep.published Author: Andrey Blueskin P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2015/04/kogda-dushno-dushnoe-pomeshhenie-i-giperkapniya.html























