448
Designed durable and cheap alternative to lithium-ion batteries
Chemists from the University of Waterloo has developed a durable zinc-ion battery, which is half the price of advanced lithium-ion batteries.
Due to the low cost and other attractive characteristics of the new product is able to reduce the dependence of communities on traditional networks for energy storage, and to simplify the transition to renewable solar and wind energy. Professor Linda Nazar colleagues published the relevant material in the edition of Nature Energy.

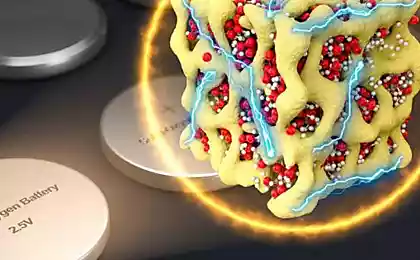
The battery used is safe, non-flammable, non-toxic materials and salt water based with a neutral pH. It consists of: a water-based electrolyte, the anode of vanadium oxide, cheap zinc cathode. The battery generates electricity during the reversible process of intercalation, in which the anions are oxidized zinc from the zinc cathode, move through the electrolyte and are introduced between the nano-sheets of vanadium oxide in the anode. Next, the flow of electrons moving in an external chip. The reverse process occurs during charging. A working prototype of the cell responds with 4 important criteria: high reversibility, high speed, big capacity, no dendritic precipitation of zinc.

More than 1000 cycles zakladki-discharge will be held before the capacity drops to 80%. The expected energy of 450 watts per liter. Lithium-ion batteries, by the way, is also managed by the intercalation of lithium ions, but the electrolyte in them is expensive and flammable."Our batteries are relatively inexpensive and absolutely safe" — said Nazar. "They fully correspond to market needs in renewable energy". published
Source: www.energy-fresh.ru/news/?id=13566
Due to the low cost and other attractive characteristics of the new product is able to reduce the dependence of communities on traditional networks for energy storage, and to simplify the transition to renewable solar and wind energy. Professor Linda Nazar colleagues published the relevant material in the edition of Nature Energy.

The battery used is safe, non-flammable, non-toxic materials and salt water based with a neutral pH. It consists of: a water-based electrolyte, the anode of vanadium oxide, cheap zinc cathode. The battery generates electricity during the reversible process of intercalation, in which the anions are oxidized zinc from the zinc cathode, move through the electrolyte and are introduced between the nano-sheets of vanadium oxide in the anode. Next, the flow of electrons moving in an external chip. The reverse process occurs during charging. A working prototype of the cell responds with 4 important criteria: high reversibility, high speed, big capacity, no dendritic precipitation of zinc.

More than 1000 cycles zakladki-discharge will be held before the capacity drops to 80%. The expected energy of 450 watts per liter. Lithium-ion batteries, by the way, is also managed by the intercalation of lithium ions, but the electrolyte in them is expensive and flammable."Our batteries are relatively inexpensive and absolutely safe" — said Nazar. "They fully correspond to market needs in renewable energy". published
Source: www.energy-fresh.ru/news/?id=13566