706
Recluse spider venom can dissolve the ear cartilage
Spider "melted" tourist uho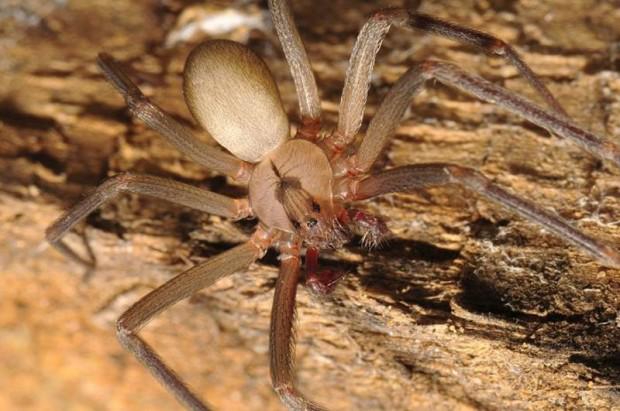
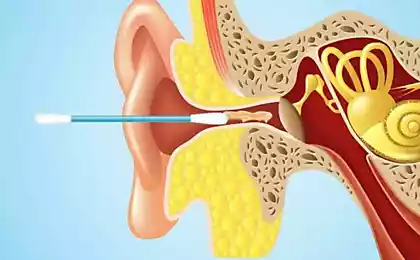
One night during a holiday in Italy, 22-year-old woman woke up because of the pain in the ear. She could not know that she had just bitten the Mediterranean recluse spider, and soon a piece of her ear dissolved under the influence of spider venom.
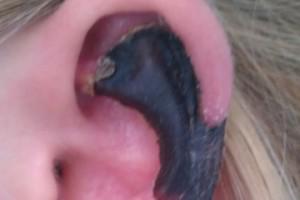
Soon, the woman turned to the Italian hospital, and doctors prescribed her antigistomin, but the pain in the ear and swelling on his face did not pass. When she returned home to the Netherlands, it has become worse, part of the ear was black - a clear sign of the fact that part of the skin and cartilage cells died.
Necrosis allowed doctors to understand that the patient was bitten by a Mediterranean recluse spider, whose venom has destroyed part of the skin and subcutaneous fat, resulting in on-site mutilated ear scar.
Plastic surgeon Marieke van Wyk in his report published in the journal "Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery", noted that the event occurred was the first proof that the recluse spider venom can dissolve the ear cartilage. Poison spiders consists of a complex mixture of chemicals, including those that break down proteins, making the bites intractable. To help the patient, van Wyk and her colleagues removed the dead tissue, and then recreate them using cartilage taken from the rib of a woman.
For the treatment of this patient had used a drug called dapsone, but there is no guarantee that it will work for the neutralization is this particular poison. So, according to van Wyk, the recommended treatment of spider bites - ice packs and painkillers.
Recluse spider rarely bite people, and usually their bites do not cause serious damage. In most cases, they bite only if the person in the dream presses them or pokes his foot in the boot, which turned out to be a spider.
The bites are difficult to diagnose in most cases they take bites biting insects and the effects of bacterial infections. However, the recluse spider venom can cause severe immune reactions that destroy red blood cells. A recent study showed that the drug is for the treatment of rare diseases are not blood-related, Ekulizumab, can reduce the destruction of blood cells in patients by 80%.
via factroom.ru

One night during a holiday in Italy, 22-year-old woman woke up because of the pain in the ear. She could not know that she had just bitten the Mediterranean recluse spider, and soon a piece of her ear dissolved under the influence of spider venom.

Soon, the woman turned to the Italian hospital, and doctors prescribed her antigistomin, but the pain in the ear and swelling on his face did not pass. When she returned home to the Netherlands, it has become worse, part of the ear was black - a clear sign of the fact that part of the skin and cartilage cells died.
Necrosis allowed doctors to understand that the patient was bitten by a Mediterranean recluse spider, whose venom has destroyed part of the skin and subcutaneous fat, resulting in on-site mutilated ear scar.
Plastic surgeon Marieke van Wyk in his report published in the journal "Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery", noted that the event occurred was the first proof that the recluse spider venom can dissolve the ear cartilage. Poison spiders consists of a complex mixture of chemicals, including those that break down proteins, making the bites intractable. To help the patient, van Wyk and her colleagues removed the dead tissue, and then recreate them using cartilage taken from the rib of a woman.
For the treatment of this patient had used a drug called dapsone, but there is no guarantee that it will work for the neutralization is this particular poison. So, according to van Wyk, the recommended treatment of spider bites - ice packs and painkillers.
Recluse spider rarely bite people, and usually their bites do not cause serious damage. In most cases, they bite only if the person in the dream presses them or pokes his foot in the boot, which turned out to be a spider.
The bites are difficult to diagnose in most cases they take bites biting insects and the effects of bacterial infections. However, the recluse spider venom can cause severe immune reactions that destroy red blood cells. A recent study showed that the drug is for the treatment of rare diseases are not blood-related, Ekulizumab, can reduce the destruction of blood cells in patients by 80%.
via factroom.ru