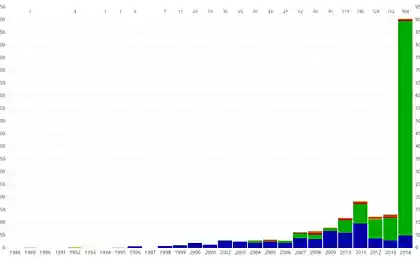
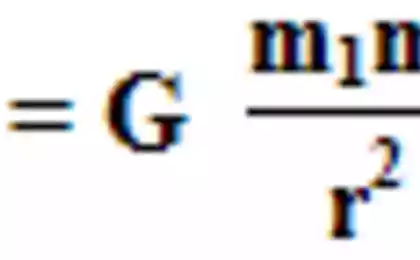1041
Red dwarfs - the best candidate for extraterrestrial life ... or the worst?
In search of habitable worlds outside our solar system, perhaps the most promising seem the smallest and cold stars. Called red dwarfs class M, these stars are several times lighter and fainter than the Sun, but their number is more than 10 times the number of stars similar to the sun.
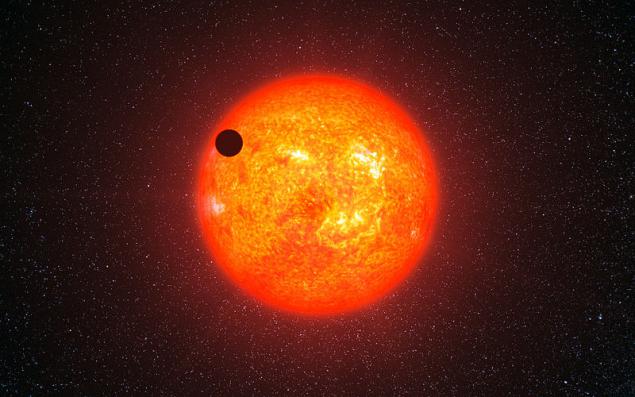
Exoplanet GJ 1214b in the red dwarf eyes of the artist. (Credit: ESO / L. Calçada)
To be warm enough for the emergence of planets orbiting red dwarfs, should be very close to the star orbits, like tourists, sitting down close to the fire. This fact makes it relatively easy to find them hunters planets and a large number of red dwarfs is that many of these planets and are available for study in our immediate neighborhood.
Astronomers are now full swing preparing for such studies. Several independent projects have been watching the closest red dwarfs, and a lot of new telescopes and satellites are designed to detect planets orbiting them. An example is NASA's TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite), the launch of which is scheduled for 2017.
These efforts make the detection of potentially habitable planets in the system of red dwarfs near inevitability. However, far less clear whether in fact proved the habitability of these worlds, the same properties that make planets red dwarfs are easily detected, may prevent the possibility of the presence of life on them.
3 reasons why the planets red dwarfs is easily detectable, but hardly inhabited
Oscillations and tides
Astronomers look for some of the planet, watching the stars fluctuations - periodic motions back and forth, caused by the gravitational influence of the unseen worlds. Planet Earth in the habitable zone the size of the red dwarf star's velocity causes fluctuations in the value of 1 m / s, it is possible to detect from Earth. These fluctuations will occur every few weeks or months.
But in this case, the tidal forces can draw energy from its own rotation of the planet, so it will make one revolution around its axis during one revolution around the star. That is, the star is rotated always the same hemisphere of the planet, similar to the way we always see only one side of the moon. In the worst case, all of the water and the air on a planet and gather freeze on unlit side, leaving its surface uninhabitable.
Shadows and flash
Another way to detect planets is to observe the shadows at their transit across the disk of the star home. Because of the small size of the orbit of the planet transit red dwarf star block more light than if they were treated in larger stars, that makes it easier to detect them by this method.
The downside, however, is that red dwarfs are much less bright than the sun-like stars, and much more variable. They are able to rapidly fade, and vice versa in case of flare on the surface of coronal holes and stellar flares, enveloping the planet stream of X-ray and ultraviolet radiation. Such unpredictability can wreak havoc with the climate and biosphere. Thus, the atmosphere is located side by side with such a violent dwarf planet, which in other circumstances could be habitable, will be destroyed by powerful flashes.
Long life and difficult adolescence
One of the reasons why so many red dwarfs, is that they are simply living longer than other stars - their number grows over time, because of the small size they burn their nuclear fuel slowly and efficiently. But that longevity comes only after a difficult youth.
Several counter-intuitive, but because of the small size and weaker gravitational red dwarf takes more time than other stars to fully form. They can remain hundreds of millions of years in a state of protostars slowly being formed from collapsing clouds of gas.
Planets, however, may be formed around a protostar in just tens of millions of years. Everything else, these worlds will be fried in the heat and light of protostars, and perhaps most of the life-giving water on the surface evaporates more just before formed a red dwarf.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/250416/
Also
bashny.net/yellowdragon/2014/12/15/mnogokvartirnyy-dom-bunker-dlya-vyzhivaniya.html

Exoplanet GJ 1214b in the red dwarf eyes of the artist. (Credit: ESO / L. Calçada)
To be warm enough for the emergence of planets orbiting red dwarfs, should be very close to the star orbits, like tourists, sitting down close to the fire. This fact makes it relatively easy to find them hunters planets and a large number of red dwarfs is that many of these planets and are available for study in our immediate neighborhood.
Astronomers are now full swing preparing for such studies. Several independent projects have been watching the closest red dwarfs, and a lot of new telescopes and satellites are designed to detect planets orbiting them. An example is NASA's TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite), the launch of which is scheduled for 2017.
These efforts make the detection of potentially habitable planets in the system of red dwarfs near inevitability. However, far less clear whether in fact proved the habitability of these worlds, the same properties that make planets red dwarfs are easily detected, may prevent the possibility of the presence of life on them.
3 reasons why the planets red dwarfs is easily detectable, but hardly inhabited
Oscillations and tides
Astronomers look for some of the planet, watching the stars fluctuations - periodic motions back and forth, caused by the gravitational influence of the unseen worlds. Planet Earth in the habitable zone the size of the red dwarf star's velocity causes fluctuations in the value of 1 m / s, it is possible to detect from Earth. These fluctuations will occur every few weeks or months.
But in this case, the tidal forces can draw energy from its own rotation of the planet, so it will make one revolution around its axis during one revolution around the star. That is, the star is rotated always the same hemisphere of the planet, similar to the way we always see only one side of the moon. In the worst case, all of the water and the air on a planet and gather freeze on unlit side, leaving its surface uninhabitable.
Shadows and flash
Another way to detect planets is to observe the shadows at their transit across the disk of the star home. Because of the small size of the orbit of the planet transit red dwarf star block more light than if they were treated in larger stars, that makes it easier to detect them by this method.
The downside, however, is that red dwarfs are much less bright than the sun-like stars, and much more variable. They are able to rapidly fade, and vice versa in case of flare on the surface of coronal holes and stellar flares, enveloping the planet stream of X-ray and ultraviolet radiation. Such unpredictability can wreak havoc with the climate and biosphere. Thus, the atmosphere is located side by side with such a violent dwarf planet, which in other circumstances could be habitable, will be destroyed by powerful flashes.
Long life and difficult adolescence
One of the reasons why so many red dwarfs, is that they are simply living longer than other stars - their number grows over time, because of the small size they burn their nuclear fuel slowly and efficiently. But that longevity comes only after a difficult youth.
Several counter-intuitive, but because of the small size and weaker gravitational red dwarf takes more time than other stars to fully form. They can remain hundreds of millions of years in a state of protostars slowly being formed from collapsing clouds of gas.
Planets, however, may be formed around a protostar in just tens of millions of years. Everything else, these worlds will be fried in the heat and light of protostars, and perhaps most of the life-giving water on the surface evaporates more just before formed a red dwarf.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/250416/
Also
bashny.net/yellowdragon/2014/12/15/mnogokvartirnyy-dom-bunker-dlya-vyzhivaniya.html
As brain waves can be judged on the effectiveness of teams and choose their leader
Robot surgeon sews grape