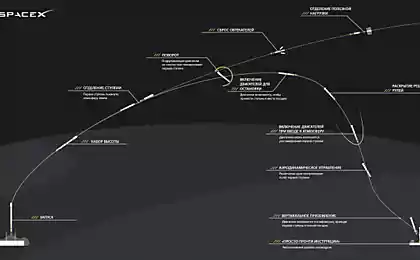
The first stage of Falcon-9 Drive to an offshore platform
Rocket made it to drone spaceport ship, but landed hard. Close, but no cigar this time. Bodes well for the future tho.- Elon Musk (elonmusk) January 10, 2015 blockquote>
Ship itself is fine. Some of the support equipment on the deck will need to be replaced ...- Elon Musk (elonmusk) January 10, 2015 blockquote>
Video landing rocket is not yet available. How writes Musk, it is very dark and murky. Accurate picture of the landing will have to recover from pieces of video capture, data analysis and telemetry missile damage when in contact with the platform.
Test technology reusable launch took place in the framework of the fifth mission SpaceX cargo delivery to the ISS under a contract with NASA (CRS-5). During the early starts were tested individual elements with a soft landing - Folding props restart the engines after separation of the second stage and before touching the surface lattice aerodynamic control surfaces and soft controlled landing in the ocean.
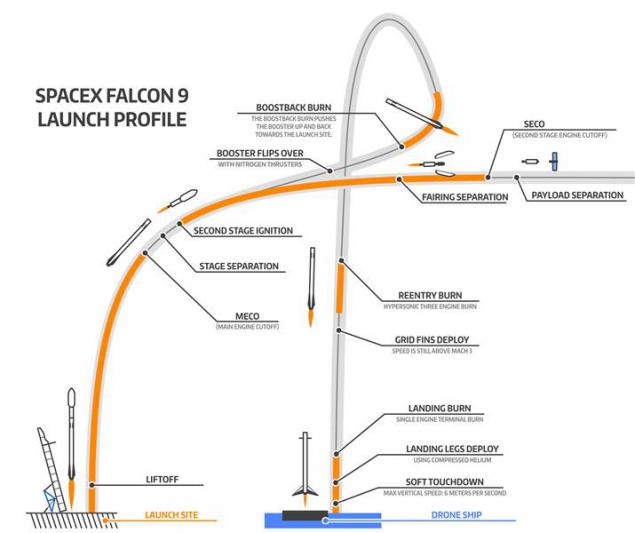
The scheme starting today, made by John Ross from NBC news i>
Today launch was originally scheduled for December 19. However, due to technical problems it was postponed for January 6. The second attempt to start also did not take place - in 1 minute 21 seconds before starting the experience trouble in the thrust vector control system of the engine of the second stage. To fly to the ISS & quot; стартовое window & quot; (The time during which the relative positioning of the spaceport and the purpose of flight allows to launch a rocket) is a narrow "schelochku" in one second width. The slightest delay leads to the transfer start for a few days. Start mission CRS-5 from Cape Canaveral was reassigned to 4:47 am on January 10, local time (12:47 Moscow time).
Video launch today i>
According to Elon Musk, reusable launch vehicles will reduce the cost of removal of cargo into orbit several times. When the technology will be a soft landing fully developed, the rocket will be able to sit on the same spaceport from which they took off, pass inspection, refuel and take off again in a few days.
Reusable launch first test conducted on a reduced model rocket Falcon, which was called Grasshopper («Grasshopper») . SpaceX successfully conducted several launches of the rocket, during which it rose to a height of several hundred meters and return to the starting point. Then worked on the "grasshopper" technology is gradually transferred to the Falcon. Test reusable launch mask holding company along with cargo flights to the ISS under a contract with NASA. Before the separation of the second stage Falcon behaves like a normal rocket, but instead of simply falling into the water of the first stage is carried out another experiment.
Flight "Grasshopper» i>
The first test elements soft landing during the actual mission concluded cargo into orbit was held September 29, 2013. The rocket put into orbit several satellites, and then tried to make a controlled descent and braking without landing gear. The test was unsuccessful due to the rotation of the first stage - the effect of a rotating centrifuge housing has led to disruptions in the supply of fuel, and the rocket crashed.
April 18, 2014 tests on a more successful . To play it safe, decided to put a rocket into the ocean - above ground inaccuracy in the positioning of the missile could lead to death and destruction. The rocket was set drop-down support for the landing. Changing the path and braking went according to plan. Supports opened, and according to the telemetry, the first step into the water and vertically with a low enough rate. Unfortunately, because of the storm it failed to quickly find and climb aboard a search of the ship. Wave smashed a rocket and she drowned. Jointly by NASA experts and enthusiasts managed to restore badly damaged video cameras rockets during landing:
In June tested aerodynamic rudders lattice , which help to control the missile in the atmosphere. Lattice compact than conventional wheels, easy to fold and unfold, require less power drives, as well as work better at high angles of attack. For the first time they began to be used in the 50s in the Soviet Union, and they are installed on many Soviet and Russian guided bombs, tactical and strategic missiles. In the US, these wheels were first used in the high-explosive bomb GBU-43 in the 2000s.
Lattice wheels work well at supersonic and subsonic speeds, but inferior to conventional transonic. It is perfect for a reusable rocket - it actively maneuvering close to the ground, directly at landing, and when entering the atmosphere at speeds of the order of several M. As заметил Musk, answering questions from users Reddit, «the atmosphere at a speed of 4 M resembles a thick syrup", so the use of aerodynamic control surfaces is much more efficient maneuvering rocket engine.
July 14 held another successful splashdown first stage. Although the sea water damaged the rocket launch this allowed us to collect important data on its systems.
That's because from the look splashdown (removed from the aircraft):
Source: geektimes.ru/post/243899/