1424
Spanish scientists have developed jointly with Corning glass with anti-reflective and hydrophobic properties
Scientists from the Institute of Photonics in Spain, with the participation of Corning - manufacturer of heavy-duty glass smartphone screen Gorilla Glass - разработали JavaScript , which is able to significantly reduce glare and reflections, as well as give glass superhydrophobic properties. The principle of the creation of such a coating has been borrowed from nature - scientists have long noticed that the eyes are usually moth has a pronounced anti-glare properties. It was found that the outer surface of the eye is covered with a network of tiny insect bumps size of the order of 200-300 nanometers. Since the wavelength of visible light greater than the size of the irregularities, the light passes through the surface of the eye so as its refractive index varies continuously - it considerably reduces reflections, as media boundary appears as if blurred.
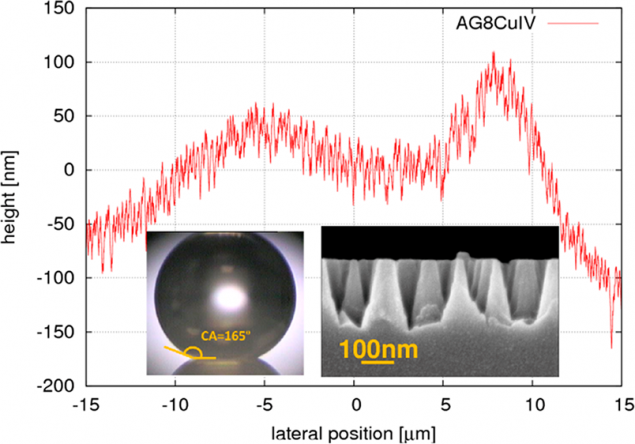
On the chart - profile irregularities on the surface of the glass produced by an atomic force microscope. The photo - a drop of water on the surface of the glass, and the three-dimensional image Nanotexture surface. I>
While this principle is already used in some types of anti-reflective coatings (in their names usually occurs the phrase «moth eye»), Spanish explorers brought significant improvements in the technology. The texture on the glass surface is created on two levels - first, creating an uneven relatively large linear sizes - from 1 to 100 micrometers in width and 10-500 nm in height, and then on the surface of these pretty gentle "hills" created a "forest" of protuberances 10 300 nanometers in width and height.
"The Hills" are created by sputtering on glass droplets of the polymer followed by etching, in which there are deepening between the droplets. To create a "forest" is used more artful process. First applied to the glass thinnest copper plating thickness of 4-8 nm. Under the influence of high (about 750 degrees) temperature of copper going into tiny clumps of tens of nanometers in diameter, uniformly distributed on the glass, which is then etched. Thereafter, residues were removed copper. This technology is highly scalable and inexpensive to manufacture.
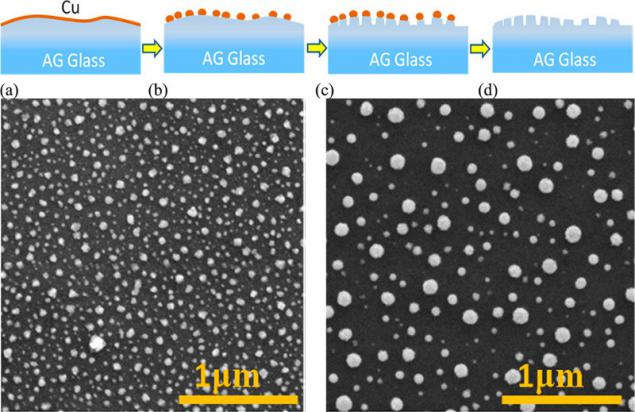
The scheme of the process of creating nanorelief using copper deposition and pictures of lumps of copper on the surface of the glass after heating to 750 degrees (left - with a layer thickness of 4 nm of copper in the right - 8 nm). I>
All nanostructures are made directly from the glass, without imposing any polymer film, and therefore, this glass can be subjected to chemical treatment dramatically increases its strength. Plays an important role and the geometric structure - the top of "hill" reliably protect against mechanical impacts "forest" located in the "lowlands". Duplex relief glass and increases its ability to repel water. As in the natural superhydrophobic surfaces exemplified by leaves of certain plants, creates microscopic texture between water droplets and the surface of the thin layer of air, which prevents water to wet the surface.
Besides the obvious use in the screens of smartphones and tablets such glass can be useful for the production of solar panels. Its hydrophobic properties allow photocells always stay clean - raindrops flowing down on them, will collect all the dust and dirt while sliding down the surface without leaving any traces and divorces.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/230397/

On the chart - profile irregularities on the surface of the glass produced by an atomic force microscope. The photo - a drop of water on the surface of the glass, and the three-dimensional image Nanotexture surface. I>
While this principle is already used in some types of anti-reflective coatings (in their names usually occurs the phrase «moth eye»), Spanish explorers brought significant improvements in the technology. The texture on the glass surface is created on two levels - first, creating an uneven relatively large linear sizes - from 1 to 100 micrometers in width and 10-500 nm in height, and then on the surface of these pretty gentle "hills" created a "forest" of protuberances 10 300 nanometers in width and height.
"The Hills" are created by sputtering on glass droplets of the polymer followed by etching, in which there are deepening between the droplets. To create a "forest" is used more artful process. First applied to the glass thinnest copper plating thickness of 4-8 nm. Under the influence of high (about 750 degrees) temperature of copper going into tiny clumps of tens of nanometers in diameter, uniformly distributed on the glass, which is then etched. Thereafter, residues were removed copper. This technology is highly scalable and inexpensive to manufacture.

The scheme of the process of creating nanorelief using copper deposition and pictures of lumps of copper on the surface of the glass after heating to 750 degrees (left - with a layer thickness of 4 nm of copper in the right - 8 nm). I>
All nanostructures are made directly from the glass, without imposing any polymer film, and therefore, this glass can be subjected to chemical treatment dramatically increases its strength. Plays an important role and the geometric structure - the top of "hill" reliably protect against mechanical impacts "forest" located in the "lowlands". Duplex relief glass and increases its ability to repel water. As in the natural superhydrophobic surfaces exemplified by leaves of certain plants, creates microscopic texture between water droplets and the surface of the thin layer of air, which prevents water to wet the surface.
Besides the obvious use in the screens of smartphones and tablets such glass can be useful for the production of solar panels. Its hydrophobic properties allow photocells always stay clean - raindrops flowing down on them, will collect all the dust and dirt while sliding down the surface without leaving any traces and divorces.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/230397/
"Holographic" displays for smartphones can appear in a couple of years
Shakira and Gerard Pique again become parents?