758
WHY MATHEMATICS photos?
Marina Egupova. here
The word "photography" - literally translated from Greek means "writing with light". Fotomasterskie first appeared in Russia in the late nineteenth - early twentieth century, the so-called - Light painting. The basis for the invention of photography laid in the IV century BC Ancient Greek scientist Aristotle. He saw and described an interesting phenomenon: the light coming in the dark room through a small hole in a window shutter, drawing on the wall of the landscape outside the window. Image obtained inverted and very pale, but nature plays without distortion. After 20 centuries, a serious step towards the invention photographing did Italian mathematician, engineer, physician and philosopher Gerolamo Cardano, who owns the invention the propeller shaft. Cardano put the camera obscura lens and with its help, got the first, albeit much vague images of objects. A fix light drawing was only in the nineteenth century, and made it FRENCH inventor Joseph Nicephore Niepce.
Making shooting, the photographer each time solves difficult task - to achieve realistic images of three-dimensional space on a flat surface. This makes it not only a perfect photographic technique, but also knowledge of the composition techniques, choosing the right lighting and more. There are at least two simple reception of the composition, which can be easily used by any amateur photographer. They are based on well-known from the school course math facts.
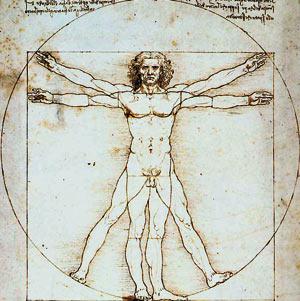
Vitruvian Man. Drawing by Leonardo da Vinci, who first coined the term "golden section" and called it "divine proportion".
LODGING FACILITIES IN RULE GOLDEN SECTION
Even a novice photographer knows that if the subject is placed in the center of the frame, the picture will turn featureless. The question arises: where to put the main object to select it among the minor objects to combine harmoniously with them and take into account a lot of other parts?
Select a point object location shooting helps knowledge of the golden section. Recall that the golden section is called a division of the whole into parts, when the ratio of the greater part to the whole equal to the ratio of the smaller to the larger. For example, if the segment AC is divided in golden section point B, it is possible to record proportions: AB: AC = BC: AB. The value of this ratio is approximately equal to 5/8, called the number of Phidias.

The golden section - recognized measure of beauty and harmony - it was known in ancient Egypt, its properties are studied Euclid and Leonardo da Vinci. In the Renaissance, the golden ratio successfully used in architecture and painting for the construction of a harmonious composition. It has been observed that certain points of the image always attracts the viewer's attention, regardless of the size of the picture. Such points - visual centers - only four. To find them, you have to hand rectangular pictorial canvas twice divided on the principle of the golden section and through the points of division to hold direct. At the intersection of these lines, and additional centers will be located.
Rule golden section extended to the art of photography. It has become one of the base of the composition. The main subject is, or should be located along straight lines dividing the frame into a golden section, or in the visual centers. Of course, the specific location depends on the type of the object, its size and design of the photographer and the like, but in order to achieve the greatest expression of the golden section rule must necessarily be taken into account, either during filming or while preparing photos for printing.
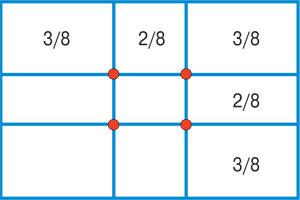
In practice it is not so easy on the eyes to build the golden section. Therefore, when shooting, you can use several simplified compositional technique - the so-called rule of thirds when the side of the frame is not divided on the golden section, but simply into three equal parts. By the way, a number of camera models this grid can be seen looking at the camera.
We show how the rule of the golden section, the example of the three pictures a sailboat at sea (a, b, c). The picture shows a horizon line coincides with the line dividing the frame in half, and placed in the sailing center of the composition. The rule of the golden section is not used. In the second case (Fig. B) The horizon line is a straight line on the bottom of the golden section, and sailing is one of the points of intersection of these lines. New composition attracts the viewer's attention to the form of the sky and sunset. Move above the horizon (Fig. C). Snapshot again gives a new impression - the focus moved to the sunset reflected in the water. Which version of the three best judge, of course, the audience.

Another application of the rule of the golden section is illustrated in Fig. and b. In both figures, built the so-called diagonal grid view of all four visual centers. The essence of the construction is to split a frame into multiple sections. These sections are the main objects of the image.
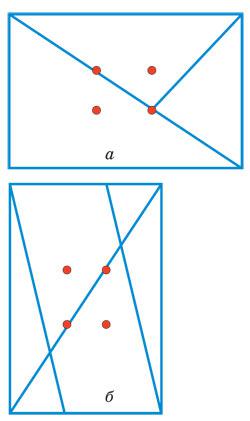
Photo 5 and 6 shows how to use one of them: the main subject should be placed in the visual centers.

The illusion of depth images using linear perspective
From the point of view of mathematics ordinary photograph - the image on the plane obtained by designing it from a single point. However, we want to show the reality with maximum reliability and, therefore, are looking for new ways to demonstrate the three-dimensional space and objects around us. One such tool - linear perspective.
Photo 6

The word "perspective" in Latin means "see clearly". In the fine art of linear perspective - this image of objects on the plane in accordance with the apparent changes in their value. The basis of the modern theory of perspectives laid the great artists of the Renaissance - Leonardo da Vinci, Albrecht Durer and others. On one of the engravings by Durer depicts a way of drawing from nature through the glass printed on a square grid. This process can be described as follows: if you stand at the window and, without changing the view, on the glass circle all that can be seen behind him, the resulting image will be a perspective view of space.

Source:
The word "photography" - literally translated from Greek means "writing with light". Fotomasterskie first appeared in Russia in the late nineteenth - early twentieth century, the so-called - Light painting. The basis for the invention of photography laid in the IV century BC Ancient Greek scientist Aristotle. He saw and described an interesting phenomenon: the light coming in the dark room through a small hole in a window shutter, drawing on the wall of the landscape outside the window. Image obtained inverted and very pale, but nature plays without distortion. After 20 centuries, a serious step towards the invention photographing did Italian mathematician, engineer, physician and philosopher Gerolamo Cardano, who owns the invention the propeller shaft. Cardano put the camera obscura lens and with its help, got the first, albeit much vague images of objects. A fix light drawing was only in the nineteenth century, and made it FRENCH inventor Joseph Nicephore Niepce.
Making shooting, the photographer each time solves difficult task - to achieve realistic images of three-dimensional space on a flat surface. This makes it not only a perfect photographic technique, but also knowledge of the composition techniques, choosing the right lighting and more. There are at least two simple reception of the composition, which can be easily used by any amateur photographer. They are based on well-known from the school course math facts.
Vitruvian Man. Drawing by Leonardo da Vinci, who first coined the term "golden section" and called it "divine proportion".

LODGING FACILITIES IN RULE GOLDEN SECTION
Even a novice photographer knows that if the subject is placed in the center of the frame, the picture will turn featureless. The question arises: where to put the main object to select it among the minor objects to combine harmoniously with them and take into account a lot of other parts?
Select a point object location shooting helps knowledge of the golden section. Recall that the golden section is called a division of the whole into parts, when the ratio of the greater part to the whole equal to the ratio of the smaller to the larger. For example, if the segment AC is divided in golden section point B, it is possible to record proportions: AB: AC = BC: AB. The value of this ratio is approximately equal to 5/8, called the number of Phidias.

The golden section - recognized measure of beauty and harmony - it was known in ancient Egypt, its properties are studied Euclid and Leonardo da Vinci. In the Renaissance, the golden ratio successfully used in architecture and painting for the construction of a harmonious composition. It has been observed that certain points of the image always attracts the viewer's attention, regardless of the size of the picture. Such points - visual centers - only four. To find them, you have to hand rectangular pictorial canvas twice divided on the principle of the golden section and through the points of division to hold direct. At the intersection of these lines, and additional centers will be located.
Rule golden section extended to the art of photography. It has become one of the base of the composition. The main subject is, or should be located along straight lines dividing the frame into a golden section, or in the visual centers. Of course, the specific location depends on the type of the object, its size and design of the photographer and the like, but in order to achieve the greatest expression of the golden section rule must necessarily be taken into account, either during filming or while preparing photos for printing.
In practice it is not so easy on the eyes to build the golden section. Therefore, when shooting, you can use several simplified compositional technique - the so-called rule of thirds when the side of the frame is not divided on the golden section, but simply into three equal parts. By the way, a number of camera models this grid can be seen looking at the camera.

We show how the rule of the golden section, the example of the three pictures a sailboat at sea (a, b, c). The picture shows a horizon line coincides with the line dividing the frame in half, and placed in the sailing center of the composition. The rule of the golden section is not used. In the second case (Fig. B) The horizon line is a straight line on the bottom of the golden section, and sailing is one of the points of intersection of these lines. New composition attracts the viewer's attention to the form of the sky and sunset. Move above the horizon (Fig. C). Snapshot again gives a new impression - the focus moved to the sunset reflected in the water. Which version of the three best judge, of course, the audience.

Another application of the rule of the golden section is illustrated in Fig. and b. In both figures, built the so-called diagonal grid view of all four visual centers. The essence of the construction is to split a frame into multiple sections. These sections are the main objects of the image.

Photo 5 and 6 shows how to use one of them: the main subject should be placed in the visual centers.

The illusion of depth images using linear perspective
From the point of view of mathematics ordinary photograph - the image on the plane obtained by designing it from a single point. However, we want to show the reality with maximum reliability and, therefore, are looking for new ways to demonstrate the three-dimensional space and objects around us. One such tool - linear perspective.
Photo 6

The word "perspective" in Latin means "see clearly". In the fine art of linear perspective - this image of objects on the plane in accordance with the apparent changes in their value. The basis of the modern theory of perspectives laid the great artists of the Renaissance - Leonardo da Vinci, Albrecht Durer and others. On one of the engravings by Durer depicts a way of drawing from nature through the glass printed on a square grid. This process can be described as follows: if you stand at the window and, without changing the view, on the glass circle all that can be seen behind him, the resulting image will be a perspective view of space.

Source: