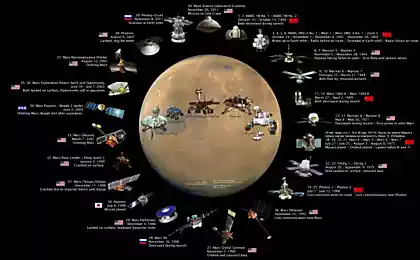
686
Mars - the red planet, not only
43 pictures
Layered sediments in the canyon Hebe.
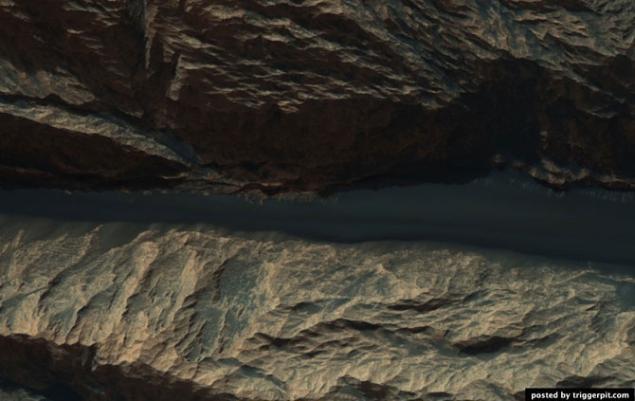

2.Vyboiny on the wall of the crater Gus.

3.Dyuny Russell crater.

4. Geysers Manhattan.
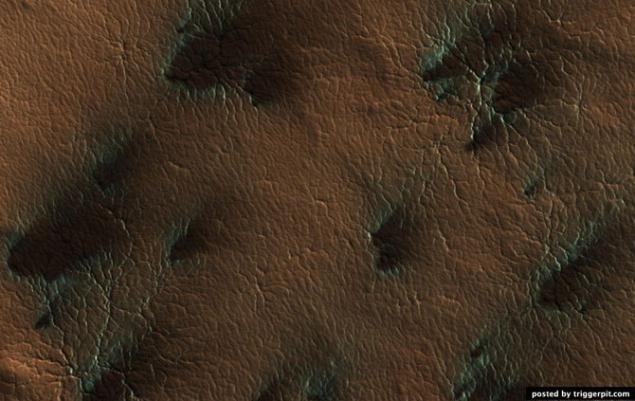

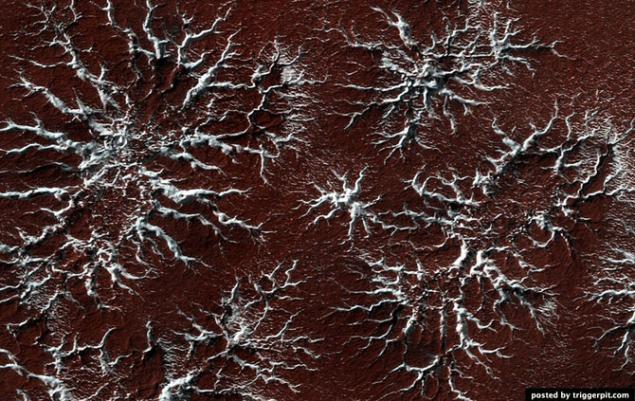
5.Poverhnost Mars covered with dry ice. You had ever play with dry ice (of course in leather gloves!)? Then you have probably noticed that the dry ice from a solid directly into a gas passes, unlike ordinary ice, which is heated, turns into water.
On Mars ice caps are composed of dry ice (carbon dioxide). When in the spring on the ice fall sunshine, it goes into a gaseous state, which causes erosion surface. Erosion creates whimsical spider form.
In this picture shows the channels that have arisen as a result of erosion and light-filled with ice, which comes in contrast to the muted red of the surrounding surface. In summer, the ice dissolves in the atmosphere, and instead will only channels like ghostly spiders carved on the surface. This kind of erosion is typical only for Mars is not possible under natural conditions in the world, because our climate is too warm.
6.Sloistye mineral deposits located on the southern tip of the crater in the middle latitudes. The bright layered deposits are visible in the center of the image; they appear along the edges of the mesas, situated on a hill. Such deposits can be found in many places on Mars, including the craters and canyons near the equator. They could be formed as a result of sedimentation under the influence of wind and / or water.
Around the mesa visible dunes or folded education. The folded structure is the result of differential erosion, when some materials can be eroded more easily than others. Perhaps this area was once covered in soft sediments, which have now disappeared due to erosion.
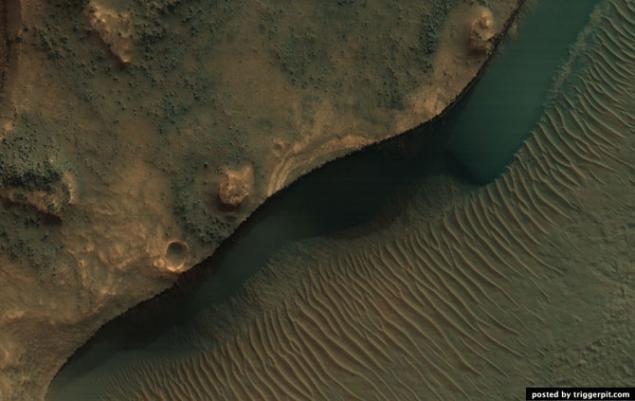

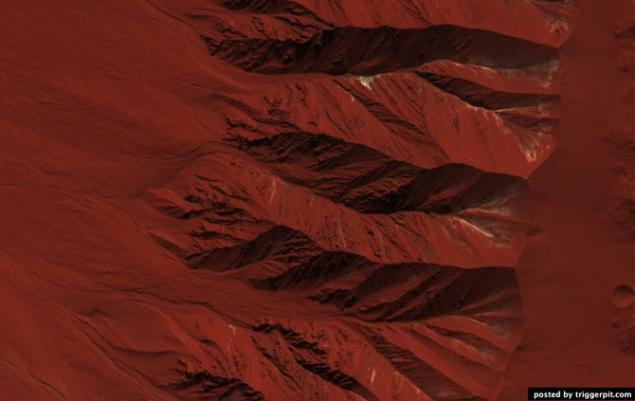
7.Podstilayuschie rocks protruding on the walls and central peaks of the crater.
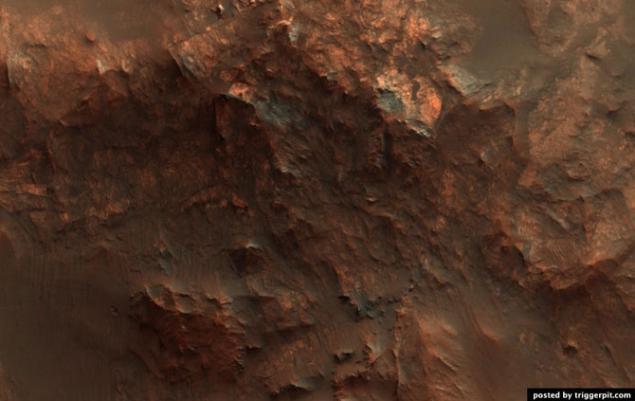

8. The solid structure of the salt mountain in a canyon Ganges.
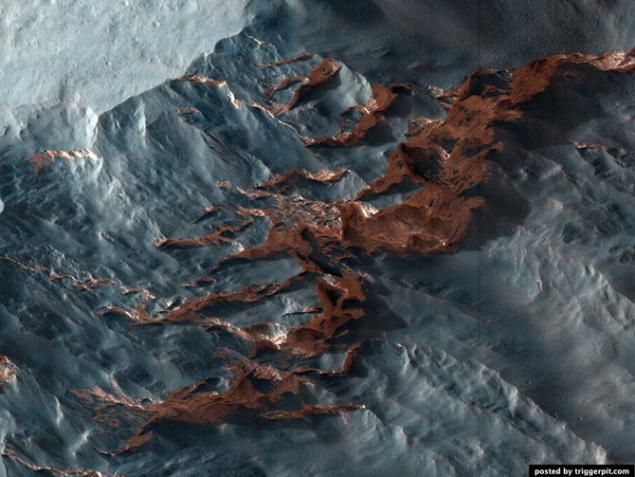

9. Someone cut a piece of the planet!
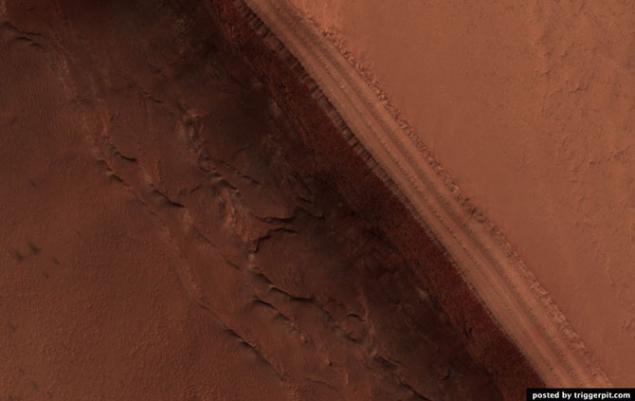

10. Sand mound formed by the spring dust storms in the North Pole.
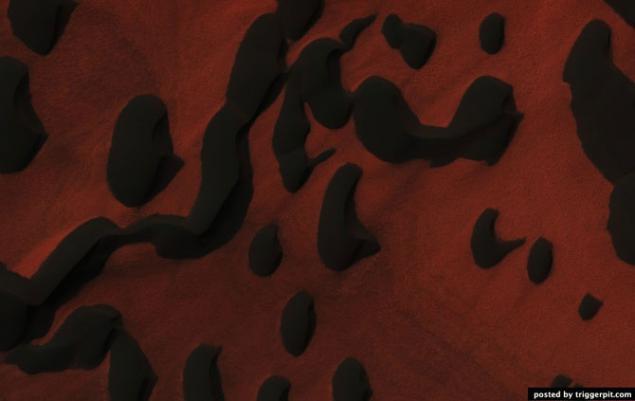

11. The crater with a central hill with a diameter of 12 kilometers.

12. The system of faults Cerberus Fossae on the surface of Mars.
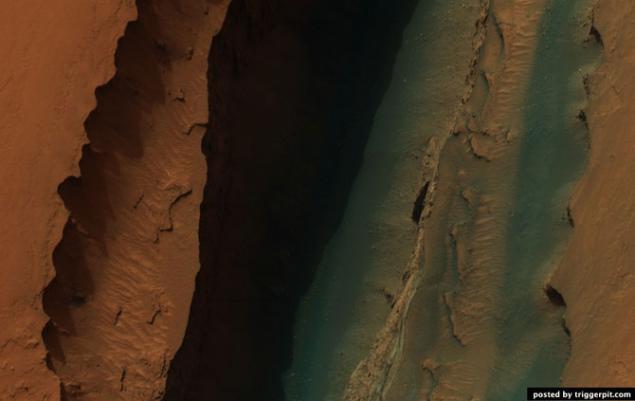

13. Purple Proctor Crater Dunes.
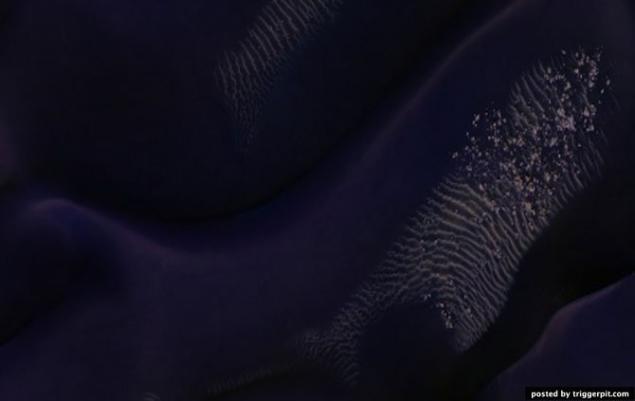

14. The light rock outcrops on the walls of the mesa located in the Land of the Sirens.
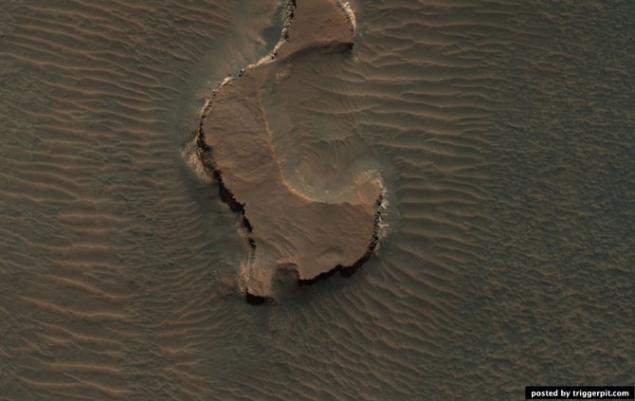

15.Vesennie changes in the Ithaca area.
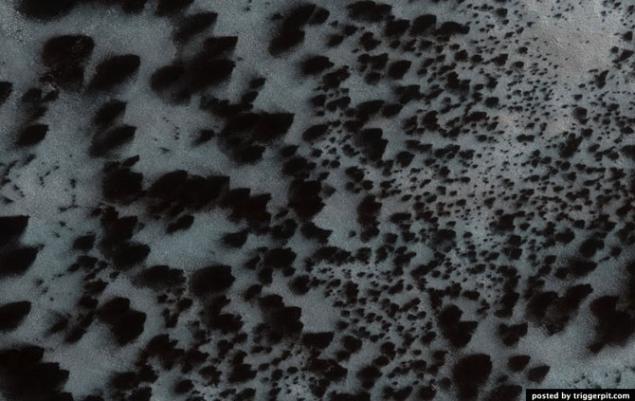

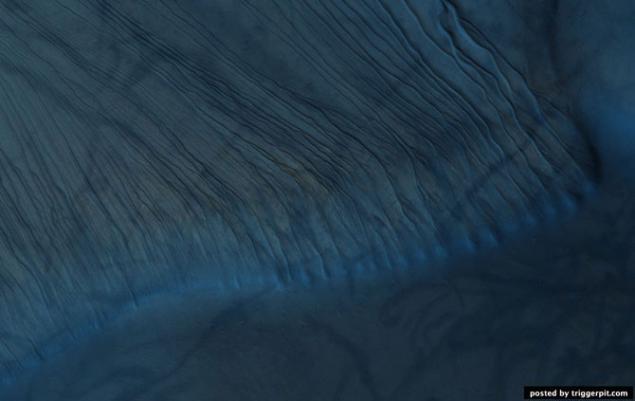
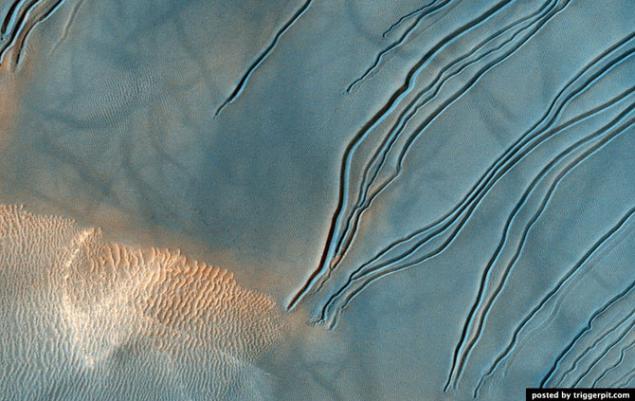
16.Dyuny Russell crater. Photos taken in the crater Russell studied repeatedly in order to monitor changes in the landscape. In this picture shows some dark education, which probably arose under the influence of multiple dust storms, which claimed the bright dust from the surface of the dunes. Narrow channels continue to be formed on the surfaces of steep sand dunes. Groove at the end of the channels can be a place where accumulated blocks of dry ice before moving on to a gaseous state.
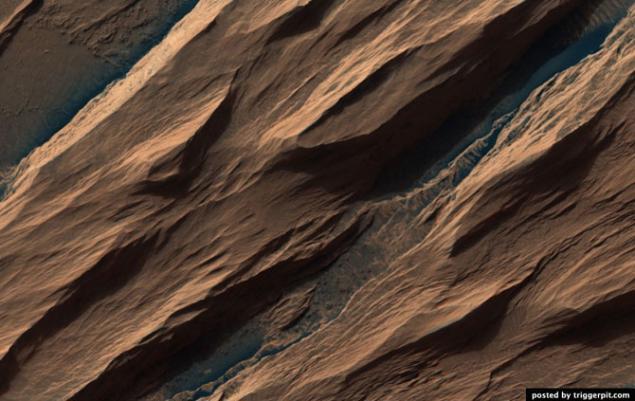
17.Zheloba on the walls of the crater at outcrop.
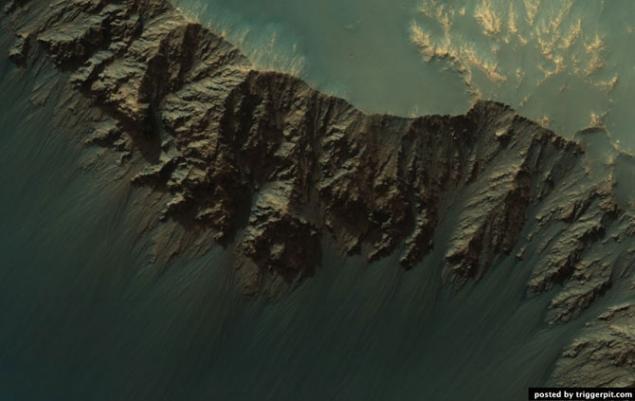

18. Runners on the walls of the crater at outcrop.
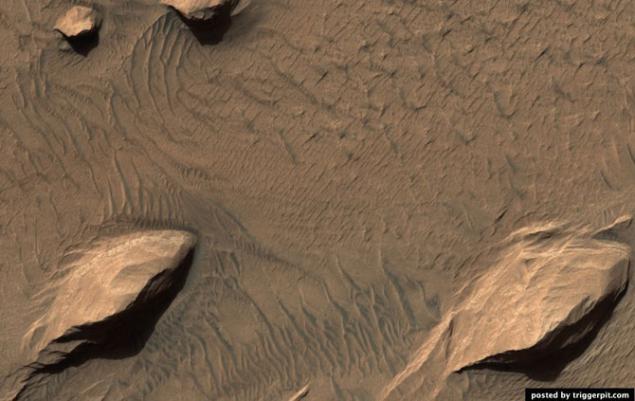

19.Territorii where possible contain a lot of olivine.
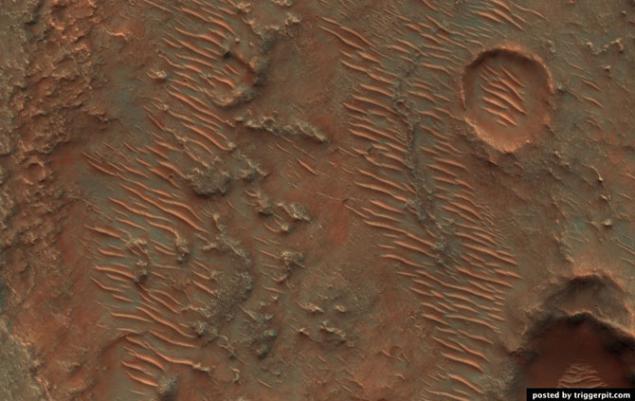

20.Ovragi between dunes on the crater floor Kaiser.

21.Dolina Mort.

22.Otlozheniya at the bottom of the canyon labyrinth of the night.
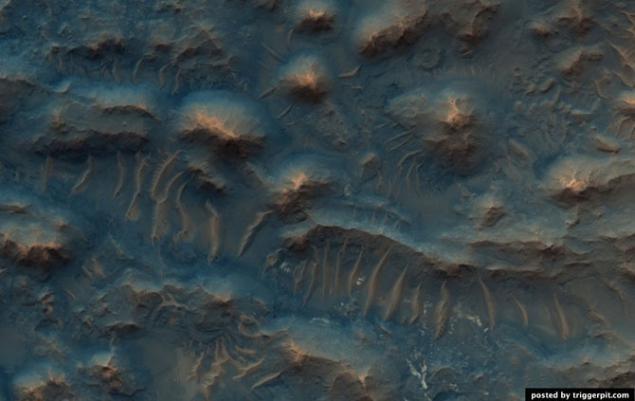

23.Krater Holden.
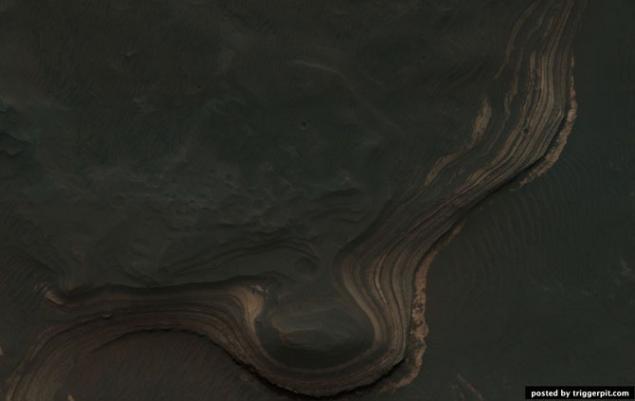

24.Krater St. Mary (Santa Maria Crater). The device made HiRISE color image crater St. Mary which is visible AGV Opportunity, which is stuck in yuzhnovostochnogo edge of the crater. AGV collected data on this relatively new crater with a diameter of 90 meters, in order to determine what factors influenced his appearance. Pay attention to the surrounding blocks and rays formations.
Spectral analysis reveals the presence CRISM hydrosulfate in this area. Debris AGV located at a distance of 6 kilometers from the edge of the crater Endeavour Crater, which are the basic materials hydrogen sulfates and phyllosilicates.
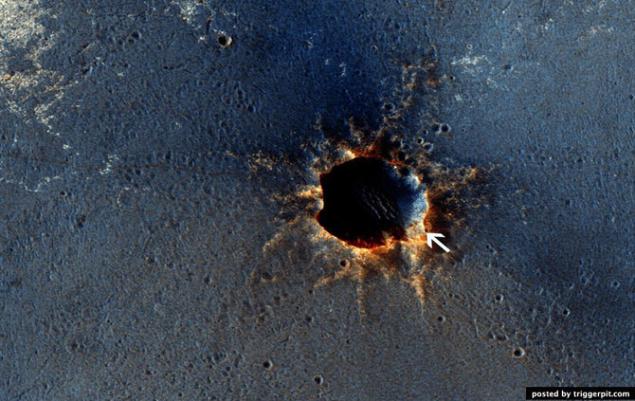

25.Tsentralnaya slide large, well-preserved crater.
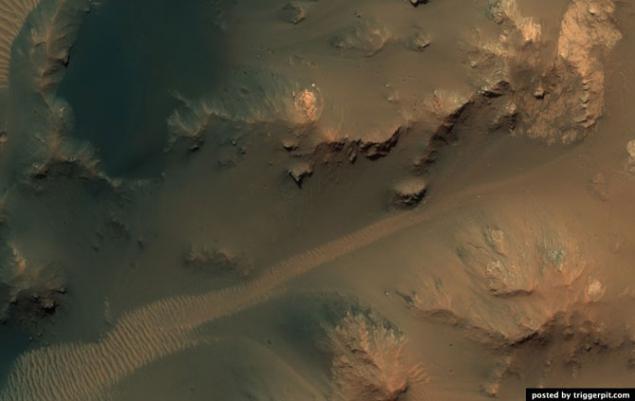

26.Dyuny Russell crater.

27.Sloistye sediments in the canyon Hebe.
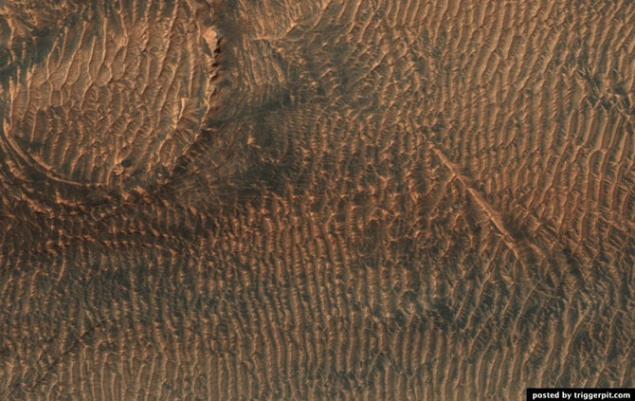

28.Rayon yardang Eumenides Dorsum.
29.Dvizheniya sand in Gusev Crater, located near the Columbia Hills.
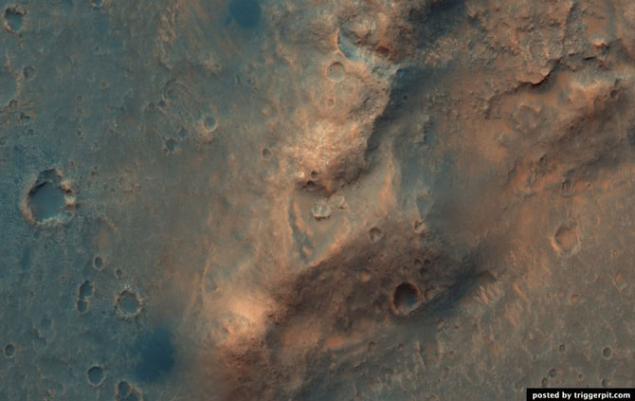

30.Severny ridge of Hellas Planitia, which is probably rich in olivine.
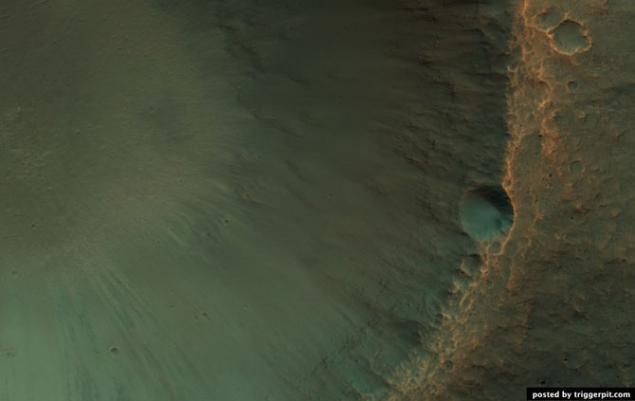

31.Sezonnye changes in the area of the South Pole covered with cracks and potholes.
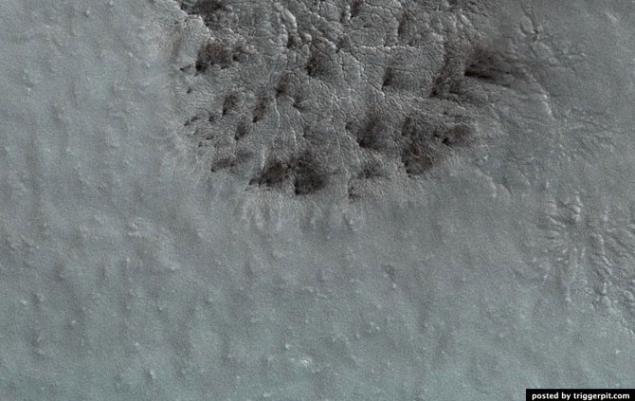

Source:
Layered sediments in the canyon Hebe.

2.Vyboiny on the wall of the crater Gus.

3.Dyuny Russell crater.

4. Geysers Manhattan.

5.Poverhnost Mars covered with dry ice. You had ever play with dry ice (of course in leather gloves!)? Then you have probably noticed that the dry ice from a solid directly into a gas passes, unlike ordinary ice, which is heated, turns into water.
On Mars ice caps are composed of dry ice (carbon dioxide). When in the spring on the ice fall sunshine, it goes into a gaseous state, which causes erosion surface. Erosion creates whimsical spider form.
In this picture shows the channels that have arisen as a result of erosion and light-filled with ice, which comes in contrast to the muted red of the surrounding surface. In summer, the ice dissolves in the atmosphere, and instead will only channels like ghostly spiders carved on the surface. This kind of erosion is typical only for Mars is not possible under natural conditions in the world, because our climate is too warm.

6.Sloistye mineral deposits located on the southern tip of the crater in the middle latitudes. The bright layered deposits are visible in the center of the image; they appear along the edges of the mesas, situated on a hill. Such deposits can be found in many places on Mars, including the craters and canyons near the equator. They could be formed as a result of sedimentation under the influence of wind and / or water.
Around the mesa visible dunes or folded education. The folded structure is the result of differential erosion, when some materials can be eroded more easily than others. Perhaps this area was once covered in soft sediments, which have now disappeared due to erosion.

7.Podstilayuschie rocks protruding on the walls and central peaks of the crater.

8. The solid structure of the salt mountain in a canyon Ganges.

9. Someone cut a piece of the planet!

10. Sand mound formed by the spring dust storms in the North Pole.

11. The crater with a central hill with a diameter of 12 kilometers.

12. The system of faults Cerberus Fossae on the surface of Mars.

13. Purple Proctor Crater Dunes.

14. The light rock outcrops on the walls of the mesa located in the Land of the Sirens.

15.Vesennie changes in the Ithaca area.

16.Dyuny Russell crater. Photos taken in the crater Russell studied repeatedly in order to monitor changes in the landscape. In this picture shows some dark education, which probably arose under the influence of multiple dust storms, which claimed the bright dust from the surface of the dunes. Narrow channels continue to be formed on the surfaces of steep sand dunes. Groove at the end of the channels can be a place where accumulated blocks of dry ice before moving on to a gaseous state.

17.Zheloba on the walls of the crater at outcrop.

18. Runners on the walls of the crater at outcrop.

19.Territorii where possible contain a lot of olivine.

20.Ovragi between dunes on the crater floor Kaiser.

21.Dolina Mort.

22.Otlozheniya at the bottom of the canyon labyrinth of the night.

23.Krater Holden.

24.Krater St. Mary (Santa Maria Crater). The device made HiRISE color image crater St. Mary which is visible AGV Opportunity, which is stuck in yuzhnovostochnogo edge of the crater. AGV collected data on this relatively new crater with a diameter of 90 meters, in order to determine what factors influenced his appearance. Pay attention to the surrounding blocks and rays formations.
Spectral analysis reveals the presence CRISM hydrosulfate in this area. Debris AGV located at a distance of 6 kilometers from the edge of the crater Endeavour Crater, which are the basic materials hydrogen sulfates and phyllosilicates.

25.Tsentralnaya slide large, well-preserved crater.

26.Dyuny Russell crater.

27.Sloistye sediments in the canyon Hebe.

28.Rayon yardang Eumenides Dorsum.

29.Dvizheniya sand in Gusev Crater, located near the Columbia Hills.

30.Severny ridge of Hellas Planitia, which is probably rich in olivine.

31.Sezonnye changes in the area of the South Pole covered with cracks and potholes.

Source: